Come creare ed eseguire un flusso di lavoro con esecuzione prolungata
Una delle funzionalità principali di Windows Workflow Foundation (WF) è la capacità del runtime di scaricare e rendere persistenti i flussi di lavoro inattivi in un database. Nei passaggi di Procedura: Eseguire un flusso di lavoro, sono state illustrate le nozioni di base dell'hosting del flusso di lavoro usando un'applicazione console. Sono stati mostrati esempi relativi all'avvio di flussi di lavoro, di gestori del ciclo di vita del flusso di lavoro e di ripresa dei segnalibri. Per illustrare la persistenza del flusso di lavoro in modo efficace, è necessario un host del flusso di lavoro più complesso che supporta l'avvio e la ripresa di più istanze del flusso di lavoro. In questo passaggio dell'esercitazione viene illustrato come creare un'applicazione host Windows Form che supporta l'avvio e la ripresa di più istanze del flusso di lavoro e la persistenza del flusso di lavoro e vengono fornite informazioni di base per le funzionalità avanzate, ad esempio il rilevamento e il controllo delle versioni illustrati nei passaggi successivi dell'esercitazione.
Nota
In questo passaggio dell'esercitazione e in quelli successivi vengono usati tutti e tre i tipi di flussi di lavoro di Procedura: Eseguire un flusso di lavoro.
Per creare il database di persistenza
Aprire SQL Server Management Studio e connettersi al server locale, ad esempio .\SQLEXPRESS. Fare clic con il pulsante destro del mouse sul nodo Database nel server locale e selezionare Nuovo database. Assegnare il nome WF45GettingStartedTutorial al nuovo database, accettare tutti gli altri valori e selezionare OK.
Nota
Assicurarsi di disporre dell'autorizzazione Crea database nel server locale prima di creare il database.
Scegliere Apri, quindi File dal menu File. Individuare la seguente cartella: C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v4.0.30319\sql\en
Selezionare i due file seguenti, quindi fare clic su Apri.
SqlWorkflowInstanceStoreLogic.sql
SqlWorkflowInstanceStoreSchema.sql
Scegliere SqlWorkflowInstanceStoreSchema.sql dal menu Finestra. Assicurarsi che WF45GettingStartedTutorial sia selezionato nell'elenco a discesa Database disponibili e scegliere Esegui dal menu Query.
Scegliere SqlWorkflowInstanceStoreLogic.sql dal menu Finestra. Assicurarsi che WF45GettingStartedTutorial sia selezionato nell'elenco a discesa Database disponibili e scegliere Esegui dal menu Query.
Avviso
È importante eseguire i due passaggi precedenti nell'ordine corretto. Se le query vengono eseguite senza rispettare l'ordine, si verificano degli errori e il database di persistenza non viene configurato correttamente.
Per aggiungere il riferimento agli assembly DurableInstancing
Fare clic con il pulsante destro del mouse su NumberGuessWorkflowHost in Esplora soluzioni e selezionare Aggiungi riferimento.
Selezionare Assembly nell'elenco Aggiungi riferimento, quindi digitare
DurableInstancingnella casella Cerca assembly. In questo modo gli assembly vengono filtrati ed è più semplice selezionare i riferimenti desiderati.Selezionare la casella di controllo accanto a System.Activities.DurableInstancing e System.Runtime.DurableInstancing nell'elenco Cerca risultati e fare clic su OK.
Per creare il form host del flusso di lavoro
Fare clic con il pulsante destro del mouse su NumberGuessWorkflowHost in Esplora soluzioni e scegliere Aggiungi, Nuovo elemento.
Nell'elenco di modelli Installato, scegliere Windows Form, digitare
WorkflowHostFormnella casella Nome, quindi fare clic su Aggiungi.Configurare le seguenti proprietà nel form.
Proprietà valore FormBorderStyle FixedSingle MaximizeBox Falso Dimensione 400, 420 Aggiungere i controlli seguenti al form nell'ordine specificato e configurare le proprietà come indicato.
Controllo Proprietà: valore Button Nome: NewGame
Posizione: 13, 13
Dimensione: 75, 23
Testo: Nuova partitaEtichetta Posizione: 94, 18
Testo: Immettere un numero da 1 aComboBox Nome: NumberRange
DropDownStyle: DropDownList
Elementi: 10, 100, 1000
Posizione: 228, 12
Dimensione: 143, 21Etichetta Posizione: 13, 43
Testo: Tipo di flusso di lavoroComboBox Nome: WorkflowType
DropDownStyle: DropDownList
Elementi: StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow, FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow, SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow
Posizione: 94, 40
Dimensione: 277, 21Etichetta Nome: WorkflowVersion
Posizione 13, 362
Testo: Versione del flusso di lavoroGroupBox Posizione 13, 67
Dimensione: 358, 287
Testo: PartitaNota
Quando si aggiungono i seguenti controlli, inserirli in GroupBox.
Controllo Proprietà: valore Etichetta Posizione: 7, 20
Testo: ID istanza del flusso di lavoroComboBox Nome: InstanceId
DropDownStyle: DropDownList
Posizione 121, 17
Dimensione: 227, 21Etichetta Posizione: 7, 47
Testo: GuessTextBox Nome: Guess
Posizione 50, 44
Dimensione: 65, 20Button Nome: EnterGuess
Posizione: 121, 42
Dimensione: 75, 23
Testo: Enter GuessButton Nome: QuitGame
Posizione: 274, 42
Dimensione: 75, 23
Testo: QuitTextBox Nome: WorkflowStatus
Posizione: 10, 73
Multiline: True
ReadOnly: True
ScrollBars: Verticali
Dimensione: 338, 208Impostare la proprietà AcceptButton del form su EnterGuess.
