Cortana の音声コマンドを使ったフォアグラウンド アプリのアクティブ化
警告
この機能は、Windows 10 May 2020 Update (バージョン 2004、コードネーム "20H1") ではサポートされなくなりました。
Cortana 内の音声コマンドを使用してシステム機能にアクセスするだけでなく、アプリの機能を使用して Cortana を拡張することもできます。 音声コマンドを使用すると、アプリをフォアグラウンドにアクティブ化し、アプリ内で実行されるアクションまたはコマンドをアクティブ化できます。
アプリがフォアグラウンドで音声コマンドを処理すると、フォーカスが設定され、Cortana は無視されます。 必要に応じて、アプリをアクティブ化し、バックグラウンド タスクとしてコマンドを実行できます。 この場合、Cortana はフォーカスを保持し、アプリは Cortana キャンバスと Cortana 音声を通じてすべてのフィードバックと結果を返します。
追加のコンテキストやユーザー入力を必要とする音声コマンド (特定の連絡先へのメッセージの送信など) はフォアグラウンド アプリで最適に処理されますが、基本的なコマンド (今後の旅行の一覧表示など) はバックグラウンド アプリを介して Cortana で処理できます。
音声コマンドを使用してバックグラウンドでアプリをアクティブ化する場合は、「Cortana の音声コマンドを使ったバックグラウンド アプリのアクティブ化」をご覧ください。
Note
音声コマンドは、特定の意図を持つ 1 つの発話であり、音声コマンド定義 (VCD) ファイルで定義されています。Cortana を通じてインストール済みアプリに指示が伝えられます。
VCD ファイルでは、1 つ以上の音声コマンドが定義されており、各音声コマンドは固有の目的を持っています。
音声コマンド定義は複雑さが異なる場合があります。 制約のある 1 つの発話から、より柔軟な自然言語の発話のコレクションまで、すべて同じ意図を示すあらゆるものをサポートできます。
フォアグラウンド アプリの機能を示すために、Cortana 音声コマンド サンプルAdventure Works という名前の旅行計画および管理アプリを使用。
Cortana を使用せずに新しい Adventure Works trip を作成するには、ユーザーがアプリを起動し、新しい乗車 ページに移動します。 既存の乗車を表示するには、ユーザーがアプリを起動し、 Upcoming trip ページに移動して、旅行を選択します。
Cortana を介して音声コマンドを使用すると、代わりに "Adventure Works add a trip" または "Add a trip on Adventure Works" (Adventure Works で旅行を追加) と言ってアプリを起動し、新しい乗車 ページに移動できます。 次に、"Adventure Works, show my trip to London" と言うと、アプリが起動し、次に示す Trip 詳細ページに移動します。
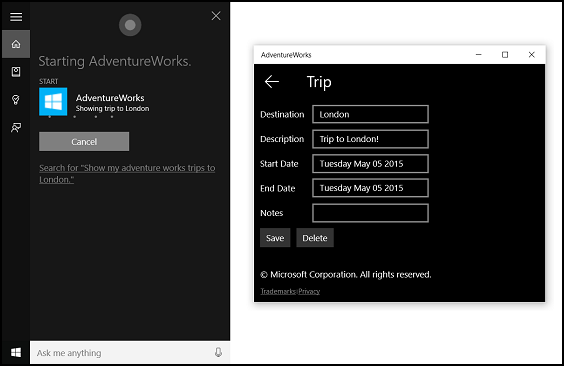
音声コマンド機能を追加し、音声またはキーボード入力を使用して Cortana をアプリと統合する基本的な手順を次に示します。
- VCD ファイルを作成します。 これは、アプリをアクティブ化するときにアクションを開始したりコマンドを呼び出したりするためにユーザーが言うことができるすべての音声コマンドを定義する XML ドキュメントです。 VCD 要素と属性 v1.2 を参照してください。
- アプリの起動時に VCD ファイルにコマンド セットを登録します。
- activation-by-voice コマンド、アプリ内のナビゲーション、およびコマンドの実行を処理します。
ヒント
必要条件
ユニバーサル Windows プラットフォーム (UWP) アプリを開発するのが初めての場合は、以下のトピックに目を通して、ここで説明されているテクノロジをよく理解できるようにしてください。
- 初めてのアプリの作成
- 「イベントとルーティング イベントの概要」に記載されているイベントの説明
ユーザー エクスペリエンス ガイドライン
アプリと Cortana を統合する方法については「Cortana の設計ガイドライン」を、便利で魅力的な音声認識対応アプリの設計に役立つヒントについては「音声操作」を参照してください。
Visual Studio でプロジェクトを使用して新しいソリューションを作成する
Microsoft Visual Studio 2015 を起動します。
Visual Studio 2015 のスタート ページが表示されます。
[ファイル] メニューで、 [新規作成]>[プロジェクト] の順に選択します
[新しいプロジェクト] ダイアログ ボックスが表示されます。 ダイアログの左側のウィンドウでは、表示するテンプレートの種類を選択できます。
左側のウィンドウで、[インストール済み] > [テンプレート] > [Visual C#] > [Windows] を展開した後、[ユニバーサル] テンプレート グループを選びます。 ダイアログの中央のウィンドウには、ユニバーサル Windows プラットフォーム (UWP) アプリのプロジェクト テンプレートの一覧が表示されます。
中央のウィンドウで、 Blank アプリ (ユニバーサル Windows) テンプレートを選択します。
Blank アプリ テンプレートは、コンパイルして実行するが、ユーザー インターフェイス コントロールやデータを含まない最小限の UWP アプリを作成します。 このチュートリアルでは、アプリにコントロールを追加します。
[ Name テキスト ボックスに、プロジェクト名を入力します。 この例では、"AdventureWorks" を使用します。
[OK] をクリックしてプロジェクトを作成します。
