Working with Azure Storage Queues from PowerShell
Hello Everyone, in this blog post I would like to introduce you to my latest PowerShell module, similarly to the AzureRmStorageTables module that I developed a while ago, this module works with Storage Queues, enabling IT Pros to rely on this great service that Azure Storage provides.
A fully function example of how IT Pros could leverage tables and queues is presented in this GitHub repository where I published an Azure Automation based solution that helps customers upload custom virtual hard drives to Azure and have it distributed amongst different regions/subscriptions and generating managed images. This solution will have a separate blog post shortly.
Introduction
Azure Storage Queues is one of the four Microsoft Azure Storage abstractions available (Blobs, Tables and Azure Files are the other ones) at the time that this blog was written. It provides cloud messaging between application components. In designing applications for scale, application components are often decoupled, so that they can scale independently. Queue storage delivers asynchronous messaging for communication between application components, whether they are running in the cloud, on the desktop, on an on-premises server, or on a mobile device. Azure also provides a more full featured alternative called Azure Service Bus which is similar in concept but provides other features.
For more information about Service Bus, please refer to Service Bus messaging: flexible data delivery in the cloud.
For more information about Azure Storage Queue, please refer to Queue storage and Get started with Azure Queue storage using .NET.
If you want to compare Service Bus against Storage Queue, please refer to Storage queues and Service Bus queues - compared and contrasted.
Since up to today there are no official cmdlets to support placing/retrieving/deleting/modifying messages on Storage Queues from Azure PowerShell module, I decided to create this simple module to help IT Pros to leverage this service without having knowledge of .NET framework through some simple cmdlets as follows:
| Cmdlet | Description |
| Add-AzureRmStorageQueueMessage | Adds a message into the queue |
| Clear-AzureRmStorageQueue | Clears all messages in a queue |
| Get-AzureRmStorageQueueQueue | Creates/Gets a queue object/resource |
| Invoke-AzureRmStorageQueueGetMessage | Get a message from queue and marks it as invisible in the queue for a period of time |
| Invoke-AzureRmStorageQueuePeekMessage | Gets a single message from the queue without removing it from the queue |
| Invoke-AzureRmStorageQueuePeekMessageList | Gets a list of messages from the queue without removing it from the queue |
| Remove-AzureRmStorageQueueMessage | Deletes a message from the queue |
| Update-AzureRmStorageQueueMessage | Updates a message in the queue |
There are a number of use cases for using it with PowerShell, specially during automation scenarios where you want to scale your automation to the next level. One example is the before mentioned solution I posted in GitHub. I would love to get more examples from the community over time in the comments section of this post.
Requirements
- PowerShell 4.0 or greater
- This module requires Azure PowerShell module installed, which can be downloaded from https://aka.ms/webpi-azps or the following minimum modules installed via PSGet module from PowerShell Gallery:
- AzureRM.Profile
- AzureRM.Storage
- AzureRM.Resources
- Azure.Storage
Installation/Source Code
Since this module is published on PowerShell Gallery, you can install this module directly from PowerShell 5.0 and Windows 10 / Windows Server 2016 by executing the following cmdlet in an elevated PowerShell command prompt window:
Install-Module AzureRmStorageQueue
Note that if you want to use the PowerShellGet module in Windows 2012 R2 with PowerShell 4, please look at the https://www.powershellgallery.com/ initial page on how to download and install it. The process is not that straight forward to enable it on Windows 2012 R2 and because of that I placed a summary of the steps below:
Download PowerShellGet source code from GitHub (https://github.com/PowerShell/PowerShellGet/releases)
Right-click the ZIP flie and click “Unblock”
Extract it anywhere
Copy the folder <your extraction folder>\PowerShellHGet-XYZ\PowerShellGet to C:\Program Files\WindowsPowerShell\Modules
Download and install PackageManagement PowerShell Modules Preview from https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=51451
Open an elevated PowerShell command prompt and execute
Install-PackageProvider Nuget –ForceClose the command prompt
Open a new elevated PowerShell command prompt and you’re ready to install the Azure Rm Storage Queue module
As an alternative, you can manually download the module from my GitHub repository (here) and extract to C:\Program Files\WindowsPowerShell\Modules and rename the folder to AzureRmStorageQueue. Please remember to unblock the zip file before extracting it.
Working with Azure Rm Storage Queue PowerShell Module
The following steps will walk you through loading the module and perform one or more example tasks of the basic operations offered in this module.
Before you start working with it, you need to authenticate to Azure and select the correct subscription if you have multiple subscriptions:
Add-AzureRmAccount
Select-AzureRmSubscription -SubscriptionName <your subscription>
Next, lets import AzureRmTableQueue PowerShell module and list the functions available on it:
Import-Module AzureRmStorageQueue
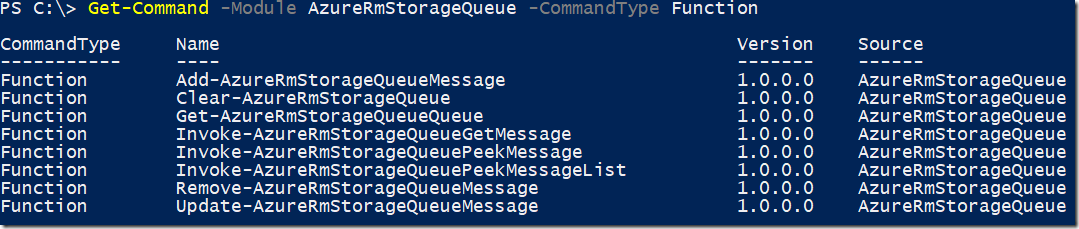
Get-Command -Module AzureRmStorageQueue -CommandType Function
You should see the following cmdlets
For the sake of simplicity, we need to define some variables at this point to make our examples a little bit more clean, please, make sure you have a general purpose storage account to use and that you change the values of the variables below to reflect your environment. Notice that one of the variables is called $partitionKey, in this example we are using only one partition, please refer to the documentation at the end of this blog in order to get a better understanding on benefits of partitions.
$resourceGroup = "imageprocess-rg"
$storageAccountName = "pmcstorage07tier0"
$queueName = "my-test-queue"
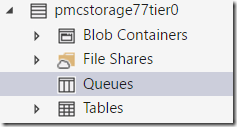
In this example I’m using the storage account named pmcstorage77tier0 and as we can see below I don’t have any queues created yet, this screen shot snippet was taken from Azure Storage Explorer, that can be installed from here.
Getting/Creating a queue
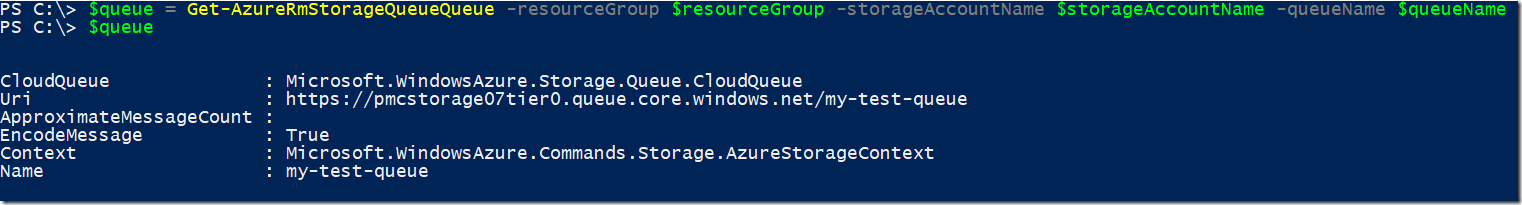
$queue = Get-AzureRmStorageQueueQueue -resourceGroup $resourceGroup -storageAccountName $storageAccountName -queueName $queueName
This is the result of the cmdlet below, it created a new queue since I didn’t had yet one named my-test-queue, notice that queue names cannot contain capital letters and spaces.
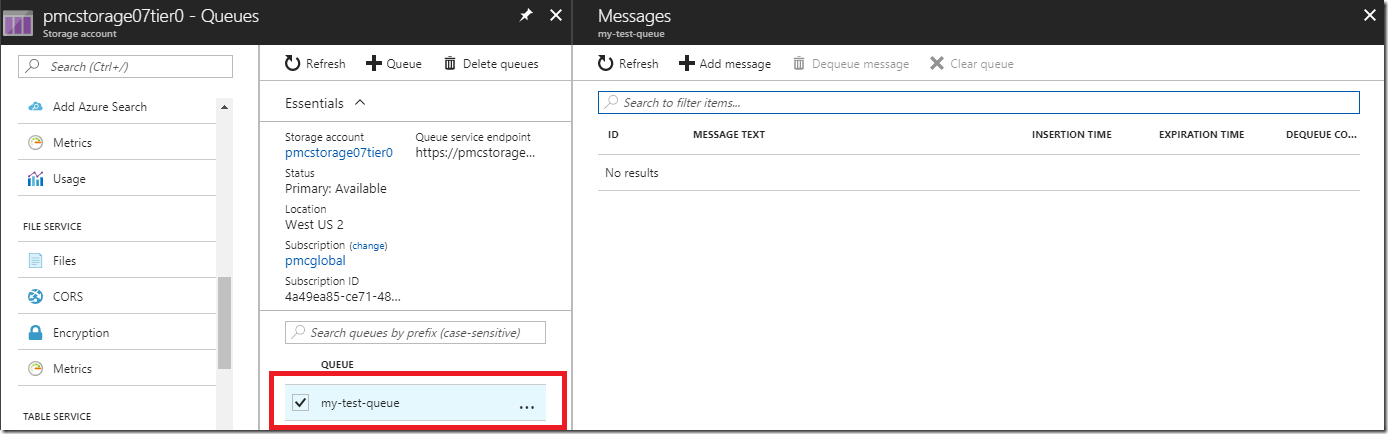
If we look at the https://portal.azure.com you can see that now I do have a new queue in my storage account:
Adding a message to the queue
In order to add messages to the queue we need to define a hash table, it can be in a separate object or directly defined in the cmdlet as you can see:
Example 1
Add-AzureRmStorageQueueMessage -queue $queue -message @{"type"="copy";"vhdname"="newvhd.vhd";"sourceStorageAccount"="pmcstorage05";"subscription"="mysubscription"}
Example 2
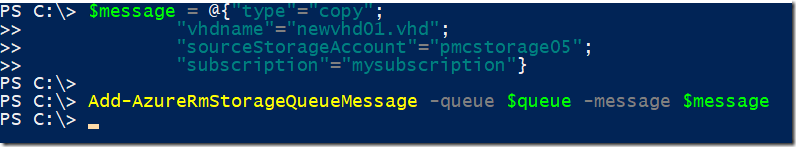
$message = @{"type"="copy";
"vhdname"="newvhd01.vhd";
"sourceStorageAccount"="pmcstorage05";
"subscription"="mysubscription"}
Add-AzureRmStorageQueueMessage -queue $queue -message $message
The effect behind the scenes is that this hash table will become a json string in the queue so you can easily consume it in whatever application you need.
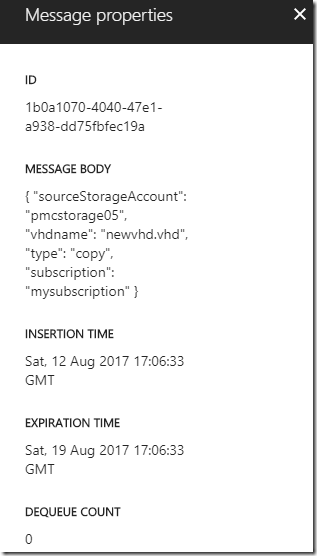
Details of message 1
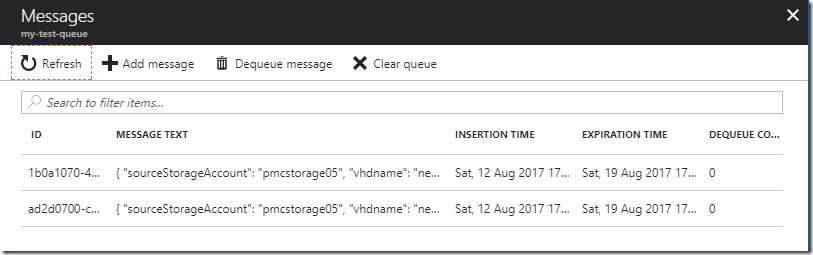
Peeking messages from the queue
Peek process in a queue allows you to get the message without de-queuing it, useful when you need to just inspect values inside of it, we do have two cmdles for this process, one that peeks the first available message (Invoke-AzureRmStorageQueuePeekMessage) or one to get the all messages in the queue (Invoke-AzureRmStorageQueuePeekMessageList).
