Локальные уведомления в Xamarin.Forms
Локальные уведомления — это оповещения, отправляемые приложениями, установленными на мобильном устройстве. Локальные уведомления часто используются для таких функций, как:
- События календаря
- Напоминания
- Триггеры на основе расположения
Каждая платформа обрабатывает создание, отображение и использование локальных уведомлений по-разному. Из этой статье вы узнаете, как создать кроссплатформенную абстракцию для отправки, планирования и получения локальных уведомлений с помощью Xamarin.Forms.
Создание кросс-платформенного интерфейса
Приложение Xamarin.Forms должно создавать и использовать уведомления, не заботясь о реализации базовой платформы. Следующий интерфейс INotificationManager реализуется в общей библиотеке кода и определяет кросс-платформенный API, который приложение может использовать для взаимодействия с уведомлениями:
public interface INotificationManager
{
event EventHandler NotificationReceived;
void Initialize();
void SendNotification(string title, string message, DateTime? notifyTime = null);
void ReceiveNotification(string title, string message);
}
Этот интерфейс будет реализован в каждом проекте платформы. Событие NotificationReceived позволяет приложению обрабатывать входящие уведомления. Метод Initialize должен выполнять любую собственную логику платформы, необходимую для подготовки системы уведомлений. С помощью метода SendNotification в определенное время, заданное с помощью необязательного параметра DateTime, должно быть отправлено уведомление. Метод ReceiveNotification должен вызываться базовой платформой при получении сообщения.
Использование интерфейса в Xamarin.Forms
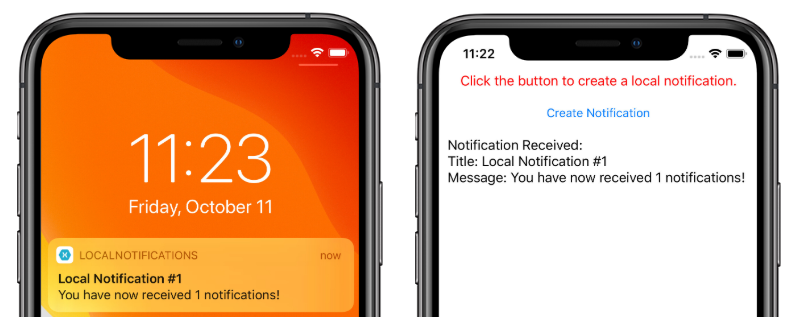
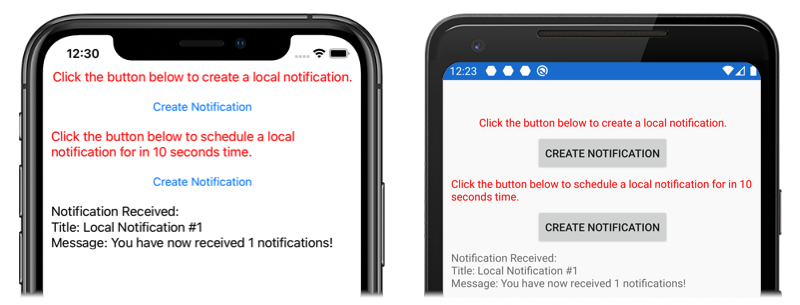
После создания интерфейса его можно использовать в общем проекте Xamarin.Forms, даже если реализация платформы еще не создана. Пример приложения содержит ContentPage с именем MainPage.xaml со следующим содержимым:
<StackLayout Margin="0,35,0,0"
x:Name="stackLayout">
<Label Text="Click the button below to create a local notification."
TextColor="Red"
HorizontalOptions="Center"
VerticalOptions="Start" />
<Button Text="Create Notification"
HorizontalOptions="Center"
VerticalOptions="Start"
Clicked="OnSendClick" />
<Label Text="Click the button below to schedule a local notification for in 10 seconds time."
TextColor="Red"
HorizontalOptions="Center"
VerticalOptions="Start" />
<Button Text="Create Notification"
HorizontalOptions="Center"
VerticalOptions="Start"
Clicked="OnScheduleClick" />
</StackLayout>
Макет содержит элементы Label с пояснением инструкций и элементы Button, которые позволяют отправить или запланировать уведомление при касании.