Microsoft Visual Studio によってプロジェクトが作成され、ソリューション エクスプローラーに表示されます。
イメージ アセットをプロジェクトに追加し、アプリ マニフェストで指定する
UWP アプリでは、特定の設定とデバイスの機能 (ハイ コントラスト、有効ピクセル、ロケールなど) に基づいて、最適な画像を自動的に選択できます。 必要なのは、イメージを提供し、アプリ プロジェクト内の適切な名前付け規則とフォルダー編成をさまざまなリソース バージョンに使用することです。 推奨されるリソースバージョン、アクセシビリティ、ローカライズ、および画質を提供しない場合は、ユーザーの設定、機能、デバイスの種類、場所に応じて、問題が発生する可能性があります。
ハイ コントラストおよびスケール ファクターの画像リソースの詳細については、「タイルアセットとアイコン アセットの Guidelines」を参照してください。
修飾子を使用してリソースに名前を付けます。 リソース修飾子は、特定のバージョンのリソースを使用するコンテキストを識別するフォルダーおよびファイル名修飾子です。
標準の名前付け規則は foldername/qualifiername-value[_qualifiername-value]/filename.qualifiername-value[_qualifiername-value].ext。 たとえば、ルート フォルダーとファイル名を使用してコード内で参照できる images/logo.scale-100_contrast-white.png: images/logo.png。 「 修飾子を使用してリソースに名前を付ける方法を参照してください。
ローカライズされたまたは複数の解決リソースを提供する予定がない場合でも、文字列リソース ファイル ( en-US\resources.resw など) の既定の言語とイメージの既定のスケール ファクター ( logo.scale-100.png など) をマークすることをお勧めします。 ただし、少なくとも、100、200、400 のスケール ファクターに資産を提供することをお勧めします。
重要
Cortana キャンバスのタイトル領域で使用されるアプリ アイコンは、"Package.appxmanifest" ファイルで指定された Square44x44Logo アイコンです。
VCD ファイルを作成する
- Visual Studio で、プライマリ プロジェクト名を右クリックし、[追加] > [新しい項目] を選択します。 XML ファイルを追加します。
- VCD ファイルの名前 (この例では "AdventureWorksCommands.xml") を入力し、[追加] をクリックします。
- ソリューション エクスプローラーで、VCD ファイルを選択します。
- Properties ウィンドウで、Build アクションを Content に設定し、Copy を出力ディレクトリに設定し新しい場合は Copy に設定。
VCD ファイルを編集する
https://schemas.microsoft.com/voicecommands/1.2を指す xmlns 属性を持つ VoiceCommands 要素を追加します。
アプリでサポートされている言語ごとに、アプリでサポートされている音声コマンドを含む CommandSet 要素を作成します。
複数の CommandSet 要素をそれぞれ異なる xml:lang 属性で宣言して、アプリをさまざまな市場で使用することができます。 たとえば、米国用のアプリには、英語の場合は CommandSet、スペイン語の場合は CommandSet があります。
注意事項
アプリをアクティブ化し、音声コマンドを使用してアクションを開始するには、 CommandSet を含む VCD ファイルを、デバイスでユーザーが選択した音声言語と一致する言語で登録する必要があります。 音声の言語は、[設定] > [システム] > [音声認識] > [音声認識の言語] にあります。
サポートするコマンドごとに Command 要素を追加します。 VCD ファイルで宣言された各 Command は、次の情報を含む必要があります。
- アプリケーションが実行時に音声コマンドを識別するために使用する AppName 属性。
- ユーザーがコマンドを呼び出す方法を説明する語句を含む Example 要素。 Cortana は、ユーザーが "What can i say?"、"Help"、または [詳細 ] をタップしたときに、この例を示します。
- ListenForアプリがコマンドとして認識する単語または語句を含む要素。 各 ListenFor 要素には、コマンドに関連する特定の単語を含む 1 つ以上の PhraseList 要素への参照を含めることができます。
Note
ListenFor 要素をプログラムで変更することはできません。 ただし、 PhraseList ListenFor 要素に関連付けられている要素は、プログラムで変更できます。 アプリケーションでは、ユーザーがアプリを使用する際に生成されたデータ セットに基づいて、実行時に PhraseList のコンテンツを変更する必要があります。 「Cortana VCD の語句一覧の動的な変更」を参照してください。
Feedback アプリケーションの起動時に表示および読み上げを行うCortanaのテキストを含む要素。
Navigate 要素は、音声コマンドによってアプリがフォアグラウンドにアクティブ化されることを示します。 この例では、 showTripToDestination コマンドはフォアグラウンド タスクです。
VoiceCommandService 要素は、音声コマンドがバックグラウンドでアプリをアクティブ化することを示します。 この要素の Target 属性の値は、package.appxmanifest ファイルの uap:AppService 要素の Name 属性の値と一致する必要があります。 この例では、 whenIsTripToDestination コマンドと cancelTripToDestination コマンドは、アプリ サービスの名前を "AdventureWorksVoiceCommandService" として指定するバックグラウンド タスクです。
詳細については、 VCD 要素と属性 v1.2 リファレンスを参照してください。
Adventure Works アプリの en-us 音声コマンドを定義する VCD ファイルの一部を次に示します。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<VoiceCommands xmlns="https://schemas.microsoft.com/voicecommands/1.2">
<CommandSet xml:lang="en-us" Name="AdventureWorksCommandSet_en-us">
<AppName> Adventure Works </AppName>
<Example> Show trip to London </Example>
<Command Name="showTripToDestination">
<Example> Show trip to London </Example>
<ListenFor RequireAppName="BeforeOrAfterPhrase"> show [my] trip to {destination} </ListenFor>
<ListenFor RequireAppName="ExplicitlySpecified"> show [my] {builtin:AppName} trip to {destination} </ListenFor>
<Feedback> Showing trip to {destination} </Feedback>
<Navigate />
</Command>
<Command Name="whenIsTripToDestination">
<Example> When is my trip to Las Vegas?</Example>
<ListenFor RequireAppName="BeforeOrAfterPhrase"> when is [my] trip to {destination}</ListenFor>
<ListenFor RequireAppName="ExplicitlySpecified"> when is [my] {builtin:AppName} trip to {destination} </ListenFor>
<Feedback> Looking for trip to {destination}</Feedback>
<VoiceCommandService Target="AdventureWorksVoiceCommandService"/>
</Command>
<Command Name="cancelTripToDestination">
<Example> Cancel my trip to Las Vegas </Example>
<ListenFor RequireAppName="BeforeOrAfterPhrase"> cancel [my] trip to {destination}</ListenFor>
<ListenFor RequireAppName="ExplicitlySpecified"> cancel [my] {builtin:AppName} trip to {destination} </ListenFor>
<Feedback> Cancelling trip to {destination}</Feedback>
<VoiceCommandService Target="AdventureWorksVoiceCommandService"/>
</Command>
<PhraseList Label="destination">
<Item>London</Item>
<Item>Las Vegas</Item>
<Item>Melbourne</Item>
<Item>Yosemite National Park</Item>
</PhraseList>
</CommandSet>
VCD コマンドをインストールする
VCD をインストールするには、アプリを 1 回実行する必要があります。
Note
音声コマンド データは、アプリのインストール間で保持されません。 アプリの音声コマンド データをそのまま維持するには、アプリが起動またはアクティブ化されるたびに VCD ファイルを初期化するか、VCD が現在インストールされているかどうかを示す設定を維持することを検討してください。
"app.xaml.cs" ファイルで次の手順を実行します。
次の using ディレクティブを追加します。
using Windows.Storage;"OnLaunched" メソッドを非同期修飾子でマークします。
protected async override void OnLaunched(LaunchActivatedEventArgs e)OnLaunched ハンドラーで InstallCommandDefinitionsFromStorageFileAsync を呼び出して、システムが認識する必要がある音声コマンドを登録します。
Adventure Works サンプルでは、最初に StorageFile オブジェクトを定義します。
次に、 GetFileAsync を呼び出して、"AdventureWorksCommands.xml" ファイルで初期化します。
この StorageFile オブジェクトは、 InstallCommandDefinitionsFromStorageFileAsync に渡されます。
try
{
// Install the main VCD.
