Govern your data
Governing data is essential for managing information throughout its lifecycle, ensuring compliance, and minimizing risk. Effective governance involves retaining important data only as long as needed and securely deleting it when no longer required. This process helps organizations meet legal standards and reduces the risk associated with storing unnecessary data. To support these efforts, Microsoft Purview provides tools like data lifecycle management and records management. These tools automate retention, manage records, and streamline deletion, helping organizations maintain compliance and protect sensitive information.
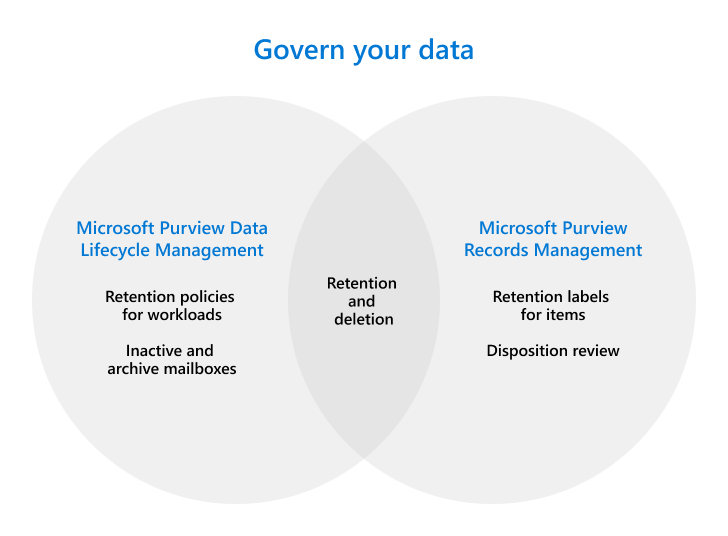
Microsoft Purview Data Lifecycle Management
Microsoft Purview Data Lifecycle Management helps manage the lifecycle of content by applying retention and deletion policies to ensure compliance. This process applies to general data, whether stored in mailboxes, SharePoint, or other workloads across Microsoft 365. Here's a framework for managing your data with data lifecycle management:
- Understand how retention and deletion work for Microsoft 365 services: Before you can manage your data lifecycle, it's essential to understand how retention and deletion function within the Microsoft 365 ecosystem. Each service, from Exchange mailboxes to SharePoint, might have different retention needs depending on how data is stored and shared.
- Create retention policies and, if needed, retention labels for exceptions: Retention policies allow you to control how long data is kept and when it's deleted. In cases where more granularity is needed, retention labels provide flexibility by applying unique retention settings to specific content.
- Manage mailboxes: Mailboxes are a critical source of information. Use data lifecycle management policies to apply retention settings that archive or delete mailboxes when necessary. This process ensures that obsolete data doesn't take up space and is securely removed when no longer needed.
- Import PST files to online mailboxes: By importing PST files into online mailboxes, you ensure that data is governed and protected under Microsoft 365 retention policies, reducing the risk of unmanaged data.

Microsoft Purview Records Management
Records management takes retention a step further by applying advanced controls to business-critical or legally required records. These records are immutable, meaning they can't be altered once classified as records, ensuring legal and regulatory compliance. Here's a framework for managing records with records management:
- Understand the records management solution: Records management provides advanced retention capabilities designed for content that must be preserved as records. It's essential to understand the capabilities of records management, such as immutability and stricter controls.
- Use a file plan to manage your retention schedules: A file plan helps organize your retention schedules by categorizing records based on their type and retention requirements. This plan acts as a roadmap for governing specific sets of content across your organization.
- Apply your retention labels: Retention labels classify content as a record and apply the appropriate retention rules. These labels ensure that content is retained according to your file plan and that records are protected against deletion or modification.
- Manage the permanent deletion of data: Once records reach the end of their retention period, the system can be configured to automatically delete or review the content for disposition. This helps maintain compliance by ensuring no records are kept beyond their required retention.

Retention labels and policies
Retention plays a central role in both data lifecycle and records management, ensuring that organizations can keep the data they need and discard what they don't. Here's a look at the retention features that you can configure within Microsoft Purview:
- Retention labels: These labels apply to specific items, like documents or emails, to control how long they're retained and when they're deleted. Retention labels can be automatically or manually applied and offer granular control over content.
- Retention label policies: Label policies allow you to publish retention labels to specific locations, such as SharePoint sites or Exchange mailboxes, ensuring that these labels are available for use across Microsoft 365 workloads.
- Retention policies: These policies apply to entire workloads, such as all mailboxes or OneDrive accounts. Retention policies allow you to manage data on a larger scale and automatically retain or delete content based on organizational needs.
By understanding and configuring these retention tools, you can ensure that your organization complies with regulatory requirements while reducing the amount of data you need to manage.
Data lifecycle management vs. records management
Microsoft Purview offers both data lifecycle management and records management to meet a wide range of governance needs. While both solutions focus on retention and deletion, they serve different purposes:
- Data lifecycle management: Handles the retention of general content, such as emails and documents, ensuring that data is kept or deleted based on organizational policies.
- Records management: Applies stricter controls to business-critical records that must be preserved for legal or regulatory reasons. Records are immutable, ensuring they can't be modified or deleted until the retention period expires.
By following these frameworks and using retention policies, you can ensure that your organization's data remains compliant, well-managed, and protected throughout its lifecycle.