Код программной части класса MainPage обрабатывает отправку и получение уведомлений:
public partial class MainPage : ContentPage
{
INotificationManager notificationManager;
int notificationNumber = 0;
public MainPage()
{
InitializeComponent();
notificationManager = DependencyService.Get<INotificationManager>();
notificationManager.NotificationReceived += (sender, eventArgs) =>
{
var evtData = (NotificationEventArgs)eventArgs;
ShowNotification(evtData.Title, evtData.Message);
};
}
void OnSendClick(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
notificationNumber++;
string title = $"Local Notification #{notificationNumber}";
string message = $"You have now received {notificationNumber} notifications!";
notificationManager.SendNotification(title, message);
}
void OnScheduleClick(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
notificationNumber++;
string title = $"Local Notification #{notificationNumber}";
string message = $"You have now received {notificationNumber} notifications!";
notificationManager.SendNotification(title, message, DateTime.Now.AddSeconds(10));
}
void ShowNotification(string title, string message)
{
Device.BeginInvokeOnMainThread(() =>
{
var msg = new Label()
{
Text = $"Notification Received:\nTitle: {title}\nMessage: {message}"
};
stackLayout.Children.Add(msg);
});
}
}
Конструктор MainPage класса используется Xamarin.FormsDependencyService для получения экземпляра конкретной INotificationManagerплатформы объекта. Методы OnSendClick и OnScheduleClicked используют экземпляр INotificationManager для отправки и планирования новых уведомлений. Метод ShowNotification вызывается из обработчика событий, присоединенного к событию NotificationReceived, и вставляет новый Label в страницу при вызове события.
Обработчик событий NotificationReceived приводит свои аргументы событий к NotificationEventArgs. Этот тип определен в общем проекте Xamarin.Forms:
public class NotificationEventArgs : EventArgs
{
public string Title { get; set; }
public string Message { get; set; }
}
Дополнительные сведения о Xamarin.FormsDependencyServiceзависимостях см. в разделе Xamarin.Forms "Зависимости".
Создание реализации интерфейса Android
Чтобы приложение Xamarin.Forms отправляло и получало уведомления на Android, оно должно предоставить реализацию интерфейса INotificationManager.
Создание класса AndroidNotificationManager
Класс AndroidNotificationManager реализует интерфейс INotificationManager:
using System;
using Android.App;
using Android.Content;
using Android.Graphics;
using Android.OS;
using AndroidX.Core.App;
using Xamarin.Forms;
using AndroidApp = Android.App.Application;
[assembly: Dependency(typeof(LocalNotifications.Droid.AndroidNotificationManager))]
namespace LocalNotifications.Droid
{
public class AndroidNotificationManager : INotificationManager
{
const string channelId = "default";
const string channelName = "Default";
const string channelDescription = "The default channel for notifications.";
public const string TitleKey = "title";
public const string MessageKey = "message";
bool channelInitialized = false;
int messageId = 0;
int pendingIntentId = 0;
NotificationManager manager;
public event EventHandler NotificationReceived;
public static AndroidNotificationManager Instance { get; private set; }
public AndroidNotificationManager() => Initialize();
public void Initialize()
{
if (Instance == null)
{
CreateNotificationChannel();
Instance = this;
}
}
public void SendNotification(string title, string message, DateTime? notifyTime = null)
{
if (!channelInitialized)
{
CreateNotificationChannel();
}
if (notifyTime != null)
{
Intent intent = new Intent(AndroidApp.Context, typeof(AlarmHandler));
intent.PutExtra(TitleKey, title);
intent.PutExtra(MessageKey, message);
PendingIntent pendingIntent = PendingIntent.GetBroadcast(AndroidApp.Context, pendingIntentId++, intent, PendingIntentFlags.CancelCurrent);
long triggerTime = GetNotifyTime(notifyTime.Value);
AlarmManager alarmManager = AndroidApp.Context.GetSystemService(Context.AlarmService) as AlarmManager;
alarmManager.Set(AlarmType.RtcWakeup, triggerTime, pendingIntent);
}
else
{
Show(title, message);
}
}
public void ReceiveNotification(string title, string message)
{
var args = new NotificationEventArgs()
{
Title = title,
Message = message,
};
NotificationReceived?.Invoke(null, args);
}
public void Show(string title, string message)
{
Intent intent = new Intent(AndroidApp.Context, typeof(MainActivity));
intent.PutExtra(TitleKey, title);
intent.PutExtra(MessageKey, message);
PendingIntent pendingIntent = PendingIntent.GetActivity(AndroidApp.Context, pendingIntentId++, intent, PendingIntentFlags.UpdateCurrent);
NotificationCompat.Builder builder = new NotificationCompat.Builder(AndroidApp.Context, channelId)
.SetContentIntent(pendingIntent)
.SetContentTitle(title)
.SetContentText(message)
.SetLargeIcon(BitmapFactory.DecodeResource(AndroidApp.Context.Resources, Resource.Drawable.xamagonBlue))
.SetSmallIcon(Resource.Drawable.xamagonBlue)
.SetDefaults((int)NotificationDefaults.Sound | (int)NotificationDefaults.Vibrate);
Notification notification = builder.Build();
manager.Notify(messageId++, notification);
}
void CreateNotificationChannel()
{
manager = (NotificationManager)AndroidApp.Context.GetSystemService(AndroidApp.NotificationService);
if (Build.VERSION.SdkInt >= BuildVersionCodes.O)
{
var channelNameJava = new Java.Lang.String(channelName);
var channel = new NotificationChannel(channelId, channelNameJava, NotificationImportance.Default)
{
Description = channelDescription
};
manager.CreateNotificationChannel(channel);
}
channelInitialized = true;
}
long GetNotifyTime(DateTime notifyTime)
{
DateTime utcTime = TimeZoneInfo.ConvertTimeToUtc(notifyTime);
double epochDiff = (new DateTime(1970, 1, 1) - DateTime.MinValue).TotalSeconds;
long utcAlarmTime = utcTime.AddSeconds(-epochDiff).Ticks / 10000;
return utcAlarmTime; // milliseconds
}
}
}
Атрибут assembly над пространством имен регистрирует реализацию INotificationManager интерфейса с DependencyService.
Android позволяет приложениям определять несколько каналов для уведомлений. Метод Initialize создает базовый канал, который образец приложения использует для отправки уведомлений. Метод SendNotification определяет логику конкретной платформы, необходимую для создания и отправки уведомления. При получении сообщения операционная система Android вызывает метод ReceiveNotification и обработчик событий.
Метод SendNotification позволяет создать локальное уведомление сразу или в определенное время (DateTime). Можно запланировать отправку уведомления на определенное время (DateTime) с помощью класса AlarmManager. Это уведомление получит объект, производный от класса BroadcastReceiver.
[BroadcastReceiver(Enabled = true, Label = "Local Notifications Broadcast Receiver")]
public class AlarmHandler : BroadcastReceiver
{
public override void OnReceive(Context context, Intent intent)
{
if (intent?.Extras != null)
{
string title = intent.GetStringExtra(AndroidNotificationManager.TitleKey);
string message = intent.GetStringExtra(AndroidNotificationManager.MessageKey);
AndroidNotificationManager manager = AndroidNotificationManager.Instance ?? new AndroidNotificationManager();
manager.Show(title, message);
}
}
}
Внимание
По умолчанию уведомления, запланированные с помощью класса AlarmManager, сбрасываются после перезагрузки устройства. Но можно реализовать в приложении возможность автоматически возобновить запланированные уведомления при перезапуске устройства. Дополнительные сведения см. в разделе Start an alarm when the device restarts (Запуск службы сигнализации при перезагрузке устройства) статьи Schedule repeating alarms (Планирование повторяющихся сигналов) на сайте developer.android.com. Сведения о фоновой обработке в Android см. в разделе Guide to Background processing (Руководство по фоновой обработке) на сайте developer.android.com.