StorageFile vcdStorageFile =
await Package.Current.InstalledLocation.GetFileAsync(
@"AdventureWorksCommands.xml");
await Windows.ApplicationModel.VoiceCommands.VoiceCommandDefinitionManager.
InstallCommandDefinitionsFromStorageFileAsync(vcdStorageFile);
// Update phrase list.
ViewModel.ViewModelLocator locator = App.Current.Resources["ViewModelLocator"] as ViewModel.ViewModelLocator;
if(locator != null)
{
await locator.TripViewModel.UpdateDestinationPhraseList();
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine("Installing Voice Commands Failed: " + ex.ToString());
}
アクティブ化を処理し音声コマンドを実行する
アプリが後続の音声コマンドのアクティブ化に応答する方法を指定します (少なくとも 1 回起動され、音声コマンド セットがインストールされた後)。
音声コマンドによってアプリがアクティブ化されたことを確認します。
Application.OnActivated イベントをオーバーライドし、IActivatedEventArgs. かどうかを確認しますKind は VoiceCommand です。
コマンドの名前と話された内容を決定します。
IActivatedEventArgs から VoiceCommandActivatedEventArgs オブジェクトへの参照を取得し、SpeechRecognitionResult オブジェクトの Result プロパティに対してクエリを実行します。
ユーザーが何を言ったかを判断するには、 Text の値、または SpeechRecognitionSemanticInterpretation ディクショナリで認識された語句のセマンティック プロパティを確認します。
目的のページに移動するなど、アプリで適切なアクションを実行します。
この例では、「手順 3: VCD ファイルを編集する」の VCD を参照してください。
音声コマンドの音声認識結果を取得したら、 RulePath 配列の最初の値からコマンド名を取得します。 VCD ファイルで複数の音声コマンドが定義されたので、VCD 内のコマンド名と値を比較し、適切なアクションを実行する必要があります。
アプリケーションで実行できる最も一般的なアクションは、音声コマンドのコンテキストに関連するコンテンツを含むページに移動することです。 この例では、 TripPage ページに移動し、音声コマンドの値、コマンドの入力方法、認識された "destination" フレーズ (該当する場合) を渡します。 または、ページに移動するときに、アプリから SpeechRecognitionResult にナビゲーション パラメーターを送信することもできます。
commandMode キーを使用して、アプリを起動した音声コマンドが実際に読み上げられたか、テキストとして入力されたのかを、SpeechRecognitionSemanticInterpretation.Properties ディクショナリから確認できます。 そのキーの値は、"voice" または "text" になります。 キーの値が "voice" の場合は、アプリで音声合成 (Windows.Media.SpeechSynthesis) を使用して、ユーザーに音声フィードバックを提供することを検討してください。
SpeechRecognitionSemanticInterpretation.Properties を使用して、ListenFor 要素の PhraseList または PhraseTopic 制約で読み上げられたコンテンツを確認します。 ディクショナリ キーは、PhraseList または PhraseTopic 要素の Label 属性の値です。 ここでは、 {destination} 語句の値にアクセスする方法を示します。
/// <summary>
/// Entry point for an application activated by some means other than normal launching.