Nell'esempio seguente viene illustrato il form completato.
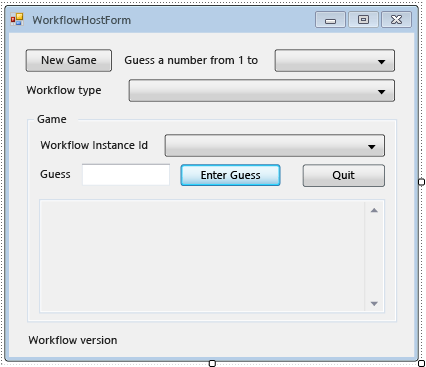
Per aggiungere proprietà e metodi di supporto del form
Tramite i passaggi di questa sezione vengono aggiunti proprietà e metodi di supporto alla classe del form tramite cui viene configurata l'interfaccia utente del form per supportare l'esecuzione e la ripresa dei flussi di lavoro per determinare un numero.
Fare clic con il pulsante destro del mouse su WorkflowHostForm in Esplora soluzioni, quindi scegliere Visualizza codice.
Aggiungere le seguenti istruzioni
using(oImports) nella parte superiore del file con le altre istruzioniusing(oImports).Imports System.Activities Imports System.Activities.DurableInstancing Imports System.Data.SqlClient Imports System.IO Imports System.Windows.Formsusing System.Activities; using System.Activities.DurableInstancing; using System.Data.SqlClient; using System.IO; using System.Windows.Forms;Aggiungere le seguenti dichiarazioni di membri alla classe WorkflowHostForm.
Importante
Microsoft consiglia di usare il flusso di autenticazione più sicuro disponibile. Se ci si connette ad Azure SQL, le Identità gestite per le risorse Azure sono il metodo di autenticazione consigliato.
Const connectionString = "Server=.\SQLEXPRESS;Initial Catalog=WF45GettingStartedTutorial;Integrated Security=SSPI" Dim store As SqlWorkflowInstanceStore Dim workflowStarting As Booleanconst string connectionString = "Server=.\\SQLEXPRESS;Initial Catalog=WF45GettingStartedTutorial;Integrated Security=SSPI"; SqlWorkflowInstanceStore store; bool workflowStarting;Nota
Se la stringa di connessione è diversa, aggiornare
connectionStringper fare riferimento al database.Aggiungere una proprietà
WorkflowInstanceIdalla classeWorkflowFormHost.Public ReadOnly Property WorkflowInstanceId() As Guid Get If InstanceId.SelectedIndex = -1 Then Return Guid.Empty Else Return New Guid(InstanceId.SelectedItem.ToString()) End If End Get End Propertypublic Guid WorkflowInstanceId { get { return InstanceId.SelectedIndex == -1 ? Guid.Empty : (Guid)InstanceId.SelectedItem; } }Nella casella combinata
InstanceIdviene visualizzato un elenco di ID istanza del flusso di lavoro persistente e tramite la proprietàWorkflowInstanceIdviene restituito il flusso di lavoro attualmente selezionato.Aggiungere un gestore per l'evento
Loaddel form. Per aggiungere il gestore, passare a Visualizzazione progettazione per il form, fare clic sull'icona Eventi nella parte superiore della finestra Proprietà, quindi fare doppio clic su Load.Private Sub WorkflowHostForm_Load(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Me.Load End Subprivate void WorkflowHostForm_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) { }Aggiungere il codice seguente a
WorkflowHostForm_Load.' Initialize the store and configure it so that it can be used for ' multiple WorkflowApplication instances. store = New SqlWorkflowInstanceStore(connectionString) WorkflowApplication.CreateDefaultInstanceOwner(store, Nothing, WorkflowIdentityFilter.Any) ' Set default ComboBox selections. NumberRange.SelectedIndex = 0 WorkflowType.SelectedIndex = 0 ListPersistedWorkflows()// Initialize the store and configure it so that it can be used for // multiple WorkflowApplication instances. store = new SqlWorkflowInstanceStore(connectionString); WorkflowApplication.CreateDefaultInstanceOwner(store, null, WorkflowIdentityFilter.Any); // Set default ComboBox selections. NumberRange.SelectedIndex = 0; WorkflowType.SelectedIndex = 0; ListPersistedWorkflows();Durante il caricamento del form, viene configurato
SqlWorkflowInstanceStore, le caselle combinate dell'intervallo e del tipo di flusso di lavoro vengono impostate sui valori predefiniti e le istanze del flusso di lavoro persistente vengono aggiunte alla casella combinataInstanceId.Aggiungere un gestore
SelectedIndexChangedperInstanceId. Per aggiungere il gestore, passare a Visualizzazione progettazione per il form, selezionare la casella combinataInstanceId, fare clic sull'icona Eventi nella parte superiore della finestra Proprietà, quindi fare doppio clic su SelectedIndexChanged.Private Sub InstanceId_SelectedIndexChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles InstanceId.SelectedIndexChanged End Subprivate void InstanceId_SelectedIndexChanged(object sender, EventArgs e) { }Aggiungere il codice seguente a