Дополнительные сведения о широковещательных приемниках см. в статье Широковещательные приемники в Xamarin.Android.
Обработка входящих уведомлений в Android
Класс MainActivity должен обнаруживать входящие уведомления и уведомлять экземпляр AndroidNotificationManager. Атрибут Activity в классе MainActivity должен указывать значение LaunchMode для LaunchMode.SingleTop:
[Activity(
//...
LaunchMode = LaunchMode.SingleTop]
public class MainActivity : global::Xamarin.Forms.Platform.Android.FormsAppCompatActivity
{
// ...
}
Режим SingleTop предотвращает запуск нескольких экземпляров Activity, пока приложение находится на переднем плане. LaunchMode не подходит для приложений, которые запускают несколько действий в более сложных сценариях уведомления. Дополнительные сведения о значениях перечисления LaunchMode см. в разделе Режим запуска действий Android.
В MainActivity класс изменен для получения входящих уведомлений:
protected override void OnCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
// ...
global::Xamarin.Forms.Forms.Init(this, savedInstanceState);
LoadApplication(new App());
CreateNotificationFromIntent(Intent);
}
protected override void OnNewIntent(Intent intent)
{
CreateNotificationFromIntent(intent);
}
void CreateNotificationFromIntent(Intent intent)
{
if (intent?.Extras != null)
{
string title = intent.GetStringExtra(AndroidNotificationManager.TitleKey);
string message = intent.GetStringExtra(AndroidNotificationManager.MessageKey);
DependencyService.Get<INotificationManager>().ReceiveNotification(title, message);
}
}
Метод CreateNotificationFromIntent извлекает данные уведомления из аргумента intent и предоставляет их AndroidNotificationManager с помощью метода ReceiveNotification. Метод CreateNotificationFromIntent вызывается как из метода OnCreate, так и с помощью метода OnNewIntent:
- При запуске приложения с помощью данных уведомления, данные
Intentпередаются в методOnCreate. - Если приложение уже находится на переднем плане, данные
Intentбудут переданы методуOnNewIntent.
Android предлагает множество дополнительных параметров для уведомлений. Дополнительные сведения см. в статье Уведомления в Xamarin.Android.
Создание реализации интерфейса iOS
Чтобы приложение Xamarin.Forms отправляло и получало уведомления на iOS, оно должно предоставить реализацию INotificationManager.
Создание класса iOSNotificationManager
Класс iOSNotificationManager реализует интерфейс INotificationManager:
using System;
using Foundation;
using UserNotifications;
using Xamarin.Forms;
[assembly: Dependency(typeof(LocalNotifications.iOS.iOSNotificationManager))]
namespace LocalNotifications.iOS
{
public class iOSNotificationManager : INotificationManager
{
int messageId = 0;
bool hasNotificationsPermission;
public event EventHandler NotificationReceived;
public void Initialize()
{
// request the permission to use local notifications
UNUserNotificationCenter.Current.RequestAuthorization(UNAuthorizationOptions.Alert, (approved, err) =>
{
hasNotificationsPermission = approved;
});
}
public void SendNotification(string title, string message, DateTime? notifyTime = null)
{
// EARLY OUT: app doesn't have permissions
if (!hasNotificationsPermission)
{
return;
}
messageId++;
var content = new UNMutableNotificationContent()
{
Title = title,
Subtitle = "",
Body = message,
Badge = 1
};
UNNotificationTrigger trigger;
if (notifyTime != null)
{
// Create a calendar-based trigger.
trigger = UNCalendarNotificationTrigger.CreateTrigger(GetNSDateComponents(notifyTime.Value), false);
}
else
{
// Create a time-based trigger, interval is in seconds and must be greater than 0.
trigger = UNTimeIntervalNotificationTrigger.CreateTrigger(0.25, false);
}
var request = UNNotificationRequest.FromIdentifier(messageId.ToString(), content, trigger);
UNUserNotificationCenter.Current.AddNotificationRequest(request, (err) =>
{
if (err != null)
{
throw new Exception($"Failed to schedule notification: {err}");
}
});
}
public void ReceiveNotification(string title, string message)
{
var args = new NotificationEventArgs()
{
Title = title,
Message = message
};
NotificationReceived?.Invoke(null, args);
}
NSDateComponents GetNSDateComponents(DateTime dateTime)
{
return new NSDateComponents
{
Month = dateTime.Month,
Day = dateTime.Day,
Year = dateTime.Year,
Hour = dateTime.Hour,
Minute = dateTime.Minute,
Second = dateTime.Second
};
}
}
}
Атрибут assembly над пространством имен регистрирует реализацию INotificationManager интерфейса с DependencyService.
В iOS перед попыткой планирования уведомления необходимо запросить разрешение на использование уведомлений. Метод Initialize запрашивает авторизацию для использования локальных уведомлений. Метод SendNotification определяет логику, необходимую для создания и отправки уведомления. При получении сообщения операционная система iOS вызовет метод ReceiveNotification и обработчик событий.
Примечание.
Метод SendNotification отвечает за немедленное создание локального уведомления с помощью объекта UNTimeIntervalNotificationTrigger или в определенное время (DateTime) с помощью объекта UNCalendarNotificationTrigger.
Обработка входящих уведомлений в iOS
В iOS необходимо создать делегат, который делит UNUserNotificationCenterDelegate на подклассы для обработки входящих сообщений. Пример приложения определяет класс iOSNotificationReceiver:
public class iOSNotificationReceiver : UNUserNotificationCenterDelegate
{
public override void WillPresentNotification(UNUserNotificationCenter center, UNNotification notification, Action<UNNotificationPresentationOptions> completionHandler)
{
ProcessNotification(notification);
completionHandler(UNNotificationPresentationOptions.Alert);
}
void ProcessNotification(UNNotification notification)
{
string title = notification.Request.Content.Title;
string message = notification.Request.Content.Body;
DependencyService.Get<INotificationManager>().ReceiveNotification(title, message);
}
}
Этот класс использует DependencyService для получения экземпляра класса iOSNotificationManager и предоставляет входные данные уведомления методу ReceiveNotification.
Во время запуска приложения класс AppDelegate должен указывать объект iOSNotificationReceiver в качестве делегата UNUserNotificationCenter. Это происходит в методе FinishedLaunching:
public override bool FinishedLaunching(UIApplication app, NSDictionary options)
{
global::Xamarin.Forms.Forms.Init();
UNUserNotificationCenter.Current.Delegate = new iOSNotificationReceiver();
LoadApplication(new App());
return base.FinishedLaunching(app, options);
}
iOS предлагает множество дополнительных параметров для уведомлений. Дополнительные сведения см. в статье Уведомления в Xamarin.iOS.
Тестирование приложения
Приложение можно тестировать на обеих платформах после того, как проекты платформы будут содержать зарегистрированную реализацию интерфейса INotificationManager. Запустите приложение и нажмите любую кнопку для создания уведомлений.
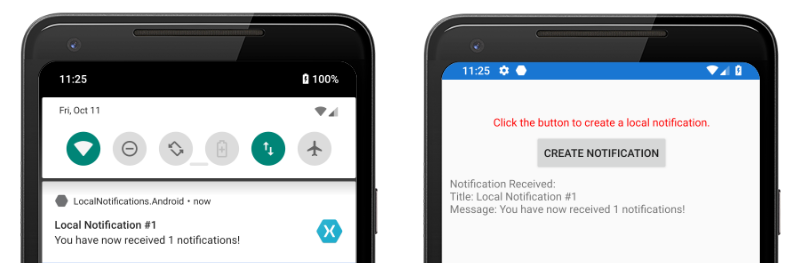
В Android уведомления появятся в области уведомлений. Когда пользователь касается уведомления, приложение получает уведомление и отображает сообщение.
В iOS приложение автоматически получает входящие уведомления без необходимости ввода данных пользователем. Приложение получает уведомление и отображает сообщение: