Measure Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL performance with a benchmarking framework
There are more choices, now than ever, on the type of database to use with your data workload. One of the key factors to picking a database is the performance of the database or service, but benchmarking performance can be cumbersome and error-prone. The benchmarking framework for Azure Databases simplifies the process of measuring performance with popular open-source benchmarking tools with low-friction recipes that implement common best practices. In Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL, the framework implements best practices for the Java SDK and uses the open-source YCSB tool. In this guide, you use this benchmarking framework to implement a read workload to familiarize yourself with the framework.
Prerequisites
- An Azure account with an active subscription. Create an account for free.
- Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL account. Create a API for NoSQL account.
- Make sure you note the endpoint URI and primary key for the account.
- Azure Storage account. Create an Azure Storage account.
- Make sure you note the connection string for the storage account. Vies Azure Storage connection string.
- Second empty resource group. Create a resource group.
- Azure Command-Line Interface (CLI).
Create Azure Cosmos DB account resources
First, you create a database and container in the existing API for NoSQL account.
Navigate to your existing API for NoSQL account in the Azure portal.
In the resource menu, select Data Explorer.
On the Data Explorer page, select the New Container option in the command bar.
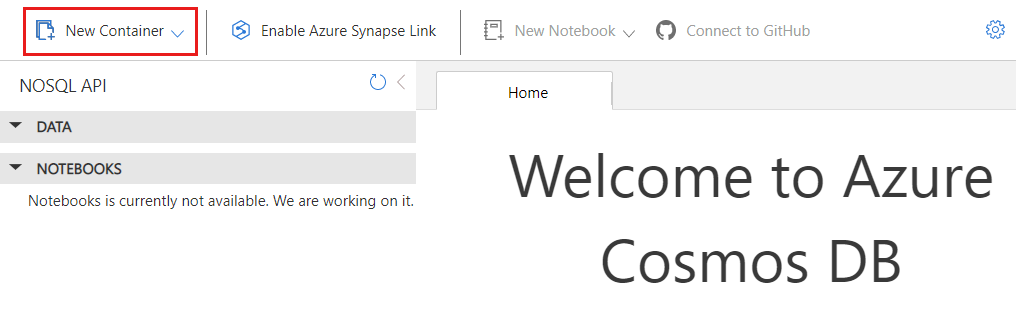
In the New Container dialog, create a new container with the following settings:
Setting Value Database id ycsbDatabase throughput type Manual Database throughput amount 400Container id usertablePartition key /id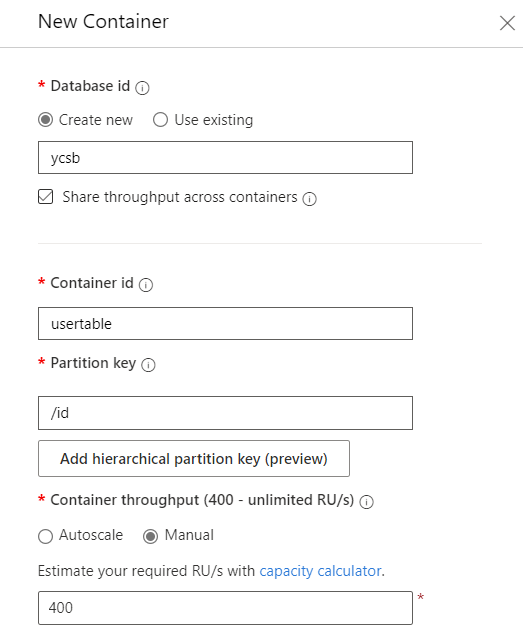
Deploy benchmarking framework to Azure
Now, you use an Azure Resource Manager template to deploy the benchmarking framework to Azure with the default read recipe.
Deploy the benchmarking framework using an Azure Resource Manager template available at this link.
On the Custom Deployment page, the following parameters
Select Review + create and then Create to deploy the template.
Wait for the deployment to complete.
Tip
The deployment can take 5-10 minutes to complete.
View results of the benchmark
Now, you can use the existing Azure Storage account to check the status of the benchmark job and view the aggregated results. The status is stored using a storage table and the results are aggregated into a storage blob using the CSV format.
Navigate to your existing Azure Storage account in the Azure portal.
