Determine mitigations for network-related security threats
Attackers will try to access your network by using various tools and techniques. Once they find a way into your network, they can exploit that success and take their attack further. For this reason, it's important to implement a comprehensive approach to network security, so that you can ensure that one loophole or omission doesn't result in further weaknesses upon which malicious users can capitalize.
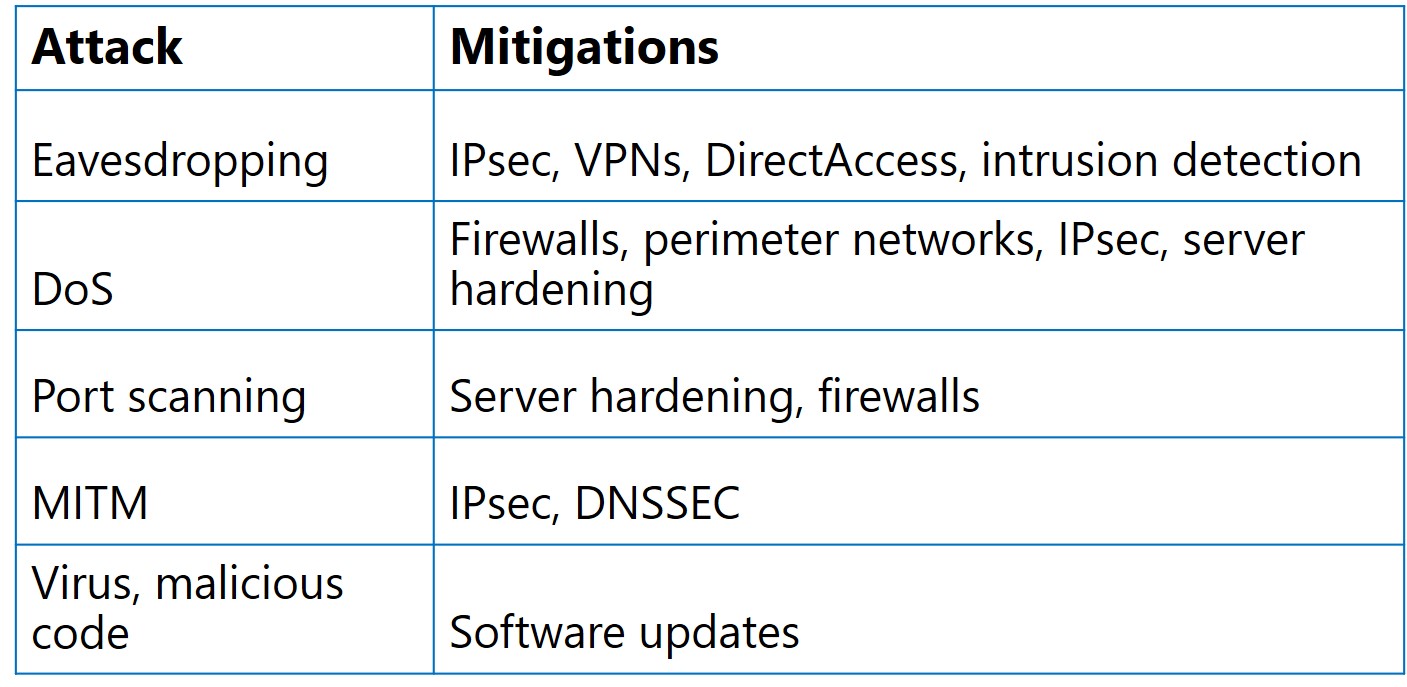
You can use any, or all, of the following defense mechanisms to help protect your network from malicious attacks:
- Internet Protocol security (IPsec), which authenticates IP-based communications between two hosts and, where desirable, encrypt that network traffic.
- Firewalls, which allow or block network traffic based on the type of traffic.
- Perimeter networks, which are isolated areas on your network to and from which you can define network traffic flow. When you need to make network services available on the Internet, it isn't advisable to connect hosting servers directly to the Internet. However, by placing these servers in a perimeter network, you can make them available to internet users without allowing those users access to your corporate intranet.
- VPNs and DirectAccess. It's important that users have the ability to connect to their organization’s intranet from the Internet as securely as possible. The Internet is a public network, and data in transit across the Internet is susceptible to eavesdropping or MITM attacks. However, by using virtual private networks (VPNs) or DirectAccess, you can authenticate and encrypt connections between remote users and your organization’s intranet. This can help to mitigate risk.
- Server hardening. When you run only the services that you need, you can make servers inherently more secure. To determine what services you require, you must establish a security baseline among your servers. To determine precisely which Windows Server services you need to support the functionality that you or your enterprise requires, you can use tools such as the Security Configuration Wizard or the Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer.
- Intrusion detection. It's important to implement the preceding techniques to secure your network, and it also is sensible to monitor your network regularly for signs of attack. You can use intrusion-detection systems to do this by implementing them on perimeter devices, such as Internet-facing routers.
- Domain Name System Security Extensions (DNSSEC), which use digital signatures for validation, so that DNS servers and resolvers can trust DNS responses. The DNS zone contains all signatures that are generated in the new resource records. When a resolver issues a query for a name, the DNS server returns the accompanying digital signature in the response. The resolver then validates the signature by using a preconfigured trust anchor. Successful validation proves that no data modification or tampering has occurred.