/// This includes voice commands, URI, share target from another app, and so on.
///
/// NOTE:
/// A previous version of the VCD file might remain in place
/// if you modify it and update the app through the store.
/// Activations might include commands from older versions of your VCD.
/// Try to handle these commands gracefully.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="args">Details about the activation method.</param>
protected override void OnActivated(IActivatedEventArgs args)
{
base.OnActivated(args);
Type navigationToPageType;
ViewModel.TripVoiceCommand? navigationCommand = null;
// Voice command activation.
if (args.Kind == ActivationKind.VoiceCommand)
{
// Event args can represent many different activation types.
// Cast it so we can get the parameters we care about out.
var commandArgs = args as VoiceCommandActivatedEventArgs;
Windows.Media.SpeechRecognition.SpeechRecognitionResult speechRecognitionResult = commandArgs.Result;
// Get the name of the voice command and the text spoken.
// See VoiceCommands.xml for supported voice commands.
string voiceCommandName = speechRecognitionResult.RulePath[0];
string textSpoken = speechRecognitionResult.Text;
// commandMode indicates whether the command was entered using speech or text.
// Apps should respect text mode by providing silent (text) feedback.
string commandMode = this.SemanticInterpretation("commandMode", speechRecognitionResult);
switch (voiceCommandName)
{
case "showTripToDestination":
// Access the value of {destination} in the voice command.
string destination = this.SemanticInterpretation("destination", speechRecognitionResult);
// Create a navigation command object to pass to the page.
navigationCommand = new ViewModel.TripVoiceCommand(
voiceCommandName,
commandMode,
textSpoken,
destination);
// Set the page to navigate to for this voice command.
navigationToPageType = typeof(View.TripDetails);
break;
default:
// If we can't determine what page to launch, go to the default entry point.
navigationToPageType = typeof(View.TripListView);
break;
}
}
// Protocol activation occurs when a card is clicked within Cortana (using a background task).
else if (args.Kind == ActivationKind.Protocol)
{
// Extract the launch context. In this case, we're just using the destination from the phrase set (passed
// along in the background task inside Cortana), which makes no attempt to be unique. A unique id or
// identifier is ideal for more complex scenarios. We let the destination page check if the
// destination trip still exists, and navigate back to the trip list if it doesn't.
var commandArgs = args as ProtocolActivatedEventArgs;
Windows.Foundation.WwwFormUrlDecoder decoder = new Windows.Foundation.WwwFormUrlDecoder(commandArgs.Uri.Query);
var destination = decoder.GetFirstValueByName("LaunchContext");
navigationCommand = new ViewModel.TripVoiceCommand(
"protocolLaunch",
"text",
"destination",
destination);
navigationToPageType = typeof(View.TripDetails);
}
else
{
// If we were launched via any other mechanism, fall back to the main page view.
// Otherwise, we'll hang at a splash screen.
navigationToPageType = typeof(View.TripListView);
}
// Repeat the same basic initialization as OnLaunched() above, taking into account whether
// or not the app is already active.
Frame rootFrame = Window.Current.Content as Frame;
// Do not repeat app initialization when the Window already has content,
// just ensure that the window is active.
if (rootFrame == null)
{
// Create a frame to act as the navigation context and navigate to the first page.
rootFrame = new Frame();
App.NavigationService = new NavigationService(rootFrame);
rootFrame.NavigationFailed += OnNavigationFailed;
// Place the frame in the current window.
Window.Current.Content = rootFrame;
}
// Since we're expecting to always show a details page, navigate even if
// a content frame is in place (unlike OnLaunched).
// Navigate to either the main trip list page, or if a valid voice command
// was provided, to the details page for that trip.
rootFrame.Navigate(navigationToPageType, navigationCommand);
// Ensure the current window is active
Window.Current.Activate();
}
/// <summary>
/// Returns the semantic interpretation of a speech result.
/// Returns null if there is no interpretation for that key.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="interpretationKey">The interpretation key.</param>
/// <param name="speechRecognitionResult">The speech recognition result to get the semantic interpretation from.</param>
/// <returns></returns>
private string SemanticInterpretation(string interpretationKey, SpeechRecognitionResult speechRecognitionResult)
{
return speechRecognitionResult.SemanticInterpretation.Properties[interpretationKey].FirstOrDefault();
}
関連記事
Windows developer