Navigate to a storage table named ycsbbenchmarkingmetadata and locate the entity with a partition key of
ycsb_sql.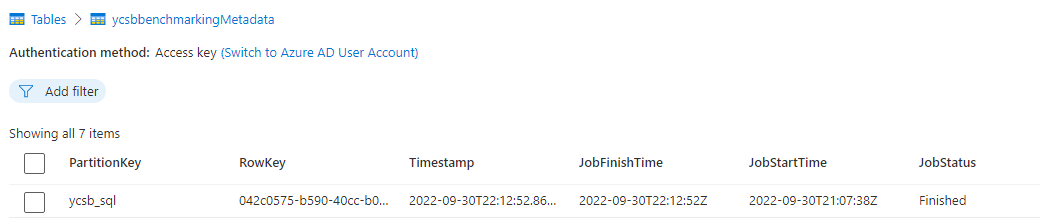
Observe the
JobStatusfield of the table entity. Initially, the status of the job isStartedand it includes a timestamp in theJobStartTimeproperty but not theJobFinishTimeproperty.Wait until the job has a status of
Finishedand includes a timestamp in theJobFinishTimeproperty.Tip
It can take approximately 20-30 minutes for the job to finish.
Navigate to the storage container in the same account with a prefix of ycsbbenchmarking-*. Observe the output and diagnostic blobs for the tool.
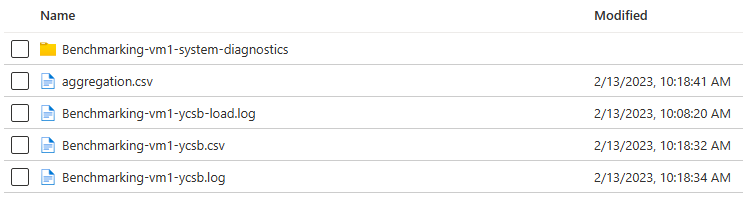
Open the aggregation.csv blob and observe the content. You should now have a CSV dataset with aggregated results from all the benchmark clients.
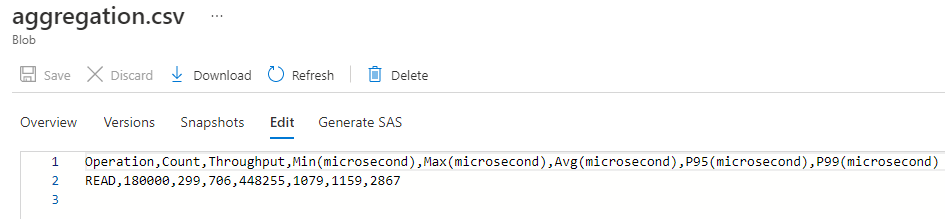
Operation,Count,Throughput,Min(microsecond),Max(microsecond),Avg(microsecond),P9S(microsecond),P99(microsecond) READ,180000,299,706,448255,1079,1159,2867
Recipes
The benchmarking framework for Azure Databases includes recipes to encapsulate the workload definitions that are passed to the underlying benchmarking tool for a "1-Click" experience. The workload definitions were designed based on the best practices published by the Azure Cosmos DB team and the benchmarking tool's team. The recipes have been tested and validated for consistent results.
You can expect to see the following latencies for all the read and write recipes in the GitHub repository.
Common issues
This section includes the common errors that may occur when running the benchmarking tool. The error logs for the tool are typically available in a container within the Azure Storage account.
If the logs aren't available in the storage account, this issue is typically caused by an incorrect or missing storage connection string. In this case, this error is listed in the agent.out file within the /home/benchmarking folder of the client virtual machine.
Error while accessing storage account, exiting from this machine in agent.out on the VMThis error is listed in the agent.out file both in the client VM and the storage account if the Azure Cosmos DB endpoint URI is incorrect or unreachable.
Caused by: java.net.UnknownHostException: rtcosmosdbsss.documents.azure.com: Name or service not knownThis error is listed in the agent.out file both in the client VM and the storage account if the Azure Cosmos DB key is incorrect.
The input authorization token can't serve the request. The wrong key is being used….
Next steps
- Learn more about the benchmarking tool with the Getting Started guide.