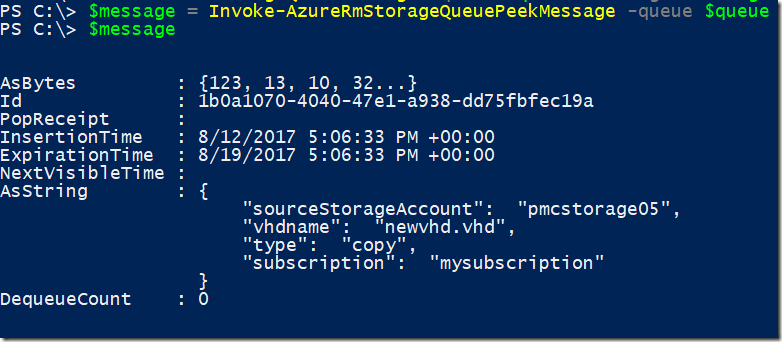
Example 1 – Peeking a single message
$message = Invoke-AzureRmStorageQueuePeekMessage -queue $queue
Result
Example 2 – Peeking all messages
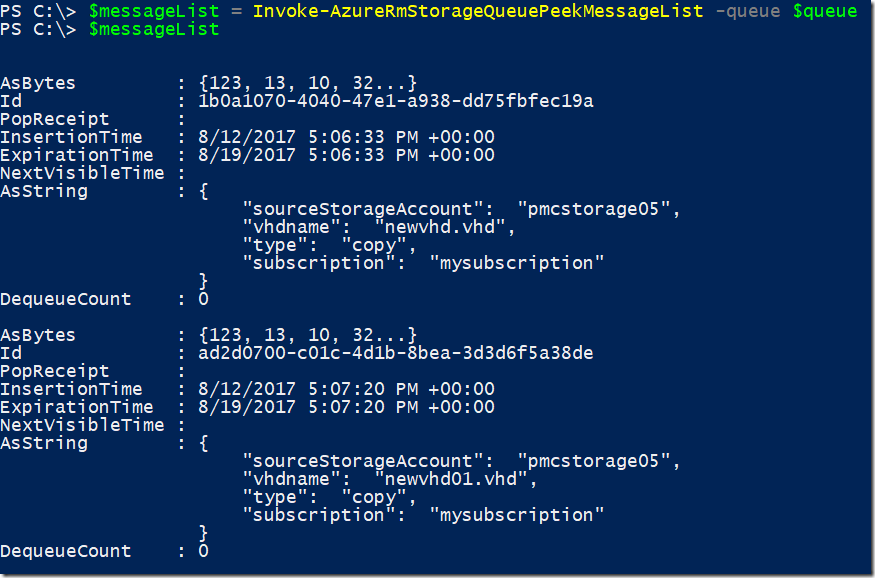
$messageList = Invoke-AzureRmStorageQueuePeekMessageList -queue $queue
Result
De-queuing messages from the queue
This process is a little different because this is the regular queue operation, it hides the message as soon as it is de-queued for processing for example.
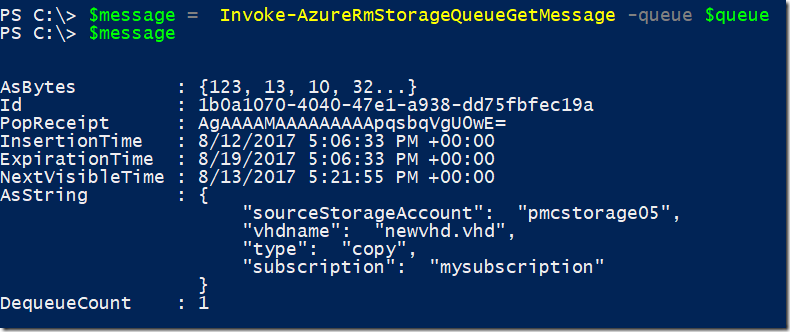
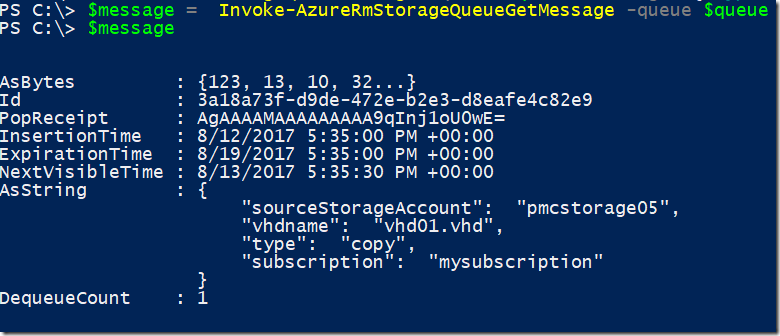
$message = Invoke-AzureRmStorageQueueGetMessage -queue $queue
Result
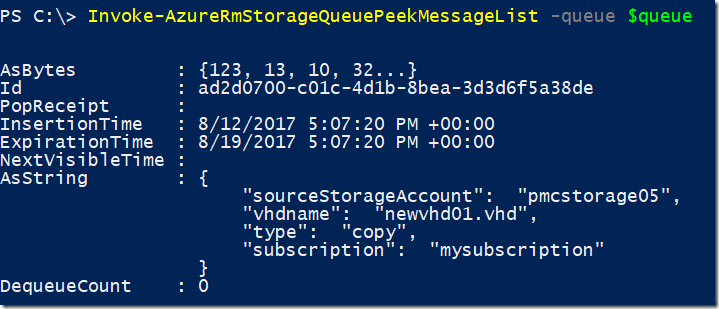
Please notice the DequeueCount property of the message, stating that it was de-queued one time. Now if we perform a peek to get all messages we just see the second message added because it was not de-queued. You can verify because the message ID is different as well.
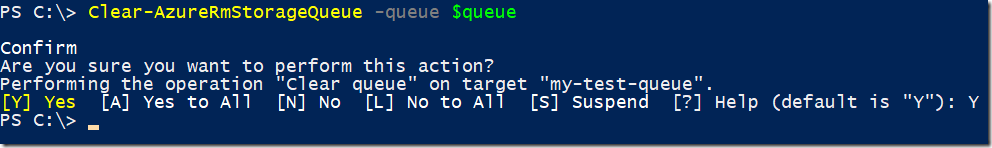
Clearing queue from all messages
Clear-AzureRmStorageQueue -queue $queue
Result
if you don’t want to be asked for confirmation you can just add –Confirm:$false to the end of the line.
Clear-AzureRmStorageQueue -queue $queue -Confirm:$false
Removing messages from the queue
In this situation we have two ways to preform this, one is by passing the CloudQueueMessage object which is obtained by using the Invoke-AzureRmStorageQueueGetMessage cmdlet or if you know the message id and the popReceipt values you can use them directly. Notice that you can only delete a message if you de-queue it first.
Example 1 – Passing CloudQueueMessage object as argument
Adding a test message to queue
Add-AzureRmStorageQueueMessage -queue $queue -message @{"type"="copy";"vhdname"="vhd01.vhd";"sourceStorageAccount"="pmcstorage05";"subscription"="mysubscription"}
De-queuing de message
$message = Invoke-AzureRmStorageQueueGetMessage -queue $queue
Removing the message based on the CloudQueueMessage object
Remove-AzureRmStorageQueueMessage -queue $queue -message $message
Notice that after deleting it I tried to de-queue the message but nothing came out because I deleted the message.
