Project Server CSOM と .NET の使用を開始する
Project Server 2013 のクライアント側オブジェクト モデル (CSOM) を使用して、.NET Framework 4 を使用した Project Online およびオンプレミスのソリューションを開発することができます。 この記事では、CSOM を使用するコンソール アプリケーションを作成して、プロジェクトを作成および発行する方法について説明します。 プロジェクトの発行後、このアプリケーションは Project Server Queue Service による発行操作の終了を待機してから、発行されたプロジェクトのリストを示します。
Project Server CSOM の一般的な概要については、「Project 2013 の開発者向け更新プログラム」を参照してください。 CSOM 名前空間のリファレンス トピックについては、「Microsoft.ProjectServer.Client 」を参照してください。
Visual Studio で CSOM プロジェクトを作成する
Project Server CSOM を使用するソリューションの開発には、Visual Studio 2010 または Visual Studio 2012 を使用できます。 Project Server CSOM には、.NET Framework 4 を使用してクライアント アプリケーション、Microsoft Silverlight アプリケーション、および Windows Phone 8 アプリケーションを開発するための 3 つのアセンブリが含まれています。 また、CSOM には Web アプリケーション開発のための JavaScript ファイルも含まれています (Microsoft.ProjectServer.Client を参照)。
Project Server コンピューターまたは Project 2013 SDK ダウンロード ファイルからリモートの開発用コンピューターに必要な CSOM アセンブリをコピーできます。 このトピックで説明する QueueCreateProject コンソール アプリケーションは、Silverlight アプリケーションまたは Windows Phone 8 アプリケーションのどちらでもないため、Microsoft.ProjectServer.Client.dll アセンブリが必要になります。 CSOM は WCF ベースまたは ASMX ベースの Project Server Interface (PSI) とは無関係なため、PSI のサービス参照を設定する必要も、Microsoft.Office.Project.Server.Library 名前空間を使用する必要もありません。
QueueCreateProject アプリケーションでは、作成するプロジェクトの名前とキューのタイムアウト制限をコマンド ライン引数で指定します。 手順 1 では、基本的なコンソール アプリケーションを作成し、コマンド ラインを解析するルーチンを追加し、コマンド ラインでエラーが発生した場合に使用方法を説明するメッセージを追加します。
手順 1. Visual Studio で CSOM プロジェクトを作成するには
microsoft.ProjectServer.Client.dll アセンブリを
%ProgramFiles%\Common Files\Microsoft Shared\Web Server Extensions\15\ISAPI\フォルダーから開発用コンピューターにコピーします。 アセンブリを、使用する他の Project Server および SharePoint 参照アセンブリ (C:\Project\Assembliesなど) の便利なフォルダーにコピーします。Microsoft.SharePoint.Client.dll アセンブリと Microsoft.SharePoint.Client.Runtime.dll アセンブリを同じソース フォルダーから開発コンピューターにコピーします。 Microsoft.ProjectServer.Client.dll アセンブリは関連する SharePoint アセンブリに依存します。
Visual Studio で、Windows コンソール アプリケーションを作成して、ターゲット フレームワークを .NET Framework 4 に設定します。 例として、アプリケーションの名前を「QueueCreateProject」にします。
注:
適切なターゲットの設定を忘れた場合、Visual Studio でプロジェクトを作成した後で、[プロジェクト] メニューの [QueueCreateProject のプロパティ] を開きます。 [アプリケーション] タブの [対象のフレームワーク] ドロップダウン リストで、[.NET Framework 4] を選択します。 [.NET Framework 4 Client Profile] は使用しないでください。
ソリューション エクスプローラーで、次のアセンブリへの参照を設定します。
- Microsoft.ProjectServer.Client.dll
- Microsoft.SharePoint.Client.dll
- Microsoft.SharePoint.Client.Runtime.dll
Program.cs ファイルで、次のように
usingステートメントを編集します。using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using Microsoft.ProjectServer.Client;プロジェクト名とキューのタイムアウト秒数を示すコマンド ライン引数を解析するメソッドを追加し、使用法の情報を表示して、アプリケーションを終了します。 Program.cs ファイルのコードの本文を次のコードに置き換えます。
namespace QueueCreateProject { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { if (!ParseCommandLine(args)) { Usage(); ExitApp(); } /* Add calls to methods here to get the project context and create a project. */ ExitApp(); } // Parse the command line. Return true if there are no errors. private static bool ParseCommandLine(string[] args) { bool error = false; int argsLen = args.Length; try { for (int i = 0; i < argsLen; i++) { if (error) break; if (args[i].StartsWith("-") || args[i].StartsWith("/")) args[i] = "*" + args[i].Substring(1).ToLower(); switch (args[i]) { case "*projname": case "*n": if (++i >= argsLen) return false; projName = args[i]; break; case "*timeout": case "*t": if (++i >= argsLen) return false; timeoutSeconds = Convert.ToInt32(args[i]); break; case "*?": default: error = true; break; } } } catch (FormatException) { error = true; } if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(projName)) error = true; return !error; } private static void Usage() { string example = "Usage: QueueCreateProject -projName | -n \"New project name\" [-timeout | -t sec]"; example += "\nExample: QueueCreateProject -n \"My new project\""; example += "\nDefault timeout seconds = " + timeoutSeconds.ToString(); Console.WriteLine(example); } private static void ExitApp() { Console.Write("\nPress any key to exit... "); Console.ReadKey(true); Environment.Exit(0); } } }
プロジェクトのコンテキストを取得する
CSOM の開発には、Project Web App の URL で初期化することになる ProjectContext オブジェクトが必要になります。 「手順 2」のコードでは、pwaPath を使用します。 Project Web App の複数のインスタンスにアプリケーションを使用する場合は、pwaPath を変数にして、もう 1 つのコマンドライン引数を追加します。
手順 2. プロジェクトのコンテキストを取得するには
QueueCreateProject アプリケーションで使用する、Program クラスの定数と変数を追加します。 Project Web App の URL に加えて、このアプリケーションでは、既定のエンタープライズ プロジェクトの種類 (EPT) の名前、作成するプロジェクトの名前、およびキューの最大タイムアウト (秒数) を使用します。 この場合、timeoutSeconds 変数を使用することで、さまざまなタイムアウトの値によるアプリケーションへの影響をテストできます。 ProjectContext オブジェクトは、CSOM にアクセスするためのプライマリ オブジェクトです。
private const string pwaPath = "https://ServerName /pwa/"; // Change the path to your Project Web App instance. private static string basicEpt = "Enterprise Project"; // Basic enterprise project type. private static string projName = string.Empty; private static int timeoutSeconds = 10; // The maximum wait time for a queue job, in seconds. private static ProjectContext projContext;/* Add calls to methods here to get the project context and create a project. */コメントを次のコードに置き換えます。 Microsoft.ProjectServer.Client.ProjectContext オブジェクトは、Project Web App の URL で初期化します。 CreateTestProject メソッドと ListPublishedProjects メソッドは、「手順 4」と「手順 5」で示します。projContext = new ProjectContext(pwaPath); if (CreateTestProject()) ListPublishedProjects(); else Console.WriteLine("\nProject creation failed: {0}", projName);
エンタープライズ プロジェクトの種類を取得する
QueueCreateProject サンプル アプリケーションでは、エンタープライズ プロジェクト テンプレート (EPT) を明示的に選択して、アプリケーションでのプロジェクトの EPT の選択方法を示しています。 プロジェクトの作成情報に EPT の GUID が指定されていない場合、アプリケーションは既定の EPT を使用します。 GetEptUid メソッドは、手順 4 で説明されている CreateTestProject メソッドで使用されます。
GetEptUid メソッドは、EnterpriseProjectTypes のコレクションに対し、EPT 名が指定した名前と等しい ProjectContext オブジェクトに対してクエリを実行します。 クエリの実行後、eptUid 変数は eptList コレクションの最初の EnterpriseProjectType オブジェクトの GUID に設定されます。 EPT 名は一意であるため、指定した名前を持つ EnterpriseProjectType オブジェクトは 1 つのみ存在します。
手順 3. 新しいプロジェクトの EPT の GUID を取得するには
Program クラスに GetEptUid メソッドを追加します。
// Get the GUID of the specified enterprise project type. private static Guid GetEptUid(string eptName) { Guid eptUid = Guid.Empty; try { // Get the list of EPTs that have the specified name. // If the EPT name exists, the list will contain only one EPT. var eptList = projContext.LoadQuery( projContext.EnterpriseProjectTypes.Where( ept => ept.Name == eptName)); projContext.ExecuteQuery(); eptUid = eptList.First().Id; } catch (Exception ex) { string msg = string.Format("GetEptUid: eptName = \"{0}\"\n\n{1}", eptName, ex.GetBaseException().ToString()); throw new ArgumentException(msg); } return eptUid; }