InstanceId_SelectedIndexChanged. Ogni volta che l'utente seleziona un flusso di lavoro usando la casella combinata, tramite questo gestore viene aggiornata la finestra di stato.If InstanceId.SelectedIndex = -1 Then Return End If ' Clear the status window. WorkflowStatus.Clear() ' Get the workflow version and display it. ' If the workflow is just starting then this info will not ' be available in the persistence store so do not try and retrieve it. If Not workflowStarting Then Dim instance As WorkflowApplicationInstance = _ WorkflowApplication.GetInstance(WorkflowInstanceId, store) WorkflowVersion.Text = _ WorkflowVersionMap.GetIdentityDescription(instance.DefinitionIdentity) ' Unload the instance. instance.Abandon() End Ifif (InstanceId.SelectedIndex == -1) { return; } // Clear the status window. WorkflowStatus.Clear(); // Get the workflow version and display it. // If the workflow is just starting then this info will not // be available in the persistence store so do not try and retrieve it. if (!workflowStarting) { WorkflowApplicationInstance instance = WorkflowApplication.GetInstance(this.WorkflowInstanceId, store); WorkflowVersion.Text = WorkflowVersionMap.GetIdentityDescription(instance.DefinitionIdentity); // Unload the instance. instance.Abandon(); }Aggiungere il seguente metodo
ListPersistedWorkflowsalla classe del form.Private Sub ListPersistedWorkflows() Using localCon As New SqlConnection(connectionString) Dim localCmd As String = _ "SELECT [InstanceId] FROM [System.Activities.DurableInstancing].[Instances] ORDER BY [CreationTime]" Dim cmd As SqlCommand = localCon.CreateCommand() cmd.CommandText = localCmd localCon.Open() Using reader As SqlDataReader = cmd.ExecuteReader(CommandBehavior.CloseConnection) While (reader.Read()) ' Get the InstanceId of the persisted Workflow. Dim id As Guid = Guid.Parse(reader(0).ToString()) InstanceId.Items.Add(id) End While End Using End Using End Subusing (var localCon = new SqlConnection(connectionString)) { string localCmd = "SELECT [InstanceId] FROM [System.Activities.DurableInstancing].[Instances] ORDER BY [CreationTime]"; SqlCommand cmd = localCon.CreateCommand(); cmd.CommandText = localCmd; localCon.Open(); using (SqlDataReader reader = cmd.ExecuteReader(CommandBehavior.CloseConnection)) { while (reader.Read()) { // Get the InstanceId of the persisted Workflow. Guid id = Guid.Parse(reader[0].ToString()); InstanceId.Items.Add(id); } } }Tramite
ListPersistedWorkflowsviene eseguita una query sull'archivio di istanze per le istanze del flusso di lavoro persistente, quindi vengono aggiunti gli ID istanza alla casella combinatacboInstanceId.Aggiungere il seguente metodo
UpdateStatuse il delegato corrispondente alla classe del form. Tramite questo metodo viene aggiornata la finestra di stato nel form con lo stato del flusso di lavoro attualmente in esecuzione.Private Delegate Sub UpdateStatusDelegate(msg As String) Public Sub UpdateStatus(msg As String) ' We may be on a different thread so we need to ' make this call using BeginInvoke. If InvokeRequired Then BeginInvoke(New UpdateStatusDelegate(AddressOf UpdateStatus), msg) Else If Not msg.EndsWith(vbCrLf) Then msg = msg & vbCrLf End If WorkflowStatus.AppendText(msg) ' Ensure that the newly added status is visible. WorkflowStatus.SelectionStart = WorkflowStatus.Text.Length WorkflowStatus.ScrollToCaret() End If End Subprivate delegate void UpdateStatusDelegate(string msg); public void UpdateStatus(string msg) { // We may be on a different thread so we need to // make this call using BeginInvoke. if (InvokeRequired) { BeginInvoke(new UpdateStatusDelegate(UpdateStatus), msg); } else { if (!msg.EndsWith("\r\n")) { msg += "\r\n"; } WorkflowStatus.AppendText(msg); WorkflowStatus.SelectionStart = WorkflowStatus.Text.Length; WorkflowStatus.ScrollToCaret(); } }Aggiungere il seguente metodo
GameOvere il delegato corrispondente alla classe del form. Una volta completato un flusso di lavoro, tramite questo metodo viene aggiornata l'interfaccia utente del form rimuovendo l'ID istanza del flusso di lavoro completato dalla casella combinata InstanceId.Private Delegate Sub GameOverDelegate() Private Sub GameOver() If InvokeRequired Then BeginInvoke(New GameOverDelegate(AddressOf GameOver)) Else ' Remove this instance from the InstanceId combo box. InstanceId.Items.Remove(InstanceId.SelectedItem) InstanceId.SelectedIndex = -1 End If End Subprivate delegate void GameOverDelegate(); private void GameOver() { if (InvokeRequired) { BeginInvoke(new GameOverDelegate(GameOver)); } else { // Remove this instance from the combo box. InstanceId.Items.Remove(InstanceId.SelectedItem); InstanceId.SelectedIndex = -1; } }
Per configurare l'archivio di istanze, i gestori del ciclo di vita del flusso di lavoro e le estensioni
Aggiungere un metodo
ConfigureWorkflowApplicationalla classe del form.Private Sub ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp As WorkflowApplication) End Subprivate void ConfigureWorkflowApplication(WorkflowApplication wfApp) { }Tramite questo metodo viene configurata l'istanza
