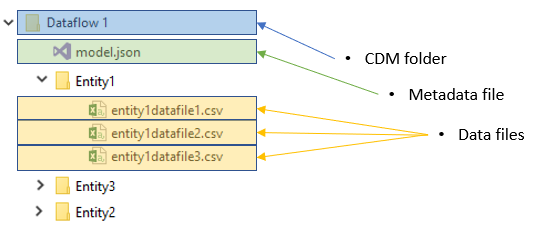
The metadata file (model.json) for the Common Data Model
The metadata file (or model.json) in a Common Data Model folder describes the data in the folder, metadata and location, as well as how the file was generated and by which data producer.
The model file enables:
- Discoverability based on data-producer metadata
- Obtaining semantic information about entity records / attributes and links to underlying data files
- Indicates compliance with Common Data Model standard entities
- Information about when entities were most recently updated
Download the schema of the model.json file.
Model-file contents
The Common Data Model folder contents are described by a standardized metadata .json file that contains these key categories of metadata:
Root elements
Metadata that applies to all entities within the folder, such as description, last modified time, and data culture
Entity information
General metadata such as type, description, etc.
Attributes, including metadata such as data types
[optional] Compliance with Common Data Model standard entity schema shapes
For example, a given entity in the folder comply with all the attributes required for a ‘base’ Account entity
Data file (partition) locations, and metadata about data encoding of data files
Reference models
Existing entities and datafiles to which this model.json file refers
Relationships
Describes the relationships among the entities
In addition to the standard elements, additional producer-specific elements or extensions can be added with a prefix, such as “pbi:mashup” where “pbi:” is the prefix. Consumers can ignore these fields, but the libraries will roundtrip the fields to ensure no loss of fidelity.
The following sections describes each standard category in more detail.
Root properties
These properties are listed at the root of the model.json file and describe properties relevant to all entities, relationships, etc.
| Property | Type | Description | Required? |
|---|---|---|---|
| application | string | The name of the producing application. A consumer uses this property to identify which application created the model.json file. | No |
| name | string | The model name | Yes |
| description | string | The model description | No |
| version | string (enum) | The model schema version (currently must be 1.0) | Yes |
| culture | string | An IETF language tag (for example, "en-US") that represents the language and country/region, supported by Windows and .NET. This value should be used to parse datatypes that can be culture-sensitive such as datetimes and numbers. When not set, the datatype formats should match the non-specified culture formats defined later in this topic. | No |
| modifiedTime | datetimeoffset | The most recent time when the model definition was updated in date time offset per ISO 8601. | No |
| isHidden | boolean | Whether this model is hidden. If set to 'true', this model isn't intended for other applications to consume. | No |
| annotations | Annotation[] | Array of optional model annotations - non-essential key/value pairs that contain contextual information that can be used to store additional context | No |
| entities | Entity[] | The model entities | Yes |
| referenceModels | ReferenceModel[] | References to other used/extended models | No |
| relationships | Relationship[] | Relationships between entities in the model. Relationships can be from/to local or reference entities. When the relationship involves a reference entity, the attributes must be resolved from the local entity in the referenced model | No |
Sample:
{
"application":"MyApplication",
"name":"OrdersProducts",
"description":"Model containing data for Order and Products.",
"version":"1.0",
"modifiedTime":"2018-01-02T12:00:00+08:00",
"annotations":[
],
"entities":[
],
"referenceModels":[
]
}
Annotations
Property name: annotations
Optional, non-essential contextual information (key/value pairs) that can be used to store additional context about a property in the model file. Annotations can be applied at multiple levels including to entities and attributes. Producers can add a prefix, such as “pbi:MappingDisplayHint” where “pbi:” is the prefix, when annotations aren't necessarily relevant to other consumers.
| Property | Type | Description | Required? |
|---|---|---|---|
| name | string | Name of the annotation | Yes |
| value | string | Value of the annotation | No |
Sample:
{
"annotations":[
{
"name":"MyApp:VersionNum",
"value":"3.0.1"
}
]
}
Reference Models
Property name: referenceModels
Reference models are existing model.json files with entities and datafiles to which that this model.json file refers. This allows existing metadata and data to be reused without copying it into this Common Data Model folder.
| Property | Type | Description | Required? |
|---|---|---|---|
| id | string | The id of the referenced model to be used within this model.json file. This value must be unique within this model file and can be used as a shorthand to the location property. The specific value is up to the implementer. | Yes |
| location | URI | The location of the model being referenced. The URI should include the model version/snapshot with which this model is consistent. (When this model is refreshed, it should update the version/snapshot accordingly.) | Yes |
Sample:
{
"referenceModels":[
{
"id":"f19bbb97-c031-441a-8bd1-61b9181c0b83 ",
"location":"https://contosostorageaccount.dfs.core.windows.net/contosoFilesystem/cdmFolder/model.json"
}
]
}
Entities
Property name: entities
An entity is a collection of attributes and metadata that defines a concept (such as Account or Contact) and can be defined by any data producer. An entity may match the schema of a standard entity, defined as part of the Common Data Model and listed in the GitHub repository. Entities that don’t match one of the standard shapes are said to be custom entities.
In the model.json file, you can specify local or reference entities. A local entity has the details about the entity (such as attributes, schemas, and partitions) defined within the model.json file, and the data files are expected to be within the same Common Data Model folder. A referenced entity is pointer to an entity defined by a referenced model, where all the metadata and data files are defined.
Depending on the type of entity, you may find different fields defined:
| Property | Local entity | Reference entity |
|---|---|---|
| $type | R | R |
| name | R | R |
| description | O | O |
| annotations | O | O |
| schemas | O | |
| attributes | R | |
| partitions | O | |
| source | R | |
| modelId | R |
R - required, O - optional, (blank) – n/a
Entity-level properties
In the required columns, “n/a” means the field shouldn’t exist for that type of entity.
| Property | Type | Description | LocalEntity Required? | ReferencedEntity Required? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| $type | Constant | Type of entity being defined in this model. This attribute must be set to: “LocalEntity”. | Yes | Yes |
| name | String | The entity name | Yes | Yes |
| description | string | The entity description | No | No |
| annotations | Annotation[] | Array of optional model annotations - non-essential key/value pairs that contain contextual information that can be used to store additional context | No | No |
| schemas | SchemaURI[] | A collection of URIs to the schema definitions to which the entity conforms. Allowed pattern: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Microsoft/CDM/master/schemaDocuments/<CDM folder hierarchy>/<entity name>.<entity version>.cdm.jsonExample: <https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Microsoft/CDM/master/schemaDocuments/core/applicationCommon/Account.0.8.cdm.json> |
No | n/a |
| attributes | Attribute[] | The attributes within the entity. Each entity must have at least one. | Yes | n/a |
| partitions | Partition[] | The entity physical partitions (data files) | No | n/a |
| source | String | The source (referenced) entity name | n/a | Yes |
| modelId | String | The source (referenced) model ID, must match the ID of one of the model’s referenceModels | n/a | Yes |
LocalEntity sample:
{
"entities":[
{
"$type":"LocalEntity",
"name":"Products",
"description":"Information about products and their pricing information.",
"annotations":[
],
"attributes":[
],
"partitions":[
],
"schemas":[
"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Microsoft/CDM/master/schemaDocuments/core/applicationCommon/foundationCommon/Product.0.7.cdm.json"
]
}
]
}
ReferencedEntity sample:
{
"entities":[
{
"$type":"ReferenceEntity",
"name":"Products",
"description":"Information about products and their pricing information.",
"source":"Products",
"modelId":"f19bbb97-c031-441a-8bd1-61b9181c0b83",
"annotations":[
]
}
]
}
Attributes
Property name: attributes
Attributes are the fields within an entity that correspond to data values within the data file. For example, a Contact entity may have attributes such as First Name and Last Name.
| Property | Type | Description | Required? |
|---|---|---|---|
| name | string | the attribute name | Yes |
| description | string | the attribute description | No |
| dataType | enum | This attribute should be set to one of these values: string, int64, double, dateTime, dateTimeOffset, decimal, boolean, GUID, or JSON. If a culture is specified, it should be used to parse the datatype. More information | Yes |
| annotations | Annotation[] | Array of optional model annotations - non-essential key/value pairs that contain contextual information that can be used to store additional context | No |
Sample:
{
"attributes":[
{
"name":"productId",
"description":"The unique identifier of the product.",
"dataType":"string",
"annotations":[
]
}
]
}
Partitions
Property name: partitions
The partition array indicates the name and location of the actual data files that correspond to the entity definition. Today, the partition contains a full URI to the location of the data file, so new data files must be manually added to the list of partitions.
| Property | Type | Description | Required? |
|---|---|---|---|
| name | string | The partition name | Yes |
| description | string | The partition description | No |
| refreshTime | datetimeoffset | The most recent date when the partition data was updated in date time offset per ISO 8601 | No |
| location | URI | The partition physical file location, including the file itself. If null, this entity definition is for schema purposes only. | No |
| fileFormatSettings | FileFormatSettings | Optional file format settings. | No |
File Format Settings
Property name: fileFormatSettings
The file-format settings provide metadata related to the data files in the partition. Depending on the type, you may find different fields defined, but only one type is supported today. Encoding of the data files is UTF-8, but you can request other encodings by creating an issue in the GitHub repository.
| Property | Type | Description | CsvFormatSetting Required? |
|---|---|---|---|
| $type | string (enum) | Defines the type of the file-format setting. As of this writing, only “CsvFormatSettings” is supported. | Yes |
| columnHeaders | boolean | Indicates whether the .csv file has headers. This attribute should be set to “true” or “false”. If not specified, this can be interpreted as false. | No |
| delimiter | string | The delimiter type in the .csv file. If not specified, this can be interpreted as “,” | No |
| encoding | string | The string encoding in the .csv file. If not specified, this can be interpreted as “UTF-8” | No |
| quoteStyle | string (enum) | The CSV quote style. This attribute should be set to “QuoteStyle.Csv” or “QuoteStyle.None”. If not specified, this can be interpreted as “QuoteStyle.Csv”. | No |
| csvStyle | string (enum) | The CSV style, values: This attribute should be set to “CsvStyle.QuoteAlways” or “CsvStyle.QuoteAfterDelimiter”. By default, this is set to “CsvStyle.QuoteAlways” | No |
Relationships
Property name: relationships
Relationships describe how entities are connected, such as an Account that has a Contact. As of this writing, only relationships based on a single attribute in the source and target entities is supported, but more types might be supported in the future.
| Property | Type | Description | SingleKeyRelationship Required? |
|---|---|---|---|
| $type | string (enum) | Defines the type relationship. Only “SingleKeyRelationship” is supported. | Yes |
| fromAttribute | ReferenceAttribute | The object in the source entity (see below) that refers to an attribute in another entity, “toAttribute”. | Yes |
| toAttribute | ReferenceAttribute | The object in the destination entity (see below) that's referred to by the “fromAttribute”. | Yes |
ReferenceAttribute
| Property | Type | Description | Required? |
|---|---|---|---|
| entityName | string | The entity name in the local model. This name must exist in the model entities list. | Yes |
| attributeName | string | The attribute name (for referenced entities that must be resolved from the target entity in the referenced model). | Yes |
Sample:
{
"relationships":[
{
"$type":"SingleKeyRelationship",
"fromAttribute":{
"entityName":"Account",
"attributeName":"ContactId"
},
"toAttribute":{
"entityName":"Contact",
"attributeName":"Id"
}
}
]
}
Datatype formats
In general, data producers should leverage datatype formats that aren't culture sensitive, such as ISO 8601 for datetime/datetimeoffsets. However, if a data producer writes data with culture-specific formats, the "culture" property must be set in the model.json format, and consumers must leverage that value to properly parse the data in the partition files.
Non-specified culture
When "culture" isn't specified in the model.json, consumers can assume these data formats:
| Datatype | Format | Description |
|---|---|---|
| datetime | 2018-01-02T12:00:00Z | A UTC datetime in ISO 8601 |
| datetimeoffset | 2018-01-02T12:00:00+08:00 | A datetime in ISO 8601 with timezone offset. |
| decimal | 1.0 | A decimal number with "." or a period as the decimal separator. |
Model-file attributes
We also suggest setting metadata as file properties directly on model.json for effective discovery of data-producer metadata by applications.
| Name | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Application Name | No | An application name that's meaningful to a business user and can appear in a user interface (UI). |
| Application Instance Name | No | An instance name for disambiguation if needed; the value should be meaningful for a business user. |
| Model Name | No | Same value as the "Name" property inside the model.json. |