EPT の GUID の検索方法はいくつかあります。 GetEptUid メソッドで示されているクエリは、EPT 名と一致する EnterpriseProjectType オブジェクトを 1 つだけダウンロードするため、効率的です。 次に示す代替ルーチンは、EPT のリスト全体をクライアント アプリケーションにダウンロードしてリストを反復処理するため、効率が低くなります。
foreach (EnterpriseProjectType ept in projSvr.EnterpriseProjectTypes)
{
if (ept.Name == eptName)
{
eptUid = ept.Id;
break;
}
}
次のルーチンでは、LINQ クエリとラムダ式を使用して EPT オブジェクト選択していますが、依然として EnterpriseProjectType オブジェクトのすべてをダウンロードしています。
var eptList = projContext.LoadQuery(projContext.EnterpriseProjectTypes);
projContext.ExecuteQuery();
eptUid = eptList.First(ept => ept.Name == eptName).Id;
作成情報を設定してプロジェクトを発行する
CreateTestProject メソッドは ProjectCreationInformation オブジェクトを作成し、プロジェクトの作成に必要な情報を指定します。 プロジェクトの GUID と名前は必須であり、開始日、プロジェクトの説明、EPT の GUID は省略可能です。
新しいプロジェクトのプロパティを設定した後、Projects.Add メソッドでプロジェクトを Projects コレクションに追加します。 プロジェクトを保存して発行するには、Projects.Update メソッドを呼び出して Project Server キューにメッセージを送信し、プロジェクトを作成します。
手順 4. 新しいプロジェクトのプロパティを設定し、プロジェクトを作成して、発行するには
CreateTestProject メソッドを Program クラスに追加します。 次のコードではプロジェクトを作成して発行しますが、キューのジョブが完了するまで待機しません。
// Create a project. private static bool CreateTestProject() { bool projCreated = false; try { Console.Write("\nCreating project: {0} ...", projName); ProjectCreationInformation newProj = new ProjectCreationInformation(); newProj.Id = Guid.NewGuid(); newProj.Name = projName; newProj.Description = "Test creating a project with CSOM"; newProj.Start = DateTime.Today.Date; // Setting the EPT GUID is optional. If no EPT is specified, Project Server // uses the default EPT. newProj.EnterpriseProjectTypeId = GetEptUid(basicEpt); PublishedProject newPublishedProj = projContext.Projects.Add(newProj); QueueJob qJob = projContext.Projects.Update(); /* Add code here to wait for the queue. */ } catch(Exception ex) { Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Red; Console.WriteLine("\nError: {0}", ex.Message); Console.ResetColor(); } return projCreated; }/* Add code here to wait for the queue. */コメントを次のコードに置き換えて、キュー ジョブを待機します。 このルーチンは、指定した timeoutSeconds の秒数まで待機します。タイムアウトの前にキュー ジョブが完了した場合は処理を進めます。 考えられるキュー ジョブの状態については、Microsoft.ProjectServer.Client.JobState を参照してください。QueueJob オブジェクトの Load メソッドおよび ExecuteQuery メソッドの呼び出しは省略可能です。 WaitForQueue メソッドの呼び出し時に QueueJob オブジェクトが未初期化の場合、Project Server で初期化されます。
// Calling Load and ExecuteQuery for the queue job is optional. // projContext.Load(qJob); // projContext.ExecuteQuery(); JobState jobState = projContext.WaitForQueue(qJob, timeoutSeconds); if (jobState == JobState.Success) { projCreated = true; } else { Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow; Console.WriteLine("\nThere is a problem in the queue. Timeout is {0} seconds.", timeoutSeconds); Console.WriteLine("\tQueue JobState: {0}", jobState.ToString()); Console.ResetColor(); } Console.WriteLine();
発行したプロジェクトをリスト表示する
ListPublishedProjects メソッドは、Project Web App で発行されたすべてのプロジェクトのコレクションを取得します。 「手順 4」のプロジェクトを作成するキュー ジョブが正常に終了しなかった場合やタイムアウトになった場合は、新しいプロジェクトが Projects コレクションに含まれなくなります。
手順 5. 発行したプロジェクトを一覧表示するには
Program クラスに ListPublishedProjects メソッドを追加します。
// List the published projects. private static void ListPublishedProjects() { // Get the list of projects on the server. projContext.Load(projContext.Projects); projContext.ExecuteQuery(); Console.WriteLine("\nProject ID : Project name : Created date"); foreach (PublishedProject pubProj in projContext.Projects) { Console.WriteLine("\n\t{0} :\n\t{1} : {2}", pubProj.Id.ToString(), pubProj.Name, pubProj.CreatedDate.ToString()); } }Project Web App の URL に適切な値を設定し、QueueCreateProject アプリケーションをコンパイルして、「手順 6」に示すようにアプリケーションをテストします。
QueueCreateProject アプリケーションをテストする
Project Web App のテスト インスタンスで最初に QueueCreateProject アプリケーションを実行する場合、特に Project Server が仮想マシンにインストールされているときには、アプリケーションの実行に既定のキューのタイムアウトである 10 秒より長い時間がかかることがあります。
手順 6. QueueCreateProject アプリケーションをテストするには
[QueueCreateProject のプロパティ] ウィンドウを開き、[デバッグ] タブを選択し、[スタート オプション] セクションに次のコマンド ライン引数を追加します。
-n "Test proj 1" -t 20アプリケーションを実行します (たとえば、F5 キーを押します)。 タイムアウト値の長さが十分であれば、アプリケーションは次の結果を示します (その他の発行済みプロジェクトが Project Web App インスタンスに存在する場合は、そのプロジェクトも表示されます)。
Creating project: Test proj 1 ... Project ID : Project name : Created date b34d7009-753f-4abb-9191-f4b15a82aac3 : Test proj 1 : 9/22/2011 11:27:57 AM Press any key to exit...キューのタイムアウトに既定の 10 秒を使用するには、コマンドライン引数
-n "Test proj 1"で再度テストを実行します。Test proj 1 は既に存在しているため、アプリケーションの出力は次のようになります。
Creating project: Test proj 1 ... Error: PJClientCallableException: ProjectNameAlreadyExists ProjectNameAlreadyExists projName = Test proj 1 Project creation failed: Test proj 1 Press any key to exit...キューのタイムアウトに既定の 10 秒を使用するには、コマンドライン引数
-n "Test proj 2"で再度テストを実行します。QueueCreateProject アプリケーションは、Test proj 2 という名前のプロジェクトを作成して発行します。
次のコマンド ライン引数を使用して別のテストを実行し、キュー ジョブが完了するまでタイムアウトを短く設定します。
-n "Test proj 3" -t 1キューのタイムアウトが短すぎるため、プロジェクトは作成されません。 アプリケーションは次の結果を表示します。
Creating project: Test proj 3 ... There is a problem in the queue. Timeout is 1 seconds. Queue JobState: Unknown Project creation failed: Test proj 3 Press any key to exit...アプリケーションがキュー ジョブを待機しないようにコードを変更します。 たとえば、次のように、
projCreated = true行を除き、キューを待機するコードをコメント アウトします。//JobState jobState = projContext.WaitForQueue(qJob, timeoutSeconds); //if (jobState == JobState.Success) //{ projCreated = true; //} //else //{ // Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow; // Console.WriteLine("\nThere is a problem in the queue. Timeout is {0} seconds.", // timeoutSeconds); // Console.WriteLine("\tQueue JobState: {0}", jobState.ToString()); // Console.ResetColor(); //}アプリケーションを再コンパイルし、次のコマンド ライン引数を使用して別のテストを実行します。
-n "Test proj 4"WaitForQueue ルーチンがコメント アウトされているため、アプリケーションでは既定のタイムアウト値は使用されません。 アプリケーションはキューを待機しませんが、Project Server の発行処理が十分に高速であれば、Test proj 4 が表示される可能性があります。
Creating project: Test proj 4 ... Project ID : Project name : Created date cdd54103-082f-425c-b075-9ff52ac7d4e6 : Test proj 2 : 9/25/2011 4:28:55 PM b34d7009-753f-4abb-9191-f4b15a82aac3 : Test proj 1 : 9/22/2011 11:27:57 AM 5c0c73f2-f5dd-499b-8bd8-ebb74bf8c122 : Test proj 4 : 9/25/2011 4:39:21 PM Press any key to exit...
Project Web App の [プロジェクト センター] ページ (https://ServerName/ProjectServerName/Projects.aspx) を最新の情報に更新して、発行されたプロジェクトを表示します。 次の図はテスト プロジェクトが発行されていることを示しています。
Project Web App で発行済みのプロジェクトを確認する
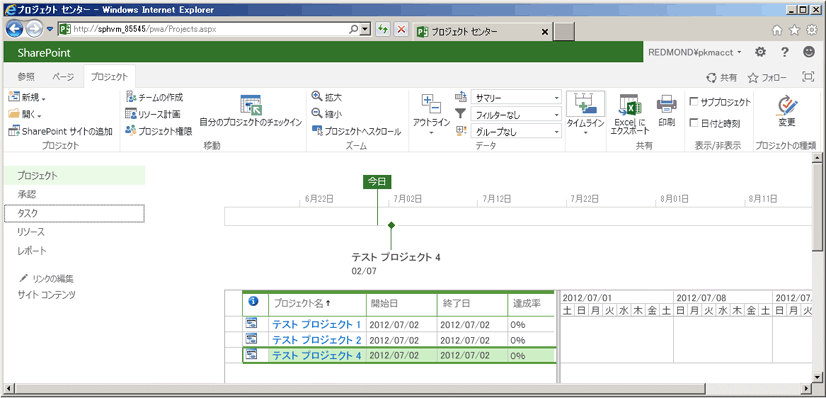 する
する
QueueCreateProject サンプル アプリケーションは、ProjectCreationInformation クラスを使用して CSOM でプロジェクト エンティティを作成する方法、発行済みコレクションにプロジェクトを追加する方法、WaitForQueue メソッドを使用してキュー ジョブを待機する方法、発行済みプロジェクトのコレクションを列挙する方法の一般的な例を示しています。
完全なコード例
QueueCreateProject サンプル アプリケーションの完全なコードを次に示します。 このトピックのコードは、Microsoft.ProjectServer.Client.ProjectCreationInformation クラス リファレンスにも含まれています。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using Microsoft.ProjectServer.Client;
namespace QueueCreateProject
{
class Program
{
private const string pwaPath = "https://ServerName /pwa/"; // Change the path to your Project Web App instance.
private static string basicEpt = "Enterprise Project"; // Basic enterprise project type.
private static string projName = string.Empty;
private static int timeoutSeconds = 10; // The maximum wait time for a queue job, in seconds.
private static ProjectContext projContext;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
if (!ParseCommandLine(args))
{
Usage();
ExitApp();
}
projContext = new ProjectContext(pwaPath);
if (CreateTestProject())
ListPublishedProjects();
else
Console.WriteLine("\nProject creation failed: {0}", projName);
ExitApp();
}
// Create a project.
private static bool CreateTestProject()
{
bool projCreated = false;
try
{
Console.Write("\nCreating project: {0} ...", projName);
ProjectCreationInformation newProj = new ProjectCreationInformation();
newProj.Id = Guid.NewGuid();
newProj.Name = projName;
newProj.Description = "Test creating a project with CSOM";
newProj.Start = DateTime.Today.Date;
// Setting the EPT GUID is optional. If no EPT is specified, Project Server uses
// the default EPT.
newProj.EnterpriseProjectTypeId = GetEptUid(basicEpt);
PublishedProject newPublishedProj = projContext.Projects.Add(newProj);
QueueJob qJob = projContext.Projects.Update();
// Calling Load and ExecuteQuery for the queue job is optional. If qJob is
// not initialized when you call WaitForQueue, Project Server initializes it.
// projContext.Load(qJob);
// projContext.ExecuteQuery();
JobState jobState = projContext.WaitForQueue(qJob, timeoutSeconds);
if (jobState == JobState.Success)
{
projCreated = true;
}
else
{
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow;
Console.WriteLine("\nThere is a problem in the queue. Timeout is {0} seconds.",
timeoutSeconds);
Console.WriteLine("\tQueue JobState: {0}", jobState.ToString());
Console.ResetColor();
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
catch(Exception ex)
{
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Red;
Console.WriteLine("\nError: {0}", ex.Message);
Console.ResetColor();
}
return projCreated;
}
// Get the GUID of the specified enterprise project type.
private static Guid GetEptUid(string eptName)
{
Guid eptUid = Guid.Empty;
try
{
// Get the list of EPTs that have the specified name.
// If the EPT name exists, the list will contain only one EPT.
var eptList = projContext.LoadQuery(
projContext.EnterpriseProjectTypes.Where(
ept => ept.Name == eptName));
projContext.ExecuteQuery();
eptUid = eptList.First().Id;
// Alternate routines to find the EPT GUID. Both (a) and (b) download the entire list of EPTs.
// (a) Using a foreach block:
//foreach (EnterpriseProjectType ept in projSvr.EnterpriseProjectTypes)
//{
// if (ept.Name == eptName)
// {
// eptUid = ept.Id;
// break;
// }
//}
// (b) Querying for the EPT list, and then using a lambda expression to select the EPT:
//var eptList = projContext.LoadQuery(projContext.EnterpriseProjectTypes);
//projContext.ExecuteQuery();
//eptUid = eptList.First(ept => ept.Name == eptName).Id;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
string msg = string.Format("GetEptUid: eptName = \"{0}\"\n\n{1}",
eptName, ex.GetBaseException().ToString());
throw new ArgumentException(msg);
}
return eptUid;
}
// List the published projects.
private static void ListPublishedProjects()
{
// Get the list of projects on the server.
projContext.Load(projContext.Projects);
projContext.ExecuteQuery();
Console.WriteLine("\nProject ID : Project name : Created date");
foreach (PublishedProject pubProj in projContext.Projects)
{
Console.WriteLine("\n\t{0} :\n\t{1} : {2}", pubProj.Id.ToString(), pubProj.Name,
pubProj.CreatedDate.ToString());
}
}
// Parse the command line. Return true if there are no errors.
private static bool ParseCommandLine(string[] args)
{
bool error = false;
int argsLen = args.Length;
try
{
for (int i = 0; i < argsLen; i++)
{
if (error) break;
if (args[i].StartsWith("-") || args[i].StartsWith("/"))
args[i] = "*" + args[i].Substring(1).ToLower();
switch (args[i])
{
case "*projname":
case "*n":
if (++i >= argsLen) return false;
projName = args[i];
break;
case "*timeout":
case "*t":
if (++i >= argsLen) return false;
timeoutSeconds = Convert.ToInt32(args[i]);
break;
case "*?":
default:
error = true;
break;
}
}
}
catch (FormatException)
{
error = true;
}
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(projName)) error = true;
return !error;
}
private static void Usage()
{
string example = "Usage: QueueCreateProject -projName | -n \"New project name\" [-timeout | -t sec]";
example += "\nExample: QueueCreateProject -n \"My new project\"";
example += "\nDefault timeout seconds = " + timeoutSeconds.ToString();
Console.WriteLine(example);
}
private static void ExitApp()
{
Console.Write("\nPress any key to exit... ");
Console.ReadKey(true);
Environment.Exit(0);
}
}
}