Azure Cloud Services (クラシック) でロール インスタンスの通信を有効にする
重要
現在、Cloud Services (クラシック) は新しいお客様に対して非推奨となっており、2024 年 8 月 31 日に、すべてのお客様に対して廃止される予定です。 新しいデプロイでは、新しい Azure Resource Manager ベースのデプロイ モデル、 Azure Cloud Services (延長サポート) を使用してください。
クラウド サービスのロールは、内部接続および外部接続で通信します。 外部接続は入力エンドポイントと呼ばれ、内部接続は内部エンドポイントと呼ばれます。 このトピックでは、 サービス定義 を変更してエンドポイントを作成する方法を説明します。
入力エンドポイント
入力エンドポイントは、ポートを外部に公開するときに使用します。 プロトコルの種類とエンドポイントのポートを指定してから、そのエンドポイントの内部ポートと外部ポートの両方に適用します。 必要に応じて、 localPort 属性を使用して、エンドポイントに異なる内部ポートを指定することができます。
入力エンドポイントには、プロトコル http、https、tcp、udpを使用できます。
入力エンドポイントを作成するには、Web ロールまたは worker ロールの Endpoints 要素に InputEndpoint 子要素を追加します。
<Endpoints>
<InputEndpoint name="StandardWeb" protocol="http" port="80" localPort="80" />
</Endpoints>
インスタンス入力エンドポイント
インスタンス入力エンドポイントは入力エンドポイントに似ていますが、ロード バランサーにポート フォワーディングを使用することで、個々のロール インスタンスごとに、特定の公開ポートをマップできます。 1 つの公開ポートまたはポートの範囲を指定できます。
インスタンス入力エンドポイントでは、tcp または udp のみをプロトコルとして使用できます。
インスタンス入力エンドポイントを作成するには、Web ロールまたは worker ロールの Endpoints 要素に InstanceInputEndpoint 子要素を追加します。
<Endpoints>
<InstanceInputEndpoint name="Endpoint2" protocol="tcp" localPort="10100">
<AllocatePublicPortFrom>
<FixedPortRange max="10109" min="10105" />
</AllocatePublicPortFrom>
</InstanceInputEndpoint>
</Endpoints>
内部エンドポイント
内部エンドポイントは、インスタンス間の通信で使用できます。 ポートは省略可能なので、省略した場合、動的なポートがエンドポイントに割り当てられます。 ポートの範囲も使用できます。 使用できる内部エンドポイントは、1 ロールあたり 5 つに制限されています。
内部エンドポイントには、プロトコル http、tcp、udp、anyを使用できます。
内部入力エンドポイントを作成するには、Web ロールまたは worker ロールの Endpoints 要素に InternalEndpoint 子要素を追加します。
<Endpoints>
<InternalEndpoint name="Endpoint3" protocol="any" port="8999" />
</Endpoints>
ポートの範囲を使用することもできます。
<Endpoints>
<InternalEndpoint name="Endpoint3" protocol="any">
<FixedPortRange max="8999" min="8995" />
</InternalEndpoint>
</Endpoints>
worker ロールとWeb ロールの比較
Worker ロールと Web ロールの両方を使用する場合は、エンドポイントにはわずかな相違点が 1 つあります。 Web ロールには、 HTTP プロトコルを使用している入力エンドポイントが少なくとも 1 つ必要です。
<Endpoints>
<InputEndpoint name="StandardWeb" protocol="http" port="80" localPort="80" />
<!-- more endpoints may be declared after the first InputEndPoint -->
</Endpoints>
.NET SDK を使用してエンドポイントにアクセスする方法
Azure マネージド ライブラリは、実行時に通信できるようロール インスタンスにメソッドを提供します。 ロール インスタンス内で実行するコードから、現在のロール インスタンスに関する情報だけでなく、他のロール インスタンスの存在およびそのエンドポイントに関する情報を取得できます。
注意
取得できるのは、自身のクラウド サービスで実行されているロール インスタンスに関する情報と、少なくとも 1 つの内部エンドポイントを定義するロール インスタンスの情報のみです。 別のサービスで実行されているロール インスタンスに関するデータは取得することはできません。
ロール インスタンスを取得するには、 Instances プロパティを使用します。 まず CurrentRoleInstance を使用して現在のロール インスタンスへの参照を返し、次に Role プロパティを使用してそのロール自体への参照を返します。
.NET SDK を介してプログラムによってロール インスタンスに接続する場合、比較的簡単にエンドポイントの情報にアクセスできます。 たとえば、特定のロール環境にすでに接続している場合、次のコードで特定のエンドポイントのポートを取得できます。
int port = RoleEnvironment.CurrentRoleInstance.InstanceEndpoints["StandardWeb"].IPEndpoint.Port;
Instances プロパティによって、RoleInstance オブジェクトのコレクションが返されます。 このコレクションには常に、現在のインスタンスが含まれています。 ロールによって内部エンドポイントが定義されていない場合、コレクションに現在のインスタンスは含まれますが、その他のインスタンスは含まれません。 コレクション内のロール インスタンスの数は、そのロールの内部エンドポイントが定義されていない場合は常に 1 になります。 ロールによって内部エンドポイントが定義されている場合は、そのインスタンスは実行時に検索可能で、コレクション内のインスタンスの数は、そのロールに対してサービス構成ファイルで指定されたインスタンスの数に一致します。