Example 2 – Passing message ID and popReceipt as argument
Adding another test message in the queue
Add-AzureRmStorageQueueMessage -queue $queue -message @{"type"="copy";"vhdname"="vhd02.vhd";"sourceStorageAccount"="pmcstorage05";"subscription"="mysubscription"}
De-queuing message
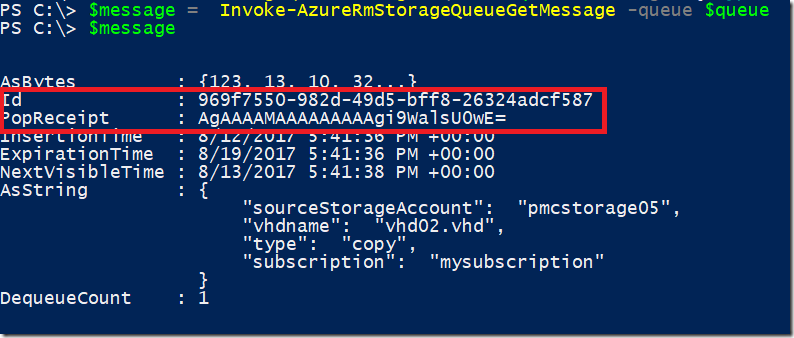
$message = Invoke-AzureRmStorageQueueGetMessage -queue $queue
Displaying message contents
Those red highlighted properties are the ones we will pass in the next cmdlet to delete the message.
Remove-AzureRmStorageQueueMessage -queue $queue -messageId "969f7550-982d-49d5-bff8-26324adcf587" -popReceipt "AgAAAAMAAAAAAAAAgi9WalsU0wE="
Of course I could use the $message object I already as $message.id and $message.popReceipt but my idea was to show how the actual values looks like.
As a side note, message only gets the popReceipt when you de-queue it.
Updating a message and placing it back to the queue
Sometimes all you need is to update the message content, this operation exemplifies how to perform this operation.
Adding a test message to the queue
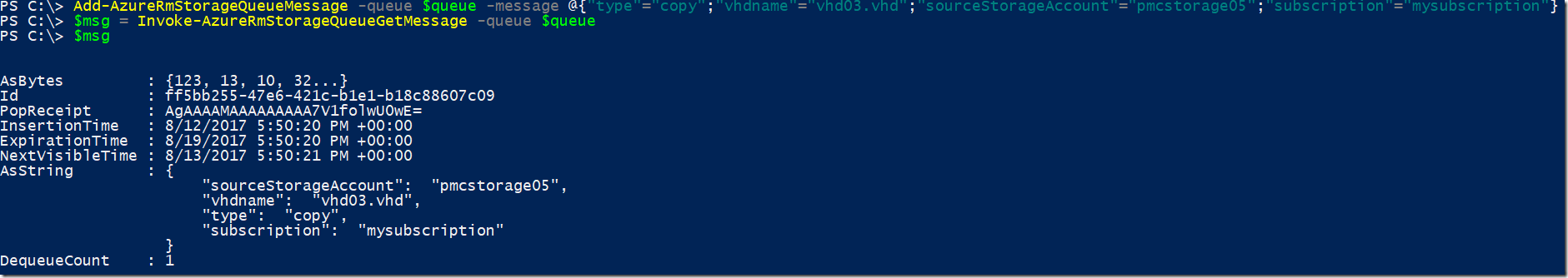
Add-AzureRmStorageQueueMessage -queue $queue -message @{"type"="copy";"vhdname"="vhd03.vhd";"sourceStorageAccount"="pmcstorage05";"subscription"="mysubscription"}
De-queuing the message
$msg = Invoke-AzureRmStorageQueueGetMessage -queue $queue
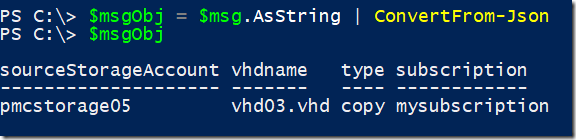
In this example we are changing the VHD name property of the JSON string with a random name, but first we need convert this JSON string into a PowerShell object to make things easier.
$msgObj = $msg.AsString | ConvertFrom-Json
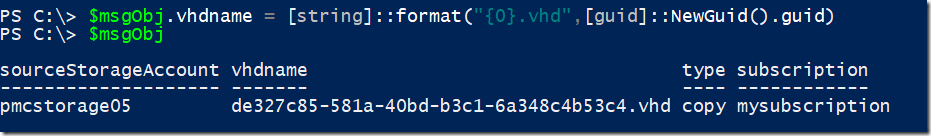
Changing the property content
$msgObj.vhdname = [string]::format("{0}.vhd",[guid]::NewGuid().guid)
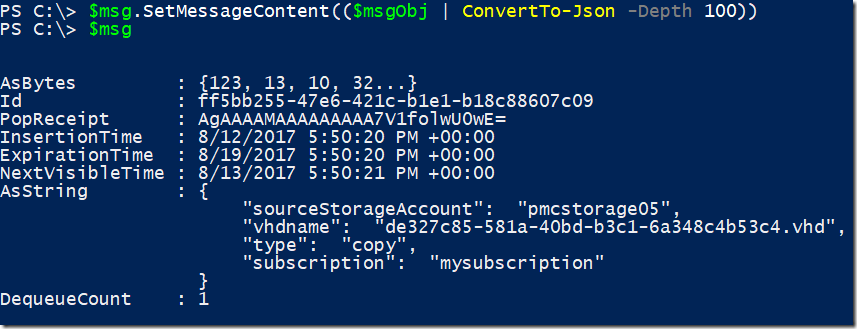
Updating the message object
$msg.SetMessageContent(($msgObj | ConvertTo-Json -Depth 100))
Updating the message in the queue
Update-AzureRmStorageQueueMessage -queue $queue -message $msg
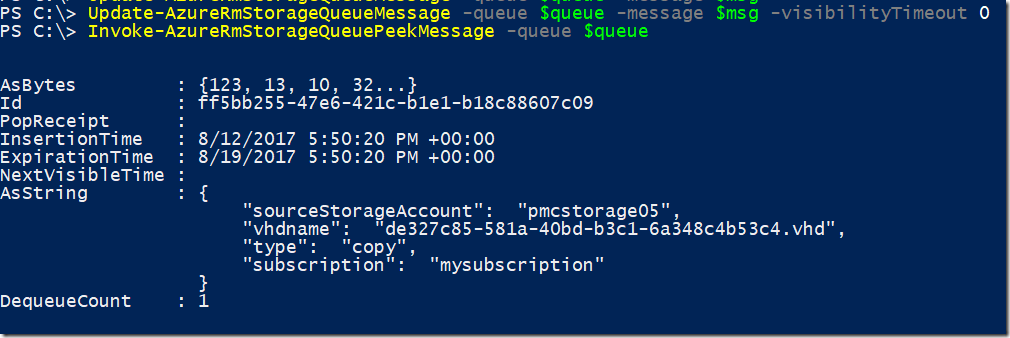
Making the message visible again in the queue and peeking the queue to check the changes made, notice that the popReceipt is null meaning the message is ready to get de-queued again.
Update-AzureRmStorageQueueMessage -queue $queue -message $msg -visibilityTimeout 0
Invoke-AzureRmStorageQueuePeekMessage -queue $queue
Well, that’s it for this post, I hope you enjoy this new PowerShell module and that it helps you build great PowerShell scripts using Azure Storage Queues.
Regards
Paulo
Comments
- Anonymous
August 16, 2017
Great description and samples! - Anonymous
November 10, 2017
This is brilliant, but I found a limitation. If you try and run Invoke-AzureRmStorageQueuePeekMessageList when there are more then 32 messages in the queue, you will get an error."Exception calling "PeekMessages" with "1" argument(s): "The remote server returned an error: (400) Bad Request." " This is not a limitation on the module, but of Azure, since even on the web portal and Storage Manager you can only see 32 messages.Since the module already counts the total messages in the queue, it might be worth it to have some messaging about a maximum queue message count.- Anonymous
November 13, 2017
Hi DC in TX,Thanks for the feedback, I will look at this and update the module.RegardsPaulo
- Anonymous