WorkflowApplicatione vengono aggiunti le estensioni desiderate e i gestori per gli eventi del ciclo di vita del flusso di lavoro.In
ConfigureWorkflowApplicationspecificareSqlWorkflowInstanceStoreper l'istanzaWorkflowApplication.' Configure the persistence store. wfApp.InstanceStore = store// Configure the persistence store. wfApp.InstanceStore = store;Successivamente, creare un'istanza
StringWritere aggiungerla alla raccoltaExtensionsdell'istanzaWorkflowApplication. QuandoStringWriterviene aggiunto alle estensioni, vengono acquisiti tutti gli output di attivitàWriteLine. Quando il flusso di lavoro diventa inattivo, l'outputWriteLinepuò essere estratto daStringWritere visualizzato nel form.' Add a StringWriter to the extensions. This captures the output ' from the WriteLine activities so we can display it in the form. Dim sw As New StringWriter() wfApp.Extensions.Add(sw)// Add a StringWriter to the extensions. This captures the output // from the WriteLine activities so we can display it in the form. var sw = new StringWriter(); wfApp.Extensions.Add(sw);Aggiungere il gestore seguente per l'evento
Completed. Quando un flusso di lavoro è stato completato, il numero di tentativi effettuati per determinare il numero viene visualizzato nella finestra di stato. Se il flusso di lavoro viene terminato, vengono visualizzate le informazioni sull'eccezione che ha provocato l'interruzione. Alla fine del gestore viene chiamato il metodoGameOvertramite cui il flusso di lavoro completato viene rimosso dall'elenco di flussi di lavoro.wfApp.Completed = _ Sub(e As WorkflowApplicationCompletedEventArgs) If e.CompletionState = ActivityInstanceState.Faulted Then UpdateStatus($"Workflow Terminated. Exception: {e.TerminationException.GetType().FullName}{vbCrLf}{e.TerminationException.Message}") ElseIf e.CompletionState = ActivityInstanceState.Canceled Then UpdateStatus("Workflow Canceled.") Else Dim turns As Integer = Convert.ToInt32(e.Outputs("Turns")) UpdateStatus($"Congratulations, you guessed the number in {turns} turns.") End If GameOver() End SubwfApp.Completed = delegate(WorkflowApplicationCompletedEventArgs e) { if (e.CompletionState == ActivityInstanceState.Faulted) { UpdateStatus($"Workflow Terminated. Exception: {e.TerminationException.GetType().FullName}\r\n{e.TerminationException.Message}"); } else if (e.CompletionState == ActivityInstanceState.Canceled) { UpdateStatus("Workflow Canceled."); } else { int turns = Convert.ToInt32(e.Outputs["Turns"]); UpdateStatus($"Congratulations, you guessed the number in {turns} turns."); } GameOver(); };Aggiungere i seguenti gestori
AbortedeOnUnhandledException. Il metodoGameOvernon viene chiamato dal gestoreAbortedperché quando un'istanza del flusso di lavoro viene interrotta, non viene terminata ed è possibile riprenderla in un secondo momento.wfApp.Aborted = _ Sub(e As WorkflowApplicationAbortedEventArgs) UpdateStatus($"Workflow Aborted. Exception: {e.Reason.GetType().FullName}{vbCrLf}{e.Reason.Message}") End Sub wfApp.OnUnhandledException = _ Function(e As WorkflowApplicationUnhandledExceptionEventArgs) UpdateStatus($"Unhandled Exception: {e.UnhandledException.GetType().FullName}{vbCrLf}{e.UnhandledException.Message}") GameOver() Return UnhandledExceptionAction.Terminate End FunctionwfApp.Aborted = delegate(WorkflowApplicationAbortedEventArgs e) { UpdateStatus($"Workflow Aborted. Exception: {e.Reason.GetType().FullName}\r\n{e.Reason.Message}"); }; wfApp.OnUnhandledException = delegate(WorkflowApplicationUnhandledExceptionEventArgs e) { UpdateStatus($"Unhandled Exception: {e.UnhandledException.GetType().FullName}\r\n{e.UnhandledException.Message}"); GameOver(); return UnhandledExceptionAction.Terminate; };Aggiungere il seguente gestore
PersistableIdle. Tramite questo gestore viene recuperata l'estensioneStringWriterche era stata aggiunta, viene estratto l'output dalle attivitàWriteLineche, successivamente, viene visualizzato nella finestra di stato.wfApp.PersistableIdle = _ Function(e As WorkflowApplicationIdleEventArgs) ' Send the current WriteLine outputs to the status window. Dim writers = e.GetInstanceExtensions(Of StringWriter)() For Each writer In writers UpdateStatus(writer.ToString()) Next Return PersistableIdleAction.Unload End FunctionwfApp.PersistableIdle = delegate(WorkflowApplicationIdleEventArgs e) { // Send the current WriteLine outputs to the status window. var writers = e.GetInstanceExtensions<StringWriter>(); foreach (var writer in writers) { UpdateStatus(writer.ToString()); } return PersistableIdleAction.Unload; };L'enumerazione PersistableIdleAction ha tre valori:None, Persist e Unload. Tramite il campo Persist il flusso di lavoro viene reso persistente, ma non scaricato. Unload rende il flusso di lavoro persistente e lo scarica.
Nell'esempio seguente viene mostrato il metodo
ConfigureWorkflowApplicationcompletato.Private Sub ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp As WorkflowApplication) ' Configure the persistence store. wfApp.InstanceStore = store ' Add a StringWriter to the extensions. This captures the output ' from the WriteLine activities so we can display it in the form. Dim sw As New StringWriter() wfApp.Extensions.Add(sw) wfApp.Completed = _ Sub(e As WorkflowApplicationCompletedEventArgs) If e.CompletionState = ActivityInstanceState.Faulted Then UpdateStatus($"Workflow Terminated. Exception: {e.TerminationException.GetType().FullName}{vbCrLf}{e.TerminationException.Message}") ElseIf e.CompletionState = ActivityInstanceState.Canceled Then UpdateStatus("Workflow Canceled.") Else Dim turns As Integer = Convert.ToInt32(e.Outputs("Turns")) UpdateStatus($"Congratulations, you guessed the number in {turns} turns.") End If GameOver() End Sub wfApp.Aborted = _ Sub(e As WorkflowApplicationAbortedEventArgs) UpdateStatus($"Workflow Aborted. Exception: {e.Reason.GetType().FullName}{vbCrLf}{e.Reason.Message}") End Sub wfApp.OnUnhandledException = _ Function(e As WorkflowApplicationUnhandledExceptionEventArgs) UpdateStatus($"Unhandled Exception: {e.UnhandledException.GetType().FullName}{vbCrLf}{e.UnhandledException.Message}") GameOver() Return UnhandledExceptionAction.Terminate End Function wfApp.PersistableIdle = _ Function(e As WorkflowApplicationIdleEventArgs) ' Send the current WriteLine outputs to the status window. Dim writers = e.GetInstanceExtensions(Of StringWriter)() For Each writer In writers UpdateStatus(writer.ToString()) Next Return PersistableIdleAction.Unload End Function End Subprivate void ConfigureWorkflowApplication(WorkflowApplication wfApp) { // Configure the persistence store. wfApp.InstanceStore = store; // Add a StringWriter to the extensions. This captures the output // from the WriteLine activities so we can display it in the form. var sw = new StringWriter(); wfApp.Extensions.Add(sw); wfApp.Completed = delegate(WorkflowApplicationCompletedEventArgs e) { if (e.CompletionState == ActivityInstanceState.Faulted) { UpdateStatus($"Workflow Terminated. Exception: {e.TerminationException.GetType().FullName}\r\n{e.TerminationException.Message}"); } else if (e.CompletionState == ActivityInstanceState.Canceled) { UpdateStatus("Workflow Canceled."); } else { int turns = Convert.ToInt32(e.Outputs["Turns"]); UpdateStatus($"Congratulations, you guessed the number in {turns} turns."); } GameOver(); }; wfApp.Aborted = delegate(WorkflowApplicationAbortedEventArgs e) { UpdateStatus($"Workflow Aborted. Exception: {e.Reason.GetType().FullName}\r\n{e.Reason.Message}"); }; wfApp.OnUnhandledException = delegate(WorkflowApplicationUnhandledExceptionEventArgs e) { UpdateStatus($"Unhandled Exception: {e.UnhandledException.GetType().FullName}\r\n{e.UnhandledException.Message}"); GameOver(); return UnhandledExceptionAction.Terminate; }; wfApp.PersistableIdle = delegate(WorkflowApplicationIdleEventArgs e) { // Send the current WriteLine outputs to the status window. var writers = e.GetInstanceExtensions<StringWriter>(); foreach (var writer in writers) { UpdateStatus(writer.ToString()); } return PersistableIdleAction.Unload; }; }
Per abilitare l'avvio e la ripresa di più tipi di flussi di lavoro
Per riprendere un'istanza del flusso di lavoro, tramite l'host deve essere fornita la definizione del flusso di lavoro. In questa esercitazione sono disponibili tre tipi di flussi di lavoro e nei passaggi successivi dell'esercitazione vengono introdotte più versioni di questi tipi. Tramite WorkflowIdentity viene fornito un modo per un'applicazione host per associare le informazioni di identificazione con un'istanza del flusso di lavoro persistente. Nei passaggi di questa sezione viene illustrato come creare una classe di utilità per consentire il mapping dell'identità del flusso di lavoro da un'istanza del flusso di lavoro persistente alla definizione del flusso di lavoro corrispondente. Per altre informazioni su WorkflowIdentity e il controllo delle versioni, vedere Uso di WorkflowIdentity e controllo delle versioni.
Fare clic con il pulsante destro del mouse su NumberGuessWorkflowHost in Esplora soluzioni e scegliere Aggiungi, Classe. Digitare
WorkflowVersionMapnella casella Nome e fare clic su Aggiungi.Aggiungere le seguenti istruzioni
usingoImportsnella parte superiore del file con le altre istruzioniusingoImports.Imports System.Activities Imports NumberGuessWorkflowActivitiesusing System.Activities; using NumberGuessWorkflowActivities;Sostituire la dichiarazione di classe
WorkflowVersionMapcon la dichiarazione seguente.Public Module WorkflowVersionMap Dim map As Dictionary(Of WorkflowIdentity, Activity) ' Current version identities. Public StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity As WorkflowIdentity Public FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity As WorkflowIdentity Public SequentialNumberGuessIdentity As WorkflowIdentity Sub New() map = New Dictionary(Of WorkflowIdentity, Activity) ' Add the current workflow version identities. StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity = New WorkflowIdentity With { .Name = "StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow", .Version = New Version(1, 0, 0, 0) } FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity = New WorkflowIdentity With { .Name = "FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow", .Version = New Version(1, 0, 0, 0) } SequentialNumberGuessIdentity = New WorkflowIdentity With { .Name = "SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow", .Version = New Version(1, 0, 0, 0) } map.Add(StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity, New StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow()) map.Add(FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity, New FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow()) map.Add(SequentialNumberGuessIdentity, New SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow()) End Sub Public Function GetWorkflowDefinition(identity As WorkflowIdentity) As Activity Return map(identity) End Function Public Function GetIdentityDescription(identity As WorkflowIdentity) As String Return identity.ToString() End Function End Modulepublic static class WorkflowVersionMap { static Dictionary<WorkflowIdentity, Activity> map; // Current version identities. static public WorkflowIdentity StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity; static public WorkflowIdentity FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity; static public WorkflowIdentity SequentialNumberGuessIdentity; static WorkflowVersionMap() { map = new Dictionary<WorkflowIdentity, Activity>(); // Add the current workflow version identities. StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity = new WorkflowIdentity { Name = "StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow", Version = new Version(1, 0, 0, 0) }; FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity = new WorkflowIdentity { Name = "FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow", Version = new Version(1, 0, 0, 0) }; SequentialNumberGuessIdentity = new WorkflowIdentity { Name = "SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow", Version = new Version(1, 0, 0, 0) }; map.Add(StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity, new StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow()); map.Add(FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity, new FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow()); map.Add(SequentialNumberGuessIdentity, new SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow()); } public static Activity GetWorkflowDefinition(WorkflowIdentity identity) { return map[identity]; } public static string GetIdentityDescription(WorkflowIdentity identity) { return identity.ToString(); } }In
WorkflowVersionMapsono contenute tre identità del flusso di lavoro tramite cui viene eseguito il mapping alle tre definizioni del flusso di lavoro di questa esercitazione e viene usato nelle sezioni seguenti quando i flussi di lavoro vengono avviati e ripresi.
Per avviare un nuovo flusso di lavoro
Aggiungere un gestore
ClickperNewGame. Per aggiungere il gestore, passare a Visualizzazione progettazione per il form, quindi fare doppio clic suNewGame. Viene aggiunto un gestoreNewGame_Clicke si passa alla visualizzazione codice per il form. Ogni volta che l'utente fa clic sul pulsante, viene avviato un nuovo flusso di lavoro.Private Sub NewGame_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles NewGame.Click End Subprivate void NewGame_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { }Aggiungere il codice seguente al gestore di eventi Click. Tramite questo codice viene creato un dizionario di argomenti di input per il flusso di lavoro, con chiave basata sul nome dell'argomento. Nel dizionario è contenuta una voce in cui è incluso l'intervallo del numero generato casualmente, recuperato dalla casella combinata dell'intervallo.
Dim inputs As New Dictionary(Of String, Object)() inputs.Add("MaxNumber", Convert.ToInt32(NumberRange.SelectedItem))var inputs = new Dictionary<string, object>(); inputs.Add("MaxNumber", Convert.ToInt32(NumberRange.SelectedItem));Successivamente, aggiungere il codice seguente tramite cui viene avviato il flusso di lavoro.
WorkflowIdentitye la definizione del flusso di lavoro corrispondente al tipo di flusso di lavoro selezionato vengono recuperati usando la classe di supportoWorkflowVersionMap. Successivamente, viene creata una nuova istanzaWorkflowApplicationusando la definizione del flusso di lavoro,WorkflowIdentitye il dizionario degli argomenti di input.Dim identity As WorkflowIdentity = Nothing Select Case WorkflowType.SelectedItem.ToString() Case "SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow" identity = WorkflowVersionMap.SequentialNumberGuessIdentity Case "StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow" identity = WorkflowVersionMap.StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity Case "FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow" identity = WorkflowVersionMap.FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity End Select Dim wf As Activity = WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(identity) Dim wfApp = New WorkflowApplication(wf, inputs, identity)WorkflowIdentity identity = null; switch (WorkflowType.SelectedItem.ToString()) { case "SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow": identity = WorkflowVersionMap.SequentialNumberGuessIdentity; break; case "StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow": identity = WorkflowVersionMap.StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity; break; case "FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow": identity = WorkflowVersionMap.FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity; break; }; Activity wf = WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(identity); WorkflowApplication wfApp = new WorkflowApplication(wf, inputs, identity);Successivamente, aggiungere il codice seguente tramite cui viene aggiunto il flusso di lavoro al relativo elenco e vengono visualizzate le informazioni sulla versione del flusso di lavoro nel form.
' Add the workflow to the list and display the version information. workflowStarting = True InstanceId.SelectedIndex = InstanceId.Items.Add(wfApp.Id) WorkflowVersion.Text = identity.ToString() workflowStarting = False// Add the workflow to the list and display the version information. workflowStarting = true; InstanceId.SelectedIndex = InstanceId.Items.Add(wfApp.Id); WorkflowVersion.Text = identity.ToString(); workflowStarting = false;Chiamare
ConfigureWorkflowApplicationper configurare l'archivio di istanze, le estensioni e i gestori del ciclo di vita del flusso di lavoro per questa istanzaWorkflowApplication.' Configure the instance store, extensions, and ' workflow lifecycle handlers. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp)// Configure the instance store, extensions, and // workflow lifecycle handlers. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp);Infine, viene chiamato
Run.' Start the workflow. wfApp.Run()// Start the workflow. wfApp.Run();Nell'esempio seguente viene mostrato il gestore
NewGame_Clickcompletato.Private Sub NewGame_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles NewGame.Click ' Start a new workflow. Dim inputs As New Dictionary(Of String, Object)() inputs.Add("MaxNumber", Convert.ToInt32(NumberRange.SelectedItem)) Dim identity As WorkflowIdentity = Nothing Select Case WorkflowType.SelectedItem.ToString() Case "SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow" identity = WorkflowVersionMap.SequentialNumberGuessIdentity Case "StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow" identity = WorkflowVersionMap.StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity Case "FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow" identity = WorkflowVersionMap.FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity End Select Dim wf As Activity = WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(identity) Dim wfApp = New WorkflowApplication(wf, inputs, identity) ' Add the workflow to the list and display the version information. workflowStarting = True InstanceId.SelectedIndex = InstanceId.Items.Add(wfApp.Id) WorkflowVersion.Text = identity.ToString() workflowStarting = False ' Configure the instance store, extensions, and ' workflow lifecycle handlers. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp) ' Start the workflow. wfApp.Run() End Subprivate void NewGame_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { var inputs = new Dictionary<string, object>(); inputs.Add("MaxNumber", Convert.ToInt32(NumberRange.SelectedItem)); WorkflowIdentity identity = null; switch (WorkflowType.SelectedItem.ToString()) { case "SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow": identity = WorkflowVersionMap.SequentialNumberGuessIdentity; break; case "StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow": identity = WorkflowVersionMap.StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity; break; case "FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow": identity = WorkflowVersionMap.FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity; break; }; Activity wf = WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(identity); var wfApp = new WorkflowApplication(wf, inputs, identity); // Add the workflow to the list and display the version information. workflowStarting = true; InstanceId.SelectedIndex = InstanceId.Items.Add(wfApp.Id); WorkflowVersion.Text = identity.ToString(); workflowStarting = false; // Configure the instance store, extensions, and // workflow lifecycle handlers. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp); // Start the workflow. wfApp.Run(); }
Per riprendere un flusso di lavoro
Aggiungere un gestore
ClickperEnterGuess. Per aggiungere il gestore, passare a Visualizzazione progettazione per il form, quindi fare doppio clic suEnterGuess. Ogni volta che l'utente fa clic sul pulsante, viene ripreso un flusso di lavoro.Private Sub EnterGuess_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles EnterGuess.Click End Subprivate void EnterGuess_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { }Aggiungere il codice seguente per assicurarsi che un flusso di lavoro venga selezionato nell'elenco di flussi di lavoro e che il tentativo dell'utente sia valido.
If WorkflowInstanceId = Guid.Empty Then MessageBox.Show("Please select a workflow.") Return End If Dim userGuess As Integer If Not Int32.TryParse(Guess.Text, userGuess) Then MessageBox.Show("Please enter an integer.") Guess.SelectAll() Guess.Focus() Return End Ifif (WorkflowInstanceId == Guid.Empty) { MessageBox.Show("Please select a workflow."); return; } int guess; if (!Int32.TryParse(Guess.Text, out guess)) { MessageBox.Show("Please enter an integer."); Guess.SelectAll(); Guess.Focus(); return; }Successivamente, recuperare l'istanza
WorkflowApplicationInstancedell'istanza del flusso di lavoro persistente. Un'istanzaWorkflowApplicationInstancerappresenta un'istanza del flusso di lavoro persistente che non è ancora stata associata a una definizione del flusso di lavoro. InDefinitionIdentitydell'istanzaWorkflowApplicationInstanceè contenutoWorkflowIdentitydell'istanza del flusso di lavoro persistente. In questa esercitazione la classe di utilitàWorkflowVersionMapviene usata per eseguire il mapping diWorkflowIdentityalla definizione del flusso di lavoro corretta. Una volta recuperata la definizione del flusso di lavoro, viene creata un'istanzaWorkflowApplicationusando la definizione del flusso di lavoro corretta.Dim instance As WorkflowApplicationInstance = _ WorkflowApplication.GetInstance(WorkflowInstanceId, store) ' Use the persisted WorkflowIdentity to retrieve the correct workflow ' definition from the dictionary. Dim wf As Activity = _ WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(instance.DefinitionIdentity) ' Associate the WorkflowApplication with the correct definition Dim wfApp As New WorkflowApplication(wf, instance.DefinitionIdentity)WorkflowApplicationInstance instance = WorkflowApplication.GetInstance(WorkflowInstanceId, store); // Use the persisted WorkflowIdentity to retrieve the correct workflow // definition from the dictionary. Activity wf = WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(instance.DefinitionIdentity); // Associate the WorkflowApplication with the correct definition var wfApp = new WorkflowApplication(wf, instance.DefinitionIdentity);Una volta creata l'istanza
WorkflowApplication, configurare l'archivio di istanze, i gestori del ciclo di vita del flusso di lavoro e le estensioni chiamandoConfigureWorkflowApplication. Questi passaggi devono essere effettuati ogni volta che viene creata una nuova istanzaWorkflowApplicatione prima che l'istanza del flusso di lavoro venga caricata nell'istanzaWorkflowApplication. Una volta caricato il flusso di lavoro, viene ripreso con il tentativo dell'utente.' Configure the extensions and lifecycle handlers. ' Do this before the instance is loaded. Once the instance is ' loaded it is too late to add extensions. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp) ' Load the workflow. wfApp.Load(instance) ' Resume the workflow. wfApp.ResumeBookmark("EnterGuess", userGuess)// Configure the extensions and lifecycle handlers. // Do this before the instance is loaded. Once the instance is // loaded it is too late to add extensions. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp); // Load the workflow. wfApp.Load(instance); // Resume the workflow. wfApp.ResumeBookmark("EnterGuess", guess);Infine, deselezionare la casella di testo del tentativo e preparare il form per accettare un altro tentativo.
' Clear the Guess textbox. Guess.Clear() Guess.Focus()// Clear the Guess textbox. Guess.Clear(); Guess.Focus();Nell'esempio seguente viene mostrato il gestore
EnterGuess_Clickcompletato.Private Sub EnterGuess_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles EnterGuess.Click If WorkflowInstanceId = Guid.Empty Then MessageBox.Show("Please select a workflow.") Return End If Dim userGuess As Integer If Not Int32.TryParse(Guess.Text, userGuess) Then MessageBox.Show("Please enter an integer.") Guess.SelectAll() Guess.Focus() Return End If Dim instance As WorkflowApplicationInstance = _ WorkflowApplication.GetInstance(WorkflowInstanceId, store) ' Use the persisted WorkflowIdentity to retrieve the correct workflow ' definition from the dictionary. Dim wf As Activity = _ WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(instance.DefinitionIdentity) ' Associate the WorkflowApplication with the correct definition Dim wfApp As New WorkflowApplication(wf, instance.DefinitionIdentity) ' Configure the extensions and lifecycle handlers. ' Do this before the instance is loaded. Once the instance is ' loaded it is too late to add extensions. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp) ' Load the workflow. wfApp.Load(instance) ' Resume the workflow. wfApp.ResumeBookmark("EnterGuess", userGuess) ' Clear the Guess textbox. Guess.Clear() Guess.Focus() End Subprivate void EnterGuess_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { if (WorkflowInstanceId == Guid.Empty) { MessageBox.Show("Please select a workflow."); return; } int guess; if (!Int32.TryParse(Guess.Text, out guess)) { MessageBox.Show("Please enter an integer."); Guess.SelectAll(); Guess.Focus(); return; } WorkflowApplicationInstance instance = WorkflowApplication.GetInstance(WorkflowInstanceId, store); // Use the persisted WorkflowIdentity to retrieve the correct workflow // definition from the dictionary. Activity wf = WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(instance.DefinitionIdentity); // Associate the WorkflowApplication with the correct definition var wfApp = new WorkflowApplication(wf, instance.DefinitionIdentity); // Configure the extensions and lifecycle handlers. // Do this before the instance is loaded. Once the instance is // loaded it is too late to add extensions. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp); // Load the workflow. wfApp.Load(instance); // Resume the workflow. wfApp.ResumeBookmark("EnterGuess", guess); // Clear the Guess textbox. Guess.Clear(); Guess.Focus(); }
Per terminare un flusso di lavoro
Aggiungere un gestore
ClickperQuitGame. Per aggiungere il gestore, passare a Visualizzazione progettazione per il form, quindi fare doppio clic suQuitGame. Ogni volta che l'utente fa clic sul pulsante, il flusso di lavoro selezionato viene interrotto.Private Sub QuitGame_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles QuitGame.Click End Subprivate void QuitGame_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { }Aggiungere al gestore
QuitGame_Clickil codice riportato di seguito. Tramite il codice viene innanzitutto verificato che un flusso di lavoro venga selezionato nell'elenco di flussi di controllo. Successivamente viene caricata l'istanza persistente in un'istanzaWorkflowApplicationInstance, viene usatoDefinitionIdentityper determinare la definizione del flusso di lavoro corretta e, infine, viene inizializzata l'istanzaWorkflowApplication. In seguito, le estensioni e i gestori del ciclo di vita del flusso di lavoro vengono configurati con una chiamata al metodoConfigureWorkflowApplication. Una volta configurata, l'istanzaWorkflowApplicationviene caricata e viene chiamatoTerminate.If WorkflowInstanceId = Guid.Empty Then MessageBox.Show("Please select a workflow.") Return End If Dim instance As WorkflowApplicationInstance = _ WorkflowApplication.GetInstance(WorkflowInstanceId, store) ' Use the persisted WorkflowIdentity to retrieve the correct workflow ' definition from the dictionary. Dim wf As Activity = WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(instance.DefinitionIdentity) ' Associate the WorkflowApplication with the correct definition. Dim wfApp As New WorkflowApplication(wf, instance.DefinitionIdentity) ' Configure the extensions and lifecycle handlers. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp) ' Load the workflow. wfApp.Load(instance) ' Terminate the workflow. wfApp.Terminate("User resigns.")if (WorkflowInstanceId == Guid.Empty) { MessageBox.Show("Please select a workflow."); return; } WorkflowApplicationInstance instance = WorkflowApplication.GetInstance(WorkflowInstanceId, store); // Use the persisted WorkflowIdentity to retrieve the correct workflow // definition from the dictionary. Activity wf = WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(instance.DefinitionIdentity); // Associate the WorkflowApplication with the correct definition var wfApp = new WorkflowApplication(wf, instance.DefinitionIdentity); // Configure the extensions and lifecycle handlers ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp); // Load the workflow. wfApp.Load(instance); // Terminate the workflow. wfApp.Terminate("User resigns.");
Per compilare ed eseguire l'applicazione
Fare doppio clic su Program.cs o (Module1.vb) in Esplora soluzioni per visualizzare il codice.
Aggiungere la seguente istruzione
using(oImports) nella parte superiore del file con le altre istruzioniusing(oImports).Imports System.Windows.Formsusing System.Windows.Forms;Rimuovere o impostare come commento il codice di hosting del flusso di lavoro esistente da Procedura: Eseguire un flusso di lavoro, quindi sostituirlo con il codice seguente.
Sub Main() Application.EnableVisualStyles() Application.Run(New WorkflowHostForm()) End Substatic void Main(string[] args) { Application.EnableVisualStyles(); Application.Run(new WorkflowHostForm()); }Fare clic con il pulsante destro del mouse su NumberGuessWorkflowHost in Esplora soluzioni, quindi scegliere Proprietà. Nella scheda Applicazione, specificare Applicazione Windows per il Tipo di output. Questo passaggio è facoltativo, ma se non viene effettuato, oltre al form viene visualizzata anche la finestra della console.
Premere CTRL+MAIUSC+B per compilare l'applicazione.
Assicurarsi che NumberGuessWorkflowHost sia impostato come applicazione di avvio e premere CTRL+F5 per avviare l'applicazione.
Selezionare un intervallo per il gioco per determinare un numero e il tipo di flusso di lavoro da avviare, quindi fare clic su Nuova partita. Immettere un tentativo nella casella Guess, quindi fare clic su Vai per inviare il tentativo. Si noti che l'output dalle attività
WriteLineviene visualizzato nel form.Avviare più flussi di lavoro usando tipi di flussi di lavoro e intervalli di numeri diversi, immettere alcuni tentativi e passare tra i vari flussi di lavoro effettuando una selezione nell'elenco ID istanza flusso di lavoro.
Si noti che quando si passa a un nuovo flusso di lavoro, i tentativi precedenti e lo stato di avanzamento del flusso di lavoro non vengono visualizzati nella finestra di stato. Lo stato non è disponibile poiché non è stato acquisito e salvato da nessuna parte. Nel passaggio successivo dell'esercitazione, Procedura: Creare un partecipante del rilevamento personalizzato, si crea un partecipante del rilevamento personalizzato che salva queste informazioni.