注意
Azure マネージド ライブラリでは、その他のロール インスタンスの正常性を判断する方法は提供されていませんが、ご利用のサービスでこのような正常性評価の機能が必要であれば、ご自身で実装することができます。 Azure Diagnostics を使用すると、実行中のロール インスタンスの情報を取得できます。
ロール インスタンスの内部エンドポイントのポート番号を確認するには、エンドポイント名および対応する IP アドレスとポートを含んだ Dictionary オブジェクトを返す InstanceEndpoints プロパティを使用できます。 IPEndpoint プロパティは、指定したエンドポイントの IP アドレスとポートを返します。 PublicIPEndpoint プロパティは、負荷分散エンドポイントのポートを返します。 PublicIPEndpoint プロパティの IP アドレス部分は使用されません。
ロール インスタンスを反復処理する例を次に示します。
foreach (RoleInstance roleInst in RoleEnvironment.CurrentRoleInstance.Role.Instances)
{
Trace.WriteLine("Instance ID: " + roleInst.Id);
foreach (RoleInstanceEndpoint roleInstEndpoint in roleInst.InstanceEndpoints.Values)
{
Trace.WriteLine("Instance endpoint IP address and port: " + roleInstEndpoint.IPEndpoint);
}
}
これは、サービス定義で公開されるエンドポイントを取得し、接続のリッスンを開始する worker ロールの例です。
警告
このコードは、デプロイ済みのサービスのみに使用できます。 Azure 計算エミュレーターでの実行時に、直接ポート エンドポイントを作成するサービス構成要素 (InstanceInputEndpoint 要素) は無視されます。
using System;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Linq;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Sockets;
using System.Threading;
using Microsoft.WindowsAzure;
using Microsoft.WindowsAzure.Diagnostics;
using Microsoft.WindowsAzure.ServiceRuntime;
using Microsoft.WindowsAzure.StorageClient;
namespace WorkerRole1
{
public class WorkerRole : RoleEntryPoint
{
public override void Run()
{
try
{
// Initialize method-wide variables
var epName = "Endpoint1";
var roleInstance = RoleEnvironment.CurrentRoleInstance;
// Identify direct communication port
var myPublicEp = roleInstance.InstanceEndpoints[epName].PublicIPEndpoint;
Trace.TraceInformation("IP:{0}, Port:{1}", myPublicEp.Address, myPublicEp.Port);
// Identify public endpoint
var myInternalEp = roleInstance.InstanceEndpoints[epName].IPEndpoint;
// Create socket listener
var listener = new Socket(
myInternalEp.AddressFamily, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp);
// Bind socket listener to internal endpoint and listen
listener.Bind(myInternalEp);
listener.Listen(10);
Trace.TraceInformation("Listening on IP:{0},Port: {1}",
myInternalEp.Address, myInternalEp.Port);
while (true)
{
// Block the thread and wait for a client request
Socket handler = listener.Accept();
Trace.TraceInformation("Client request received.");
// Define body of socket handler
var handlerThread = new Thread(
new ParameterizedThreadStart(h =>
{
var socket = h as Socket;
Trace.TraceInformation("Local:{0} Remote{1}",
socket.LocalEndPoint, socket.RemoteEndPoint);
// Shut down and close socket
socket.Shutdown(SocketShutdown.Both);
socket.Close();
}
));
// Start socket handler on new thread
handlerThread.Start(handler);
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Trace.TraceError("Caught exception in run. Details: {0}", e);
}
}
public override bool OnStart()
{
// Set the maximum number of concurrent connections
ServicePointManager.DefaultConnectionLimit = 12;
// For information on handling configuration changes
// see the MSDN topic at https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=166357.
return base.OnStart();
}
}
}
ロール通信を制御するためのネットワーク トラフィック規則
内部エンドポイントを定義した後、作成したエンドポイントに基づいてネットワーク トラフィック規則を追加して、ロール インスタンス間の通信方法を制御できます。 次の図は、ロール通信を制御するためのいくつかの一般的なシナリオを示しています。
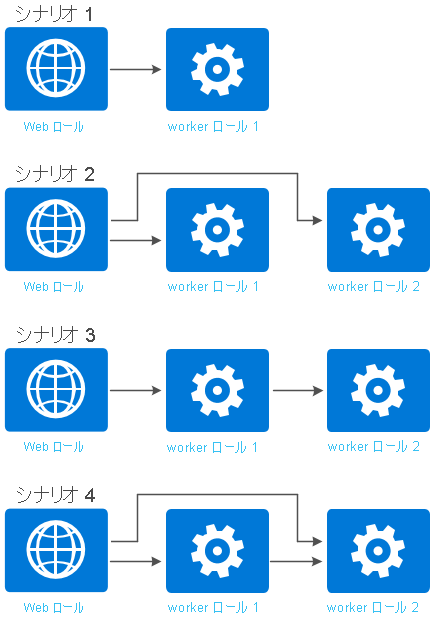
次のコード例は、前の図で示されたロールのロール定義を示しています。 各ロール定義では、少なくとも 1 つの内部エンドポイントが定義されています。
<ServiceDefinition name="MyService" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/ServiceHosting/2008/10/ServiceDefinition">
<WebRole name="WebRole1" vmsize="Medium">
<Sites>
<Site name="Web">
<Bindings>
<Binding name="HttpIn" endpointName="HttpIn" />
</Bindings>
</Site>
</Sites>
<Endpoints>
<InputEndpoint name="HttpIn" protocol="http" port="80" />
<InternalEndpoint name="InternalTCP1" protocol="tcp" />
</Endpoints>
</WebRole>
<WorkerRole name="WorkerRole1">
<Endpoints>
<InternalEndpoint name="InternalTCP2" protocol="tcp" />
</Endpoints>
</WorkerRole>
<WorkerRole name="WorkerRole2">
<Endpoints>
<InternalEndpoint name="InternalTCP3" protocol="tcp" />
<InternalEndpoint name="InternalTCP4" protocol="tcp" />
</Endpoints>
</WorkerRole>
</ServiceDefinition>
注意
ロール間の通信の制限は、固定ポートと自動割り当てポートの両方の内部エンドポイントで行うことができます。
既定では、内部エンドポイントを定義すると、任意のロールから別のロールの内部エンドポイントに、無制限で通信を行うことができます。 通信を制限するには、サービス定義ファイル内で、NetworkTrafficRules 要素を ServiceDefinition 要素に追加する必要があります。
シナリオ 1
WebRole1 から WorkerRole1 へのネットワーク トラフィックのみを許可する。
<ServiceDefinition name="MyService" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/ServiceHosting/2008/10/ServiceDefinition">
<NetworkTrafficRules>
<OnlyAllowTrafficTo>
<Destinations>
<RoleEndpoint endpointName="InternalTCP2" roleName="WorkerRole1"/>
</Destinations>
<AllowAllTraffic/>
<WhenSource matches="AnyRule">
<FromRole roleName="WebRole1"/>
</WhenSource>
</OnlyAllowTrafficTo>
</NetworkTrafficRules>
</ServiceDefinition>
シナリオ 2
WebRole1 から WorkerRole1 へのネットワーク トラフィック、および WorkerRole2 へのネットワーク トラフィックのみを許可する。
<ServiceDefinition name="MyService" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/ServiceHosting/2008/10/ServiceDefinition">
<NetworkTrafficRules>
<OnlyAllowTrafficTo>
<Destinations>
<RoleEndpoint endpointName="InternalTCP2" roleName="WorkerRole1"/>
<RoleEndpoint endpointName="InternalTCP3" roleName="WorkerRole2"/>
</Destinations>
<WhenSource matches="AnyRule">
<FromRole roleName="WebRole1"/>
</WhenSource>
</OnlyAllowTrafficTo>
</NetworkTrafficRules>
</ServiceDefinition>
シナリオ 3
WebRole1 から WorkerRole1 へのネットワーク トラフィック、WorkerRole1 から WorkerRole2 へのネットワーク トラフィックのみを許可する。
<ServiceDefinition name="MyService" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/ServiceHosting/2008/10/ServiceDefinition">
<NetworkTrafficRules>
<OnlyAllowTrafficTo>
<Destinations>
<RoleEndpoint endpointName="InternalTCP2" roleName="WorkerRole1"/>
</Destinations>
<AllowAllTraffic/>
<WhenSource matches="AnyRule">
<FromRole roleName="WebRole1"/>
</WhenSource>
</OnlyAllowTrafficTo>
</NetworkTrafficRules>
<NetworkTrafficRules>
<OnlyAllowTrafficTo>
<Destinations>
<RoleEndpoint endpointName="InternalTCP3" roleName="WorkerRole2"/>
</Destinations>
<WhenSource matches="AnyRule">
<FromRole roleName="WorkerRole1"/>
</WhenSource>
</OnlyAllowTrafficTo>
</NetworkTrafficRules>
</ServiceDefinition>
シナリオ 4
WebRole1 から WorkerRole1 へのネットワーク トラフィック、WebRole1 から WorkerRole2 へのネットワーク トラフィック、および WorkerRole1 から WorkerRole2 へのネットワーク トラフィックのみを許可する。
<ServiceDefinition name="MyService" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/ServiceHosting/2008/10/ServiceDefinition">
<NetworkTrafficRules>
<OnlyAllowTrafficTo>
<Destinations>
<RoleEndpoint endpointName="InternalTCP2" roleName="WorkerRole1"/>
</Destinations>
<AllowAllTraffic/>
<WhenSource matches="AnyRule">
<FromRole roleName="WebRole1"/>
</WhenSource>
</OnlyAllowTrafficTo>
</NetworkTrafficRules>
<NetworkTrafficRules>
<OnlyAllowTrafficTo >
<Destinations>
<RoleEndpoint endpointName="InternalTCP3" roleName="WorkerRole2"/>
</Destinations>
<AllowAllTraffic/>
<WhenSource matches="AnyRule">
<FromRole roleName="WorkerRole1"/>
</WhenSource>
</OnlyAllowTrafficTo>
</NetworkTrafficRules>
<NetworkTrafficRules>
<OnlyAllowTrafficTo >
<Destinations>
<RoleEndpoint endpointName="InternalTCP4" roleName="WorkerRole2"/>
</Destinations>
<AllowAllTraffic/>
<WhenSource matches="AnyRule">
<FromRole roleName="WebRole1"/>
</WhenSource>
</OnlyAllowTrafficTo>
</NetworkTrafficRules>
</ServiceDefinition>
上記で使用される要素の XML スキーマ参照は こちらでご覧ください。
次のステップ
Cloud Service モデルの詳細について参照できます。
フィードバック
以下は間もなく提供いたします。2024 年を通じて、コンテンツのフィードバック メカニズムとして GitHub の issue を段階的に廃止し、新しいフィードバック システムに置き換えます。 詳細については、「https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback」を参照してください。
フィードバックの送信と表示