Step 6: Work with Git
Applies to: ![]() Visual Studio
Visual Studio ![]() Visual Studio for Mac
Visual Studio for Mac
Note
This article applies to Visual Studio 2017. If you're looking for the latest Visual Studio documentation, see Visual Studio documentation. We recommend upgrading to the latest version of Visual Studio. Download it here
Previous step: Install packages and manage your Python environment
Visual Studio provides direct integration with local Git repositories and remote repositories. It helps you on services like GitHub and Azure Repos. The integration includes cloning a repository, committing changes, and managing branches.
This article provides a basic overview of creating a local Git repository for an existing project, and familiarizing yourself with some of Visual Studio's Git-related features.
With a project open in Visual Studio, such as the project from the previous step, right-click the solution and select Add Solution to Source Control. Visual Studio creates a local Git repository that contains your project code.
When Visual Studio detects the project is managed in a Git repository, Git-related controls appear. The Git-related controls appear along the bottom right corner of the Visual Studio window. The controls show pending commits, changes, the name of the repository, and the branch. Hover over the controls to see additional information.
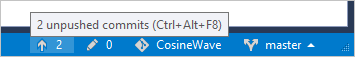
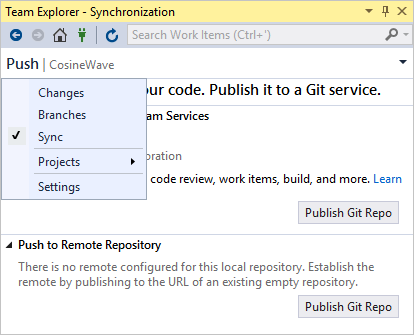
When you create a new repository or select any of the Git controls, Visual Studio opens the Team Explorer window. (You can open the window at any time with the View > Team Explorer menu command.) The window has three main panes, which you switch between using the drop-down on the Team Explorer header. The Sync pane, which provides publishing operations, also appears when you select the Push control (the up arrow icon):
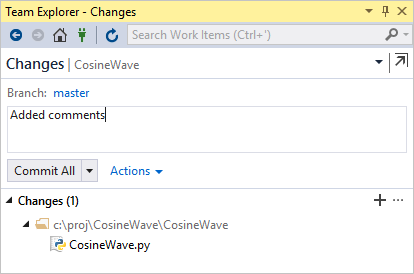
Select Changes (or the Git control with the pencil icon) to review uncommitted changes and to commit them when desired.
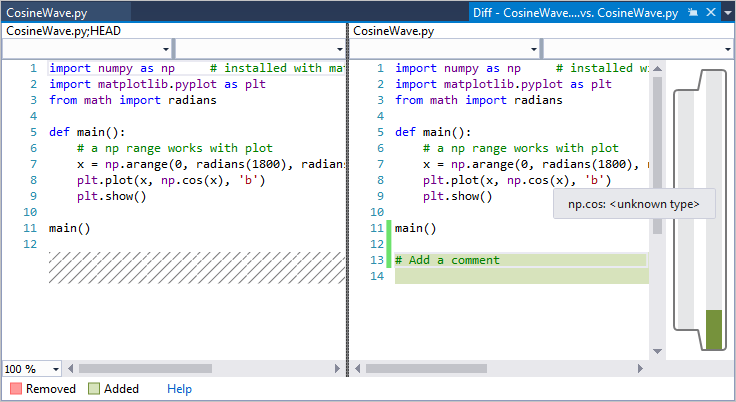
Double-click a file in the Changes list to open a diff view for that file:
Select Branches (or the Git control with a branch name) to examine branches and perform merge and rebase operations:
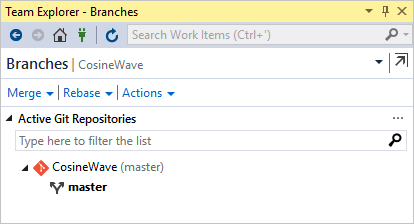
To switch to another repository, select the Git control with the repository name (CosineWave in a previous image), and then in Team Explorer, use the Connect interface.
When you use a local repository, committed changes go directly into the repository. If you're connected to a remote repository, select the drop-down header in Team Explorer, select Sync to switch to the Synchronization section, and work with the Pull and Fetch commands presented there.
Go deeper
For a short walkthrough of creating a project from a remote Git repository, see Quickstart: Clone a repository of Python code in Visual Studio.
For a much more comprehensive tutorial, including handling merge conflicts, reviewing code with pull requests, rebasing, and cherry-picking changes between branches, see Get started with Git and Azure Repos.
Tutorial review
Congratulations on completing this tutorial on Python in Visual Studio. In this tutorial you've learned how to:
- Create projects and view a project's contents.
- Use the code editor and run a project.
- Use the Interactive window to develop new code and easily copy that code into the editor.
- Run a completed program in the Visual Studio debugger.
- Install packages and manage Python environments.
- Work with code in a Git repository.
From here, explore the Concepts and How-to guides, including the following articles: