Tutorial: Transform data with Azure Stack Edge Pro FPGA for advanced deployment flow
Important
Azure Stack Edge Pro FPGA devices will reach end-of-life in February 2024. If you are considering new deployments, we recommend that you explore Azure Stack Edge Pro 2 or Azure Stack Edge Pro GPU devices for your workloads.
This tutorial describes how to configure a compute role for an advanced deployment flow on your Azure Stack Edge Pro FPGA device. After you configure the compute role, Azure Stack Edge Pro FPGA can transform data before sending it to Azure.
Compute can be configured for simple or advanced deployment flow on your device.
| Criteria | Simple deployment | Advanced deployment |
|---|---|---|
| Intended for | IT administrators | Developers |
| Type | Use Azure Stack Edge service to deploy modules | Use IoT Hub service to deploy modules |
| Modules deployed | Single | Chained or multiple modules |
This procedure can take around 20 to 30 minutes to complete.
In this tutorial, you learn how to:
- Configure compute
- Add shares
- Add a trigger
- Add a compute module
- Verify data transform and transfer
Prerequisites
Before you set up a compute role on your Azure Stack Edge Pro FPGA device, make sure that:
- You've activated your Azure Stack Edge Pro FPGA device as described in Connect, set up, and activate Azure Stack Edge Pro FPGA.
Configure compute
To configure compute on your Azure Stack Edge Pro FPGA, you'll create an IoT Hub resource.
In the Azure portal of your Azure Stack Edge resource, go to Overview. In the right-pane, select the IoT Edge tile.
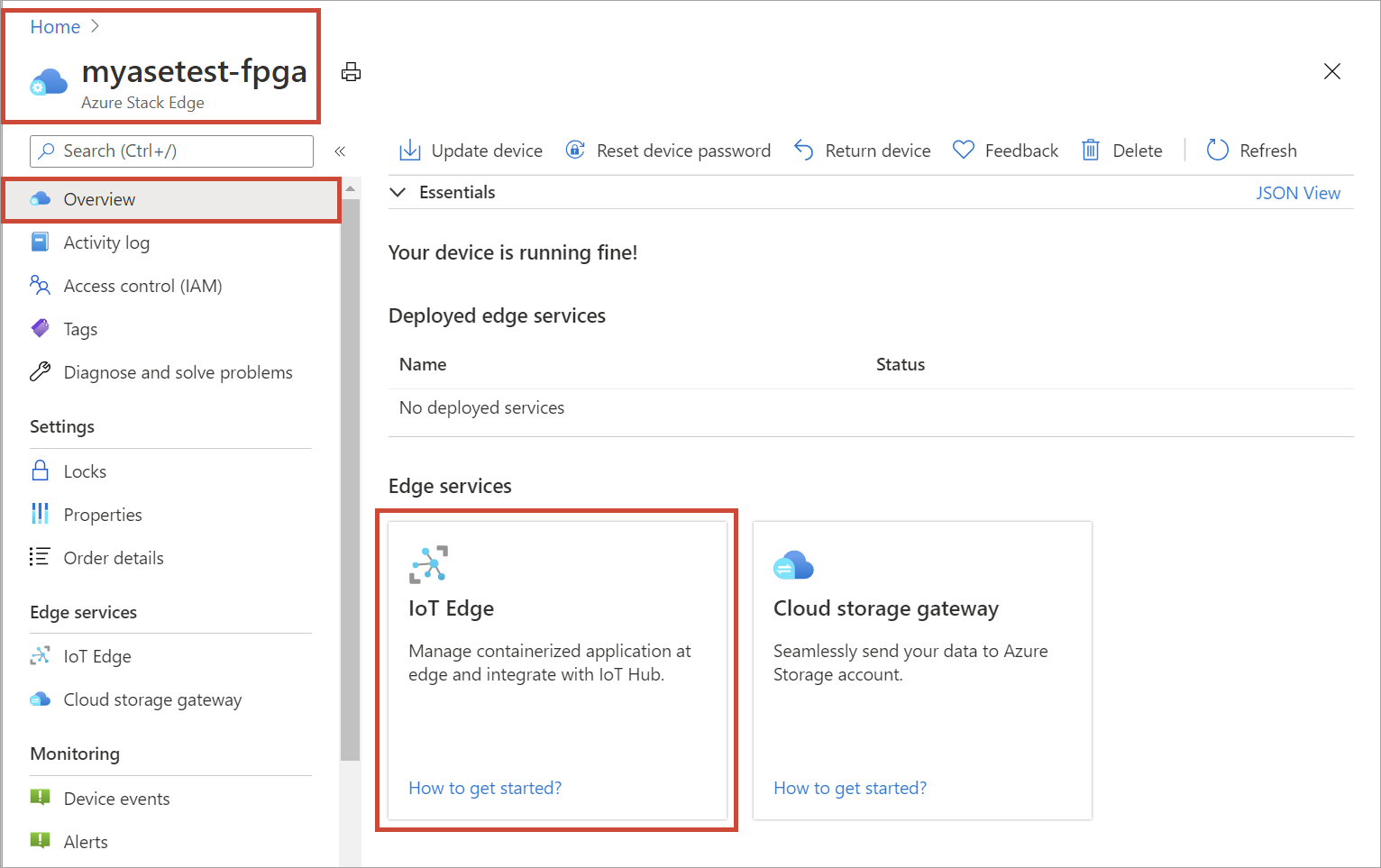
On the Enable IoT Edge service tile, select Add. This action enables IoT Edge service that lets you deploy IoT Edge modules locally on your device.
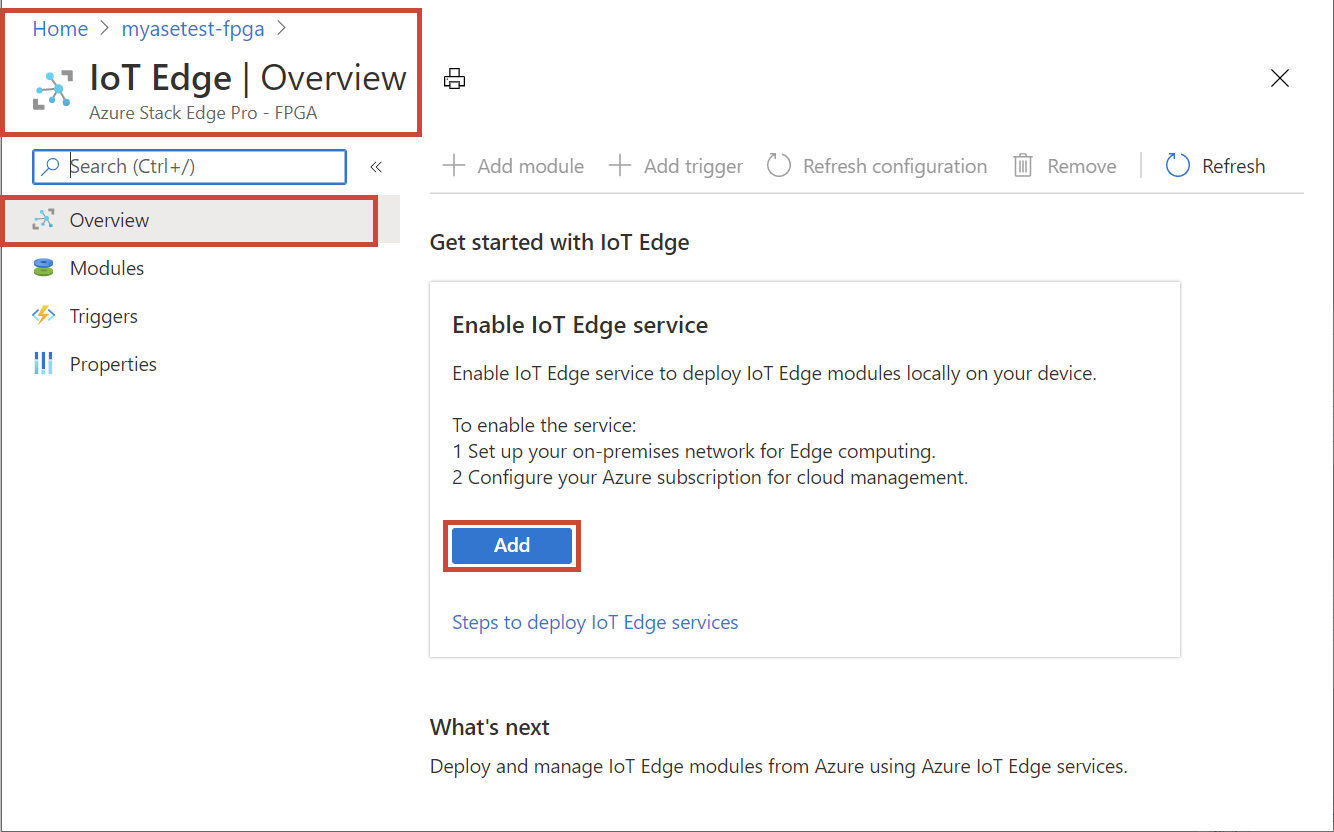
On the Create IoT Edge service, input the following:
Field Value Subscription Select a subscription for your IoT Hub resource. You can select the same subscription as that used by the Azure Stack Edge resource. Resource group Enter a name for the resource group for your IoT Hub resource. You can select the same resource group as that used by the Azure Stack Edge resource. IoT Hub Choose from New or Existing.
By default, a Standard tier (S1) is used to create an IoT resource. To use a free tier IoT resource, create one and then select the existing resource.Name Accept the default or enter a name for your IoT Hub resource. 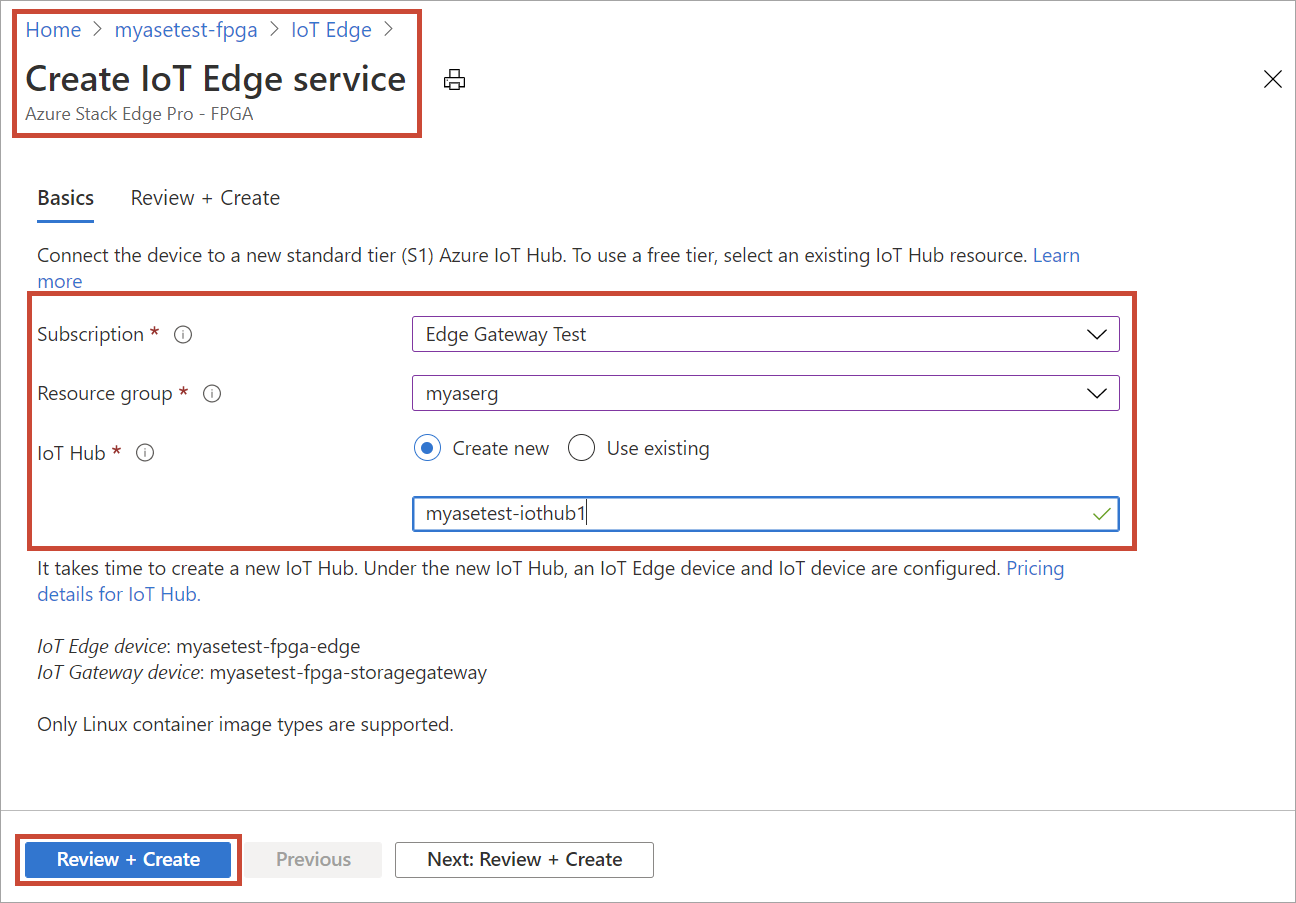
Select Review + Create. The IoT Hub resource creation takes a couple minutes. After the IoT Hub resource is created, the Overview updates to indicate that the IoT Edge service is running.
When the IoT Edge service is configured on the Edge device, it creates two devices: an IoT device and an IoT Edge device. Both devices can be viewed in the IoT Hub resource. An IoT Edge Runtime is also running on this IoT Edge device. At this point, only the Linux platform is available for your IoT Edge device.
To confirm that the Edge compute role has been configured, select IoT Edge service > Properties and view the IoT device and the IoT Edge device.
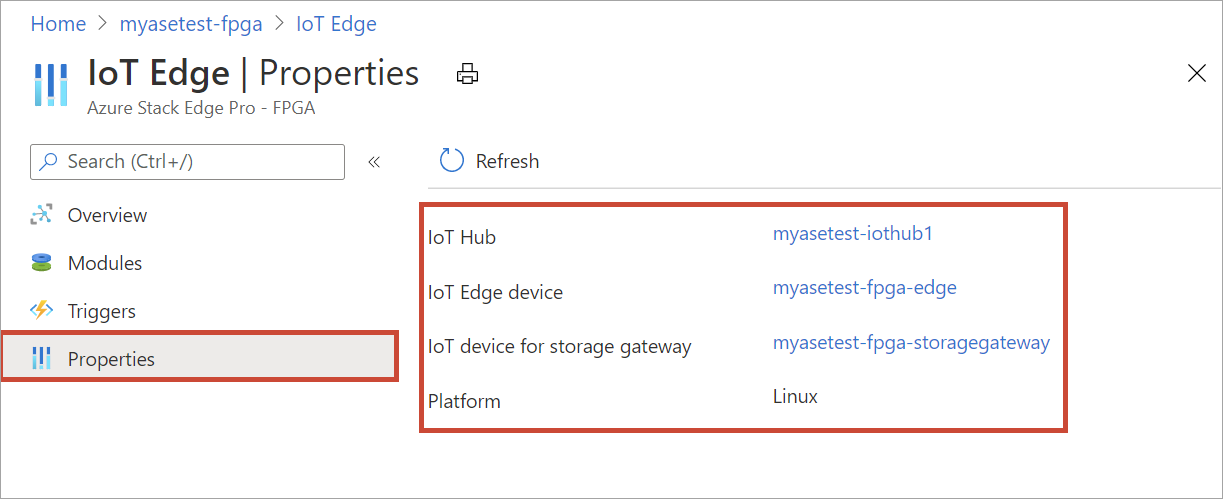
Add shares
For the advanced deployment in this tutorial, you'll need two shares: one Edge share and another Edge local share.
Add an Edge share on the device by doing the following steps:
In your Azure Stack Edge resource, go to IoT Edge > Shares.
On the Shares page, from the command bar, select + Add share.
On the Add share blade, provide the share name and select the share type.
To mount the Edge share, select the check box for Use the share with Edge compute.
Select the Storage account, Storage service, an existing user, and then select Create.
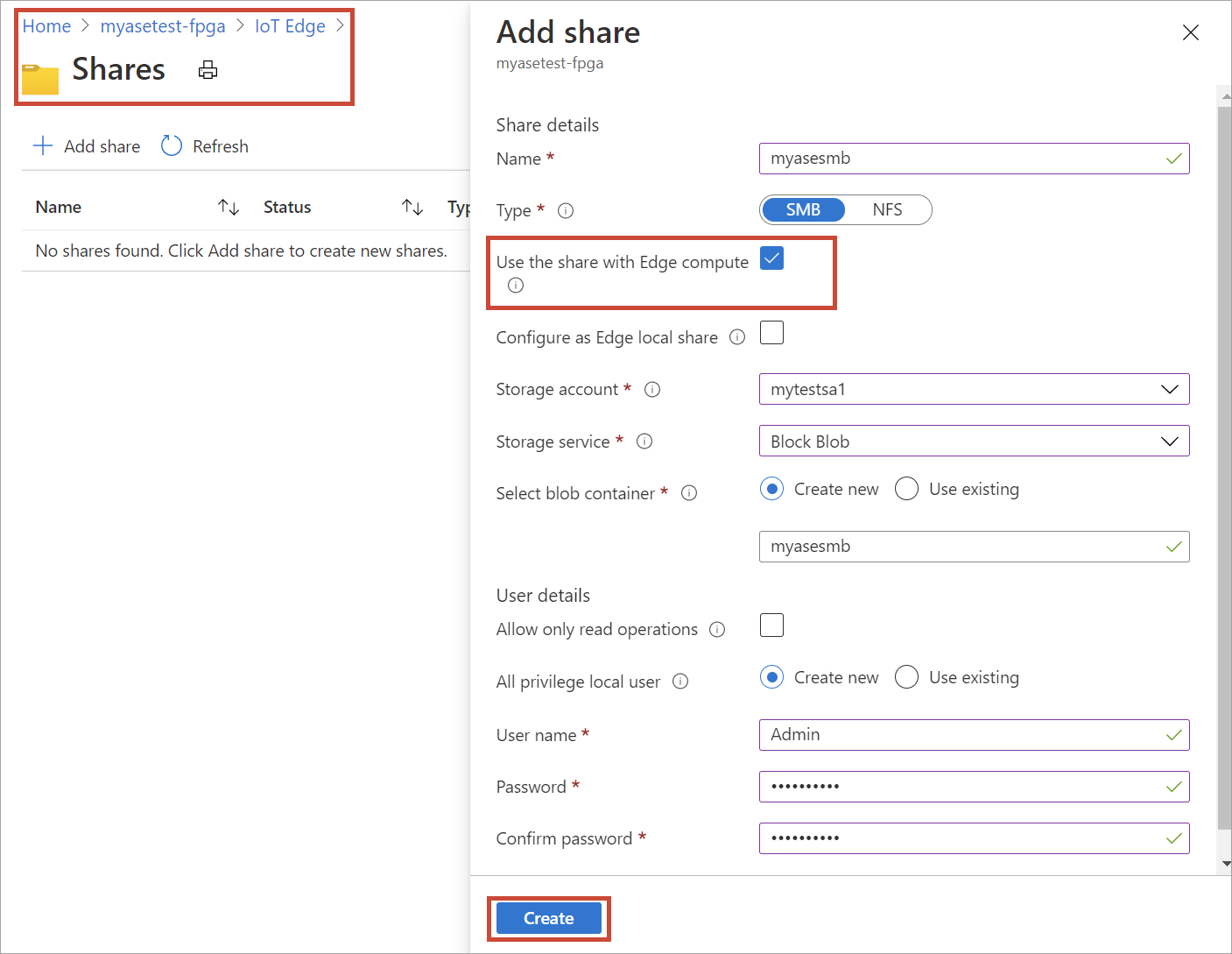
After the Edge share is created, you'll receive a successful creation notification. The share list is updated to reflect the new share.
Add an Edge local share on the Edge device by repeating all the steps in the preceding step and selecting the check box for Configure as Edge local share. The data in the local share stays on the device.
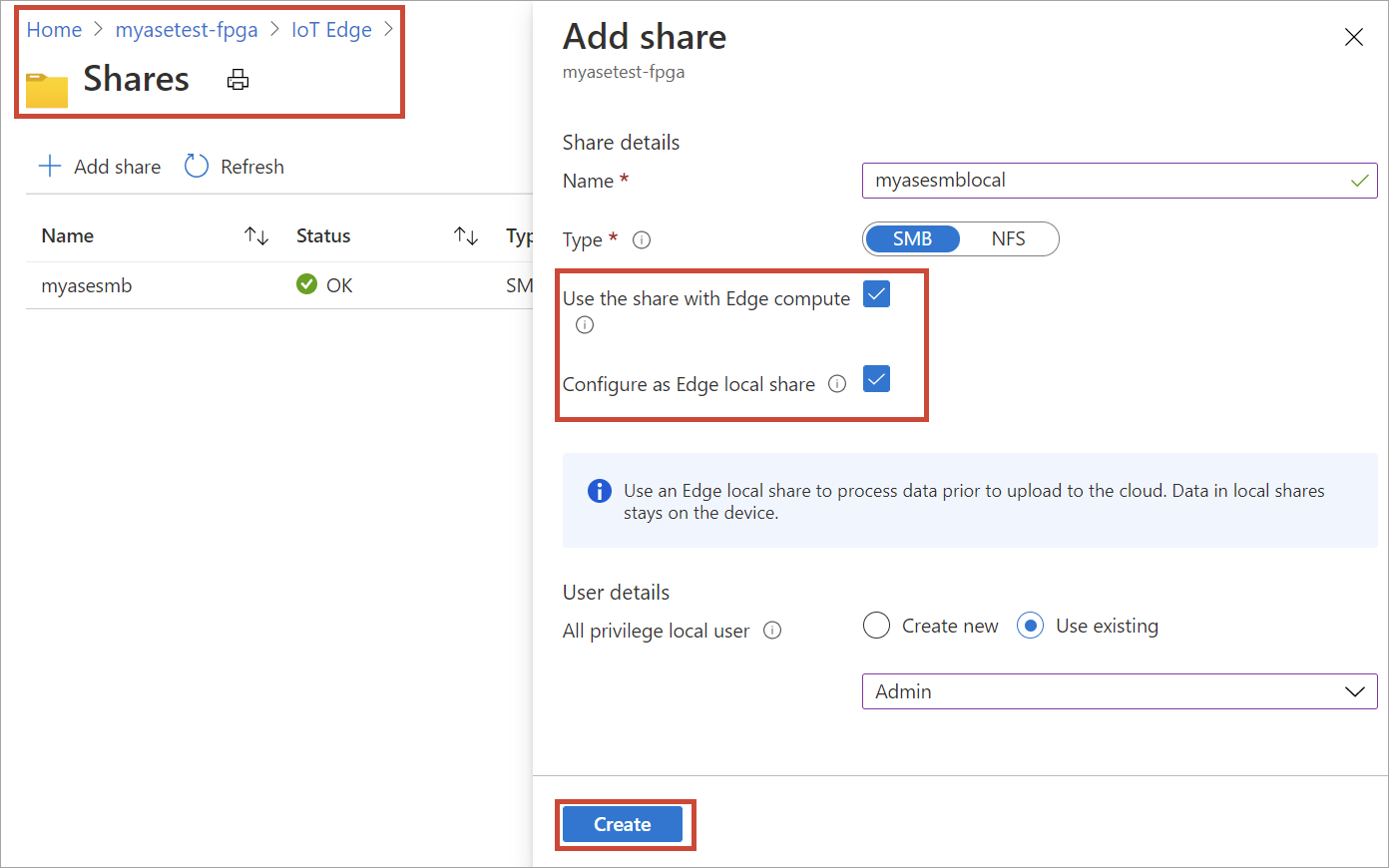
On the Shares blade, you see the updated list of shares.
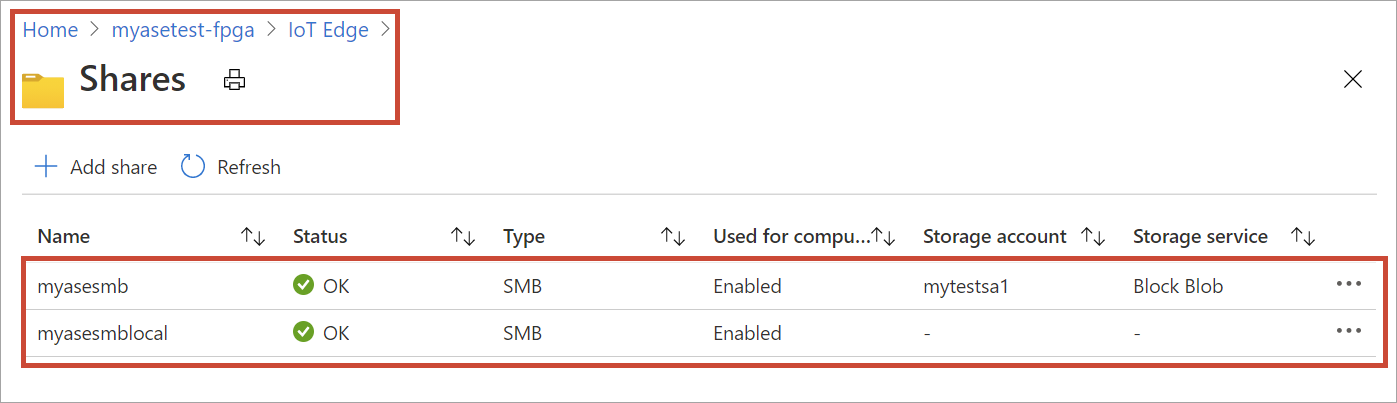
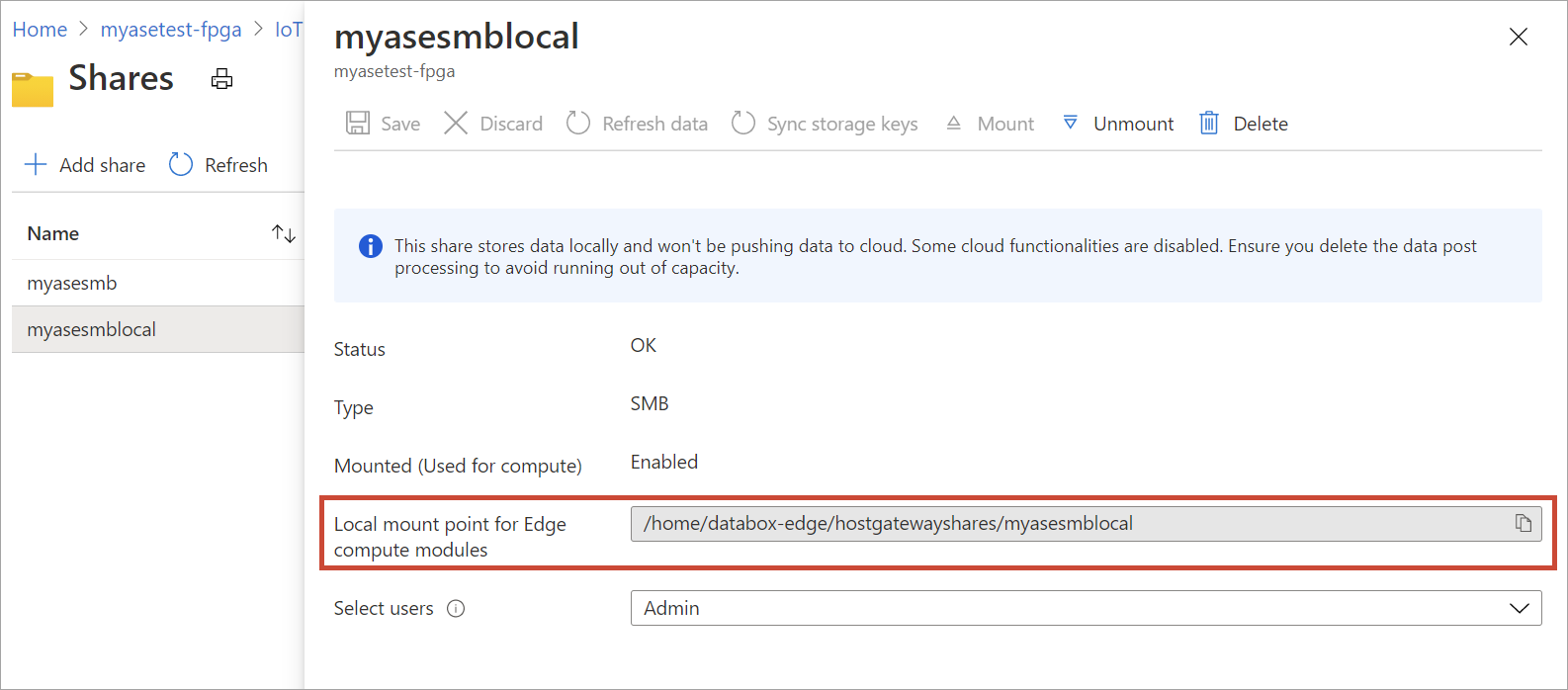
To view the properties of the newly created local share, select the share from the list. In the Local mount point for Edge compute modules box, copy the value corresponding to this share.
You'll use this local mount point when you deploy the module.
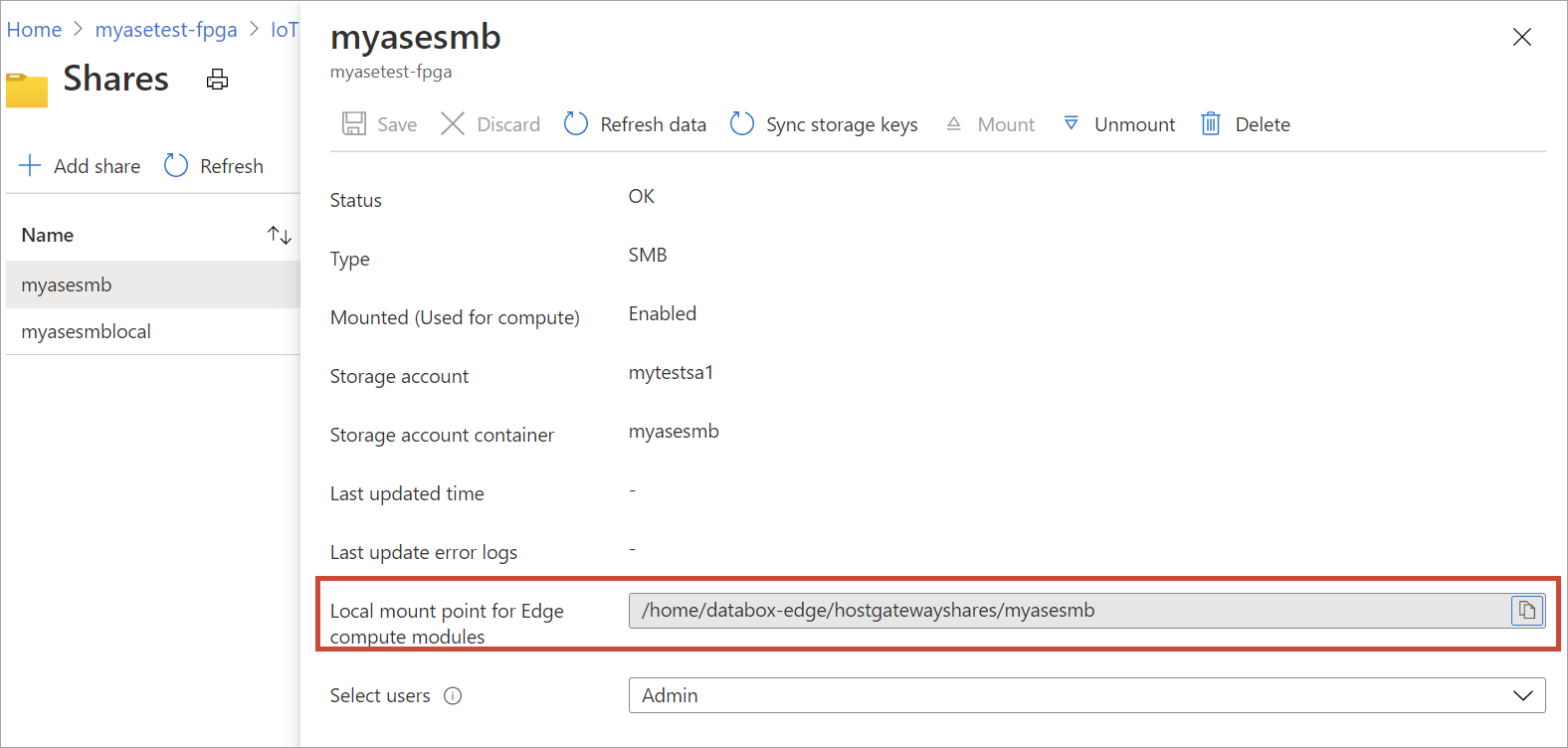
To view the properties of the Edge share that you created, select the share from the list. In the Local mount point for Edge compute modules box, copy the value corresponding to this share.
You'll use this local mount point when you deploy the module.
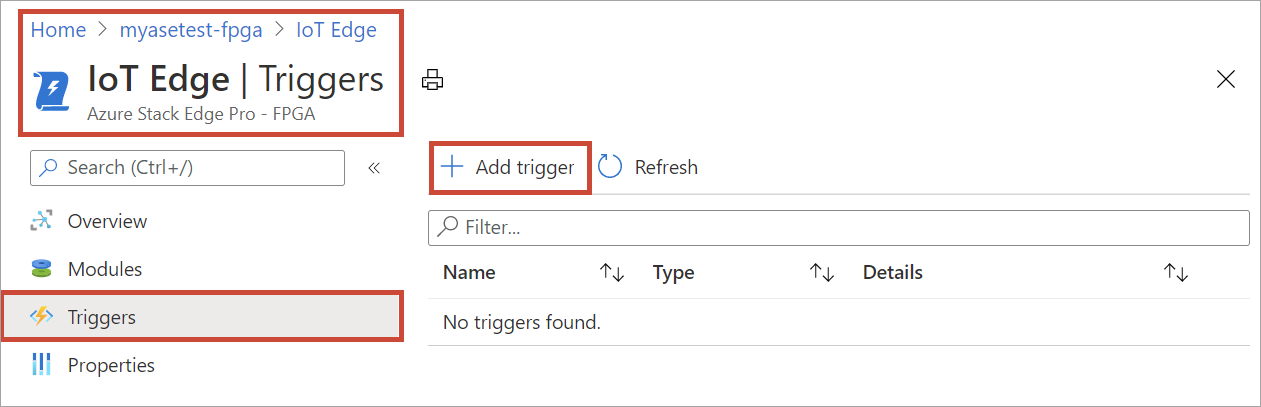
Add a trigger
Go to your Azure Stack Edge resource and then go to IoT Edge > Triggers. Select + Add trigger.
In the Add trigger blade, input the following values.
Field Value Trigger name A unique name for your trigger. Trigger type Select File trigger. A file trigger fires whenever a file event occurs such as a file is written to the input share. A scheduled trigger on the other hand, fires up based on a schedule defined by you. For this example, we need a file trigger. Input share Select an input share. The Edge local share is the input share in this case. The module used here moves files from the Edge local share to an Edge share where they are uploaded into the cloud. 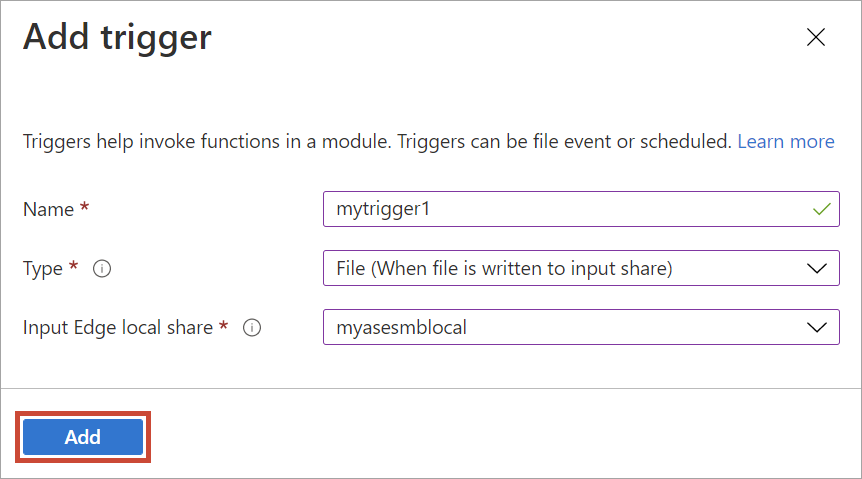
You are notified after the trigger is created. The list of triggers is updated to display the newly created trigger. Select the trigger you just created.
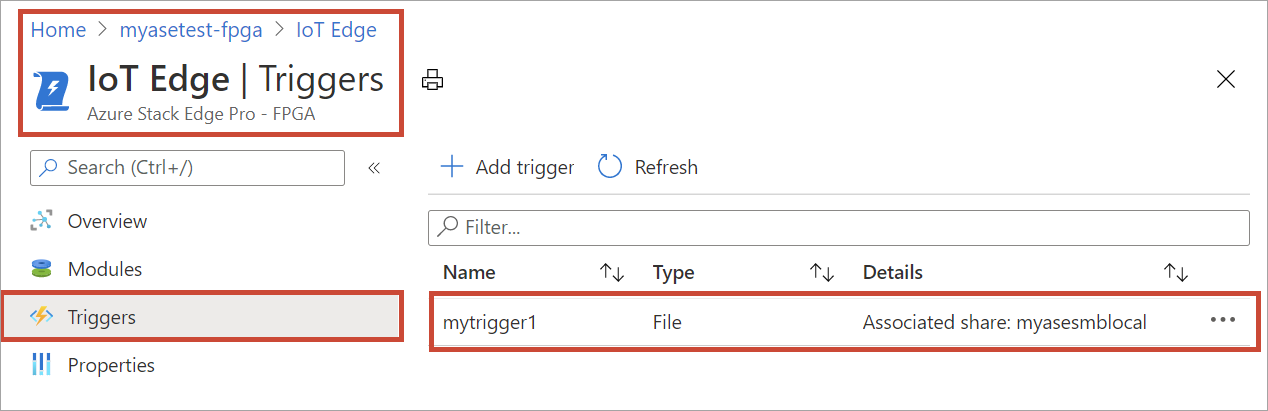
Copy and save the sample route. You will modify this sample route and use it later in the IoT Hub.
"sampleroute": "FROM /* WHERE topic = 'mydbesmbedgelocalshare1' INTO BrokeredEndpoint(\"/modules/modulename/inputs/input1\")"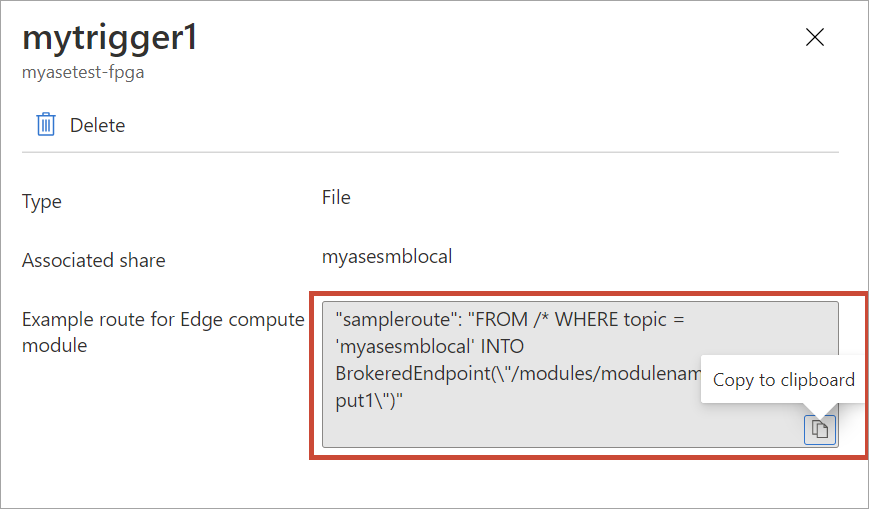
Add a module
There are no custom modules on this Edge device. You could add a custom or a pre-built module. To learn how to create a custom module, go to Develop a C# module for your Azure Stack Edge Pro FPGA device.
In this section, you add a custom module to the IoT Edge device that you created in Develop a C# module for your Azure Stack Edge Pro FPGA. This custom module takes files from an Edge local share on the Edge device and moves them to an Edge (cloud) share on the device. The cloud share then pushes the files to the Azure storage account that's associated with the cloud share.
Go to your Azure Stack Edge resource and then go to IoT Edge > Overview. On the Modules tile, select Go to Azure IoT Hub.
In your IoT Hub resource, go to IoT Edge device and then select your IoT Edge device.
On Device details, select Set Modules.
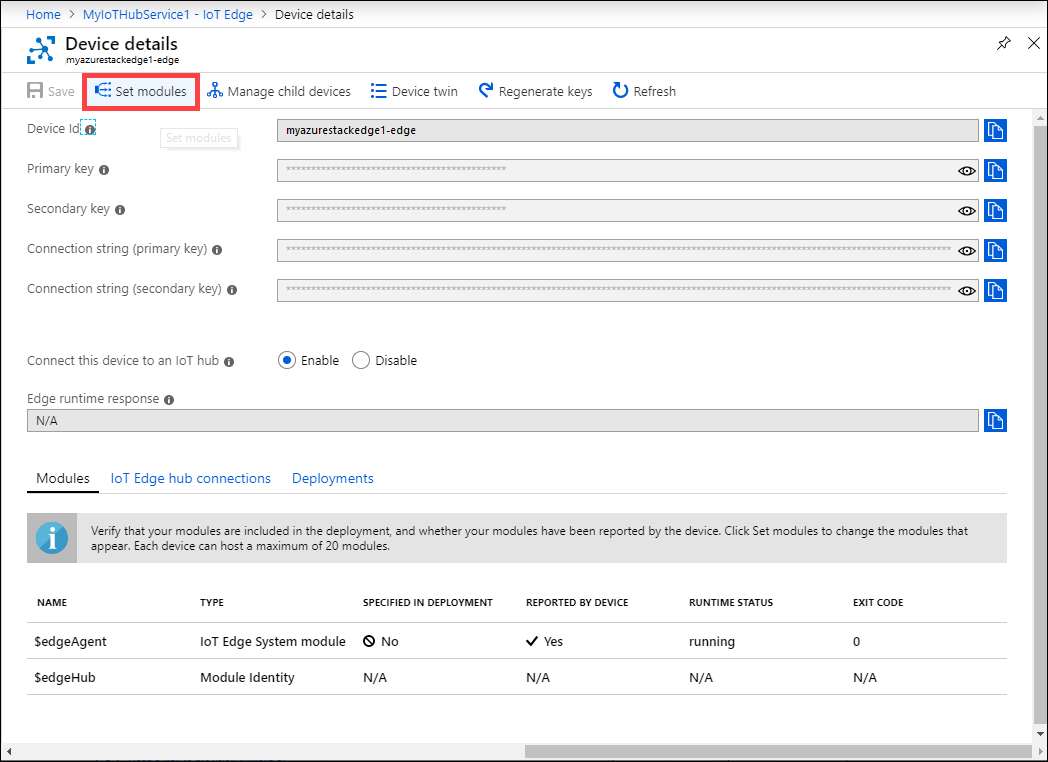
Under Add Modules, do the following:
Enter the name, address, user name, and password for the container registry settings for the custom module. The name, address, and listed credentials are used to retrieve modules with a matching URL. To deploy this module, under Deployment modules, select IoT Edge module. This IoT Edge module is a docker container that you can deploy to the IoT Edge device that's associated with your Azure Stack Edge Pro FPGA device.
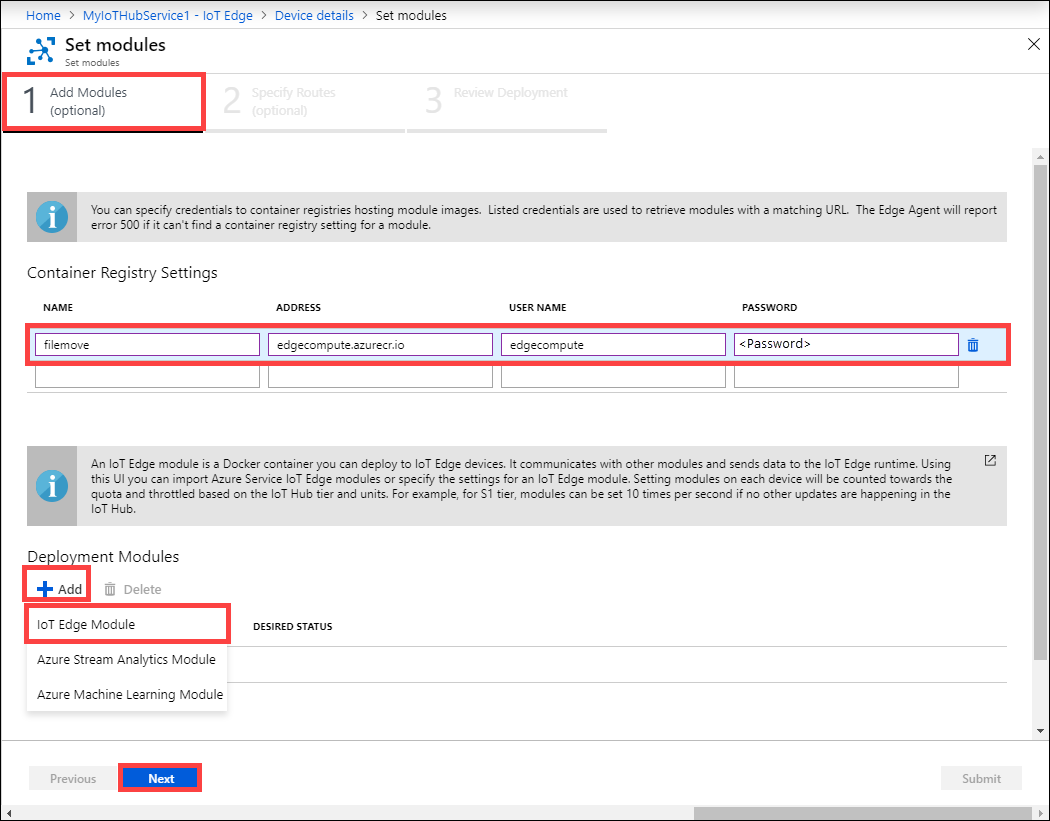
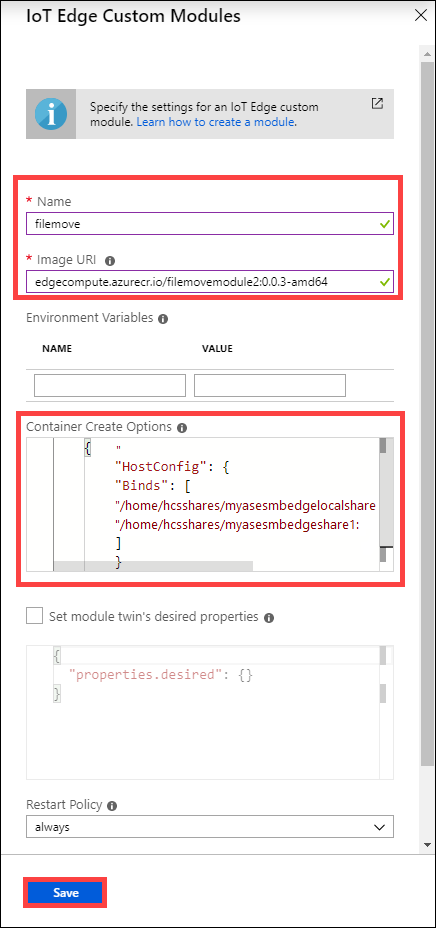
Specify the settings for the IoT Edge custom module. Input the following values.
Field Value Name A unique name for the module. This module is a docker container that you can deploy to the IoT Edge device associated with your Azure Stack Edge Pro FPGA. Image URI The image URI for the corresponding container image for the module. Credentials required If checked, username and password are used to retrieve modules with a matching URL. In the Container Create Options box, enter the local mount points for the Edge modules that you copied in the preceding steps for the Edge share and Edge local share.
Important
The paths used here are mounted into your container, so they must match what the functionality in your container expects. If you're following Create a custom module, the code specified in that module expects the copied paths. Do not modify these paths.
In the Container Create Options box, you can paste the following sample:
{ "HostConfig": { "Binds": [ "/home/hcsshares/mydbesmbedgelocalshare1:/home/input", "/home/hcsshares/mydbesmbedgeshare1:/home/output" ] } }Provide any environmental variables used for your module. Environmental variables provide optional information that help define the environment in which your module runs.
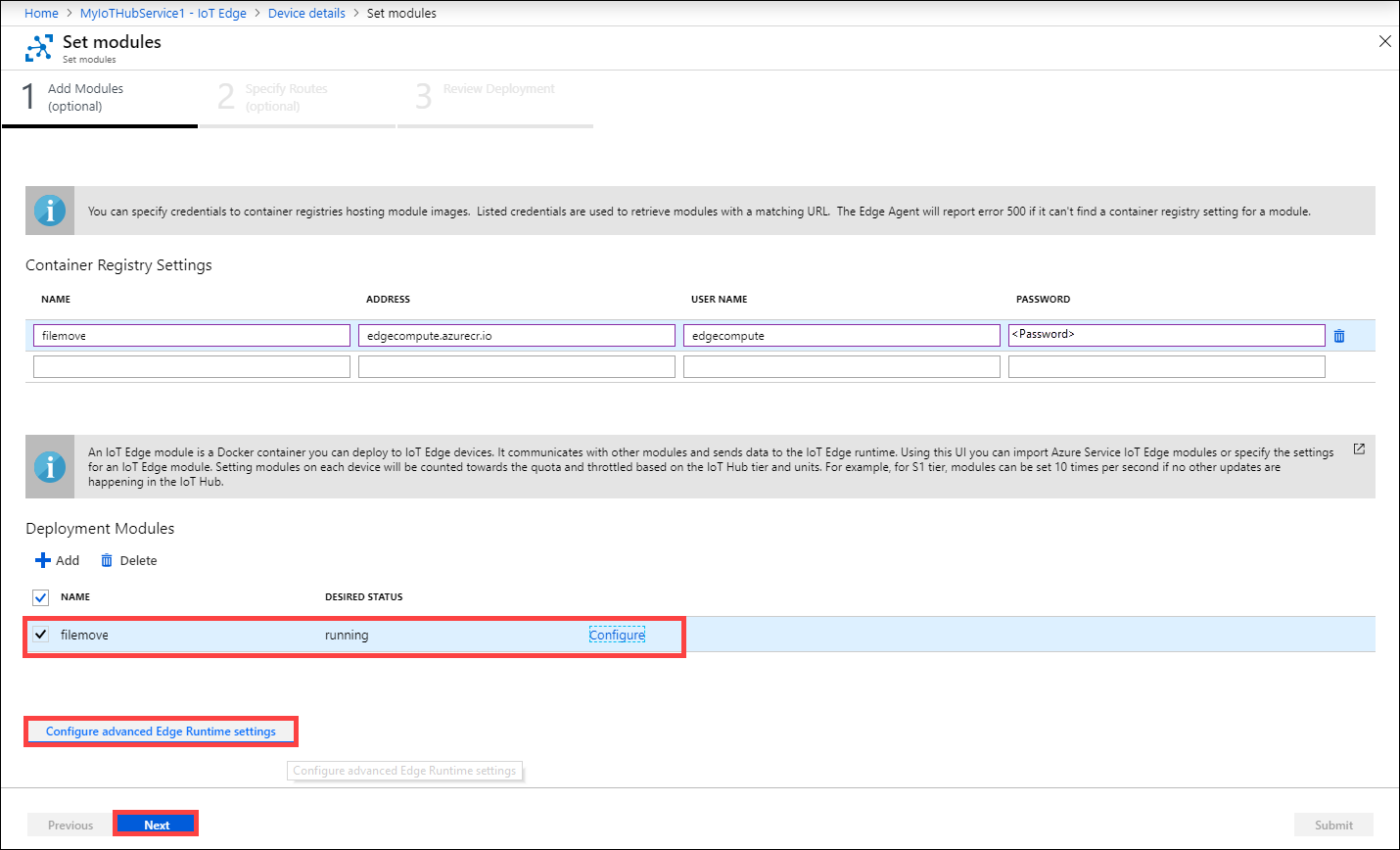
If necessary, configure the advanced Edge runtime settings, and then click Next.
Under Specify Routes, set routes between modules.
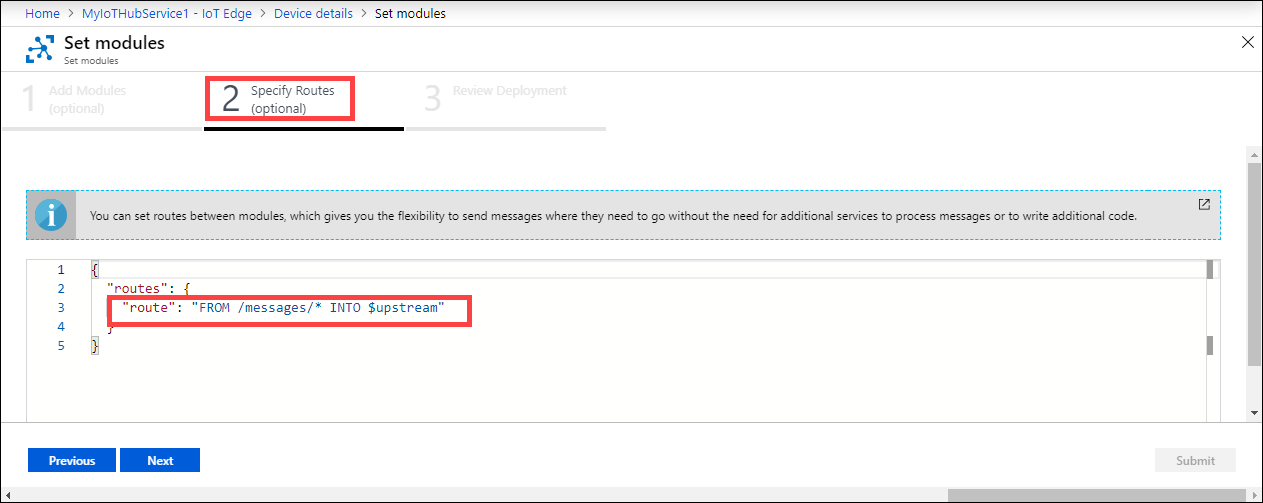
You can replace route with the following route string that you copied earlier. In this example, enter the name of the local share that will push data to the cloud share. Replace the
modulenamewith the name of the module. Select Next."route": "FROM /* WHERE topic = 'mydbesmbedgelocalshare1' INTO BrokeredEndpoint(\"/modules/filemove/inputs/input1\")"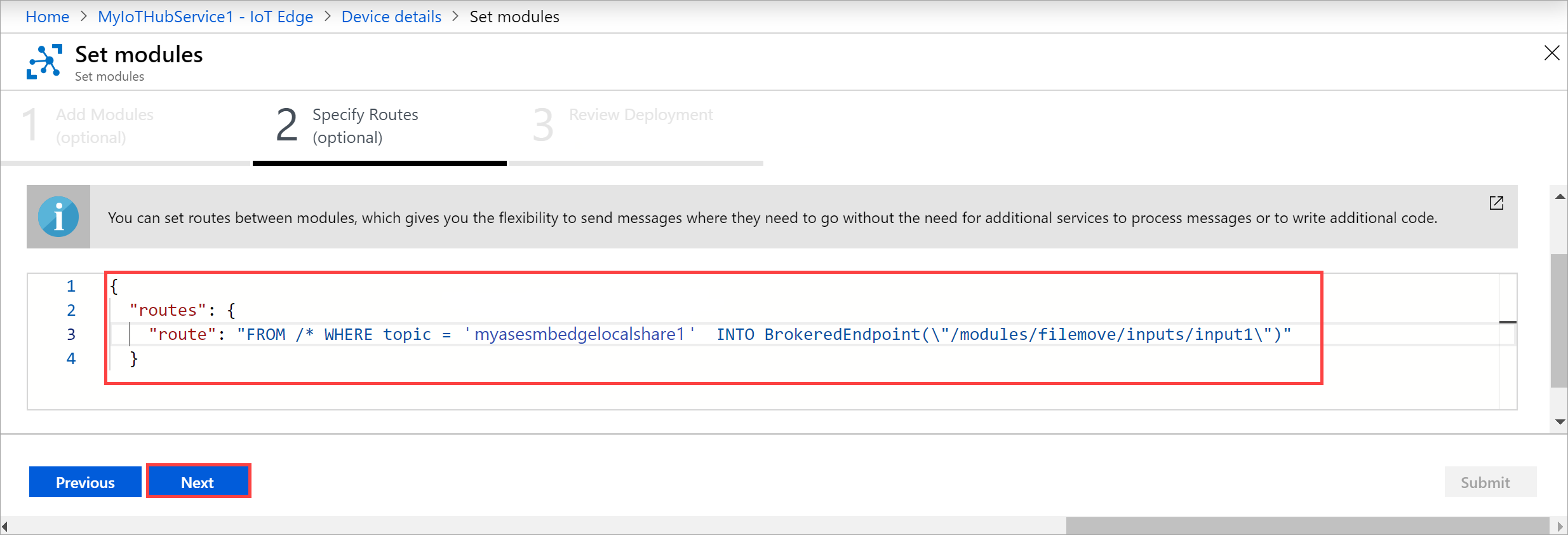
Under Review deployment, review all the settings, and then select Submit to submit the module for deployment.
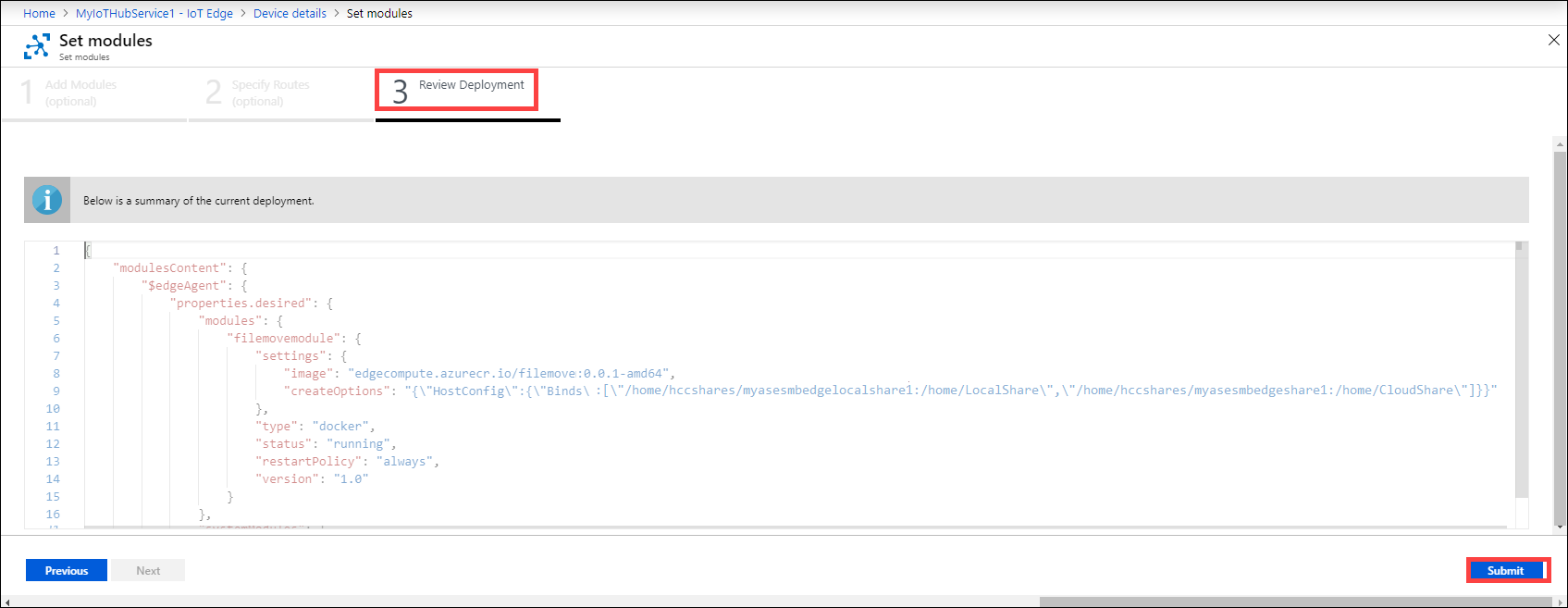
This action starts the module deployment. After the deployment is complete, the Runtime status of module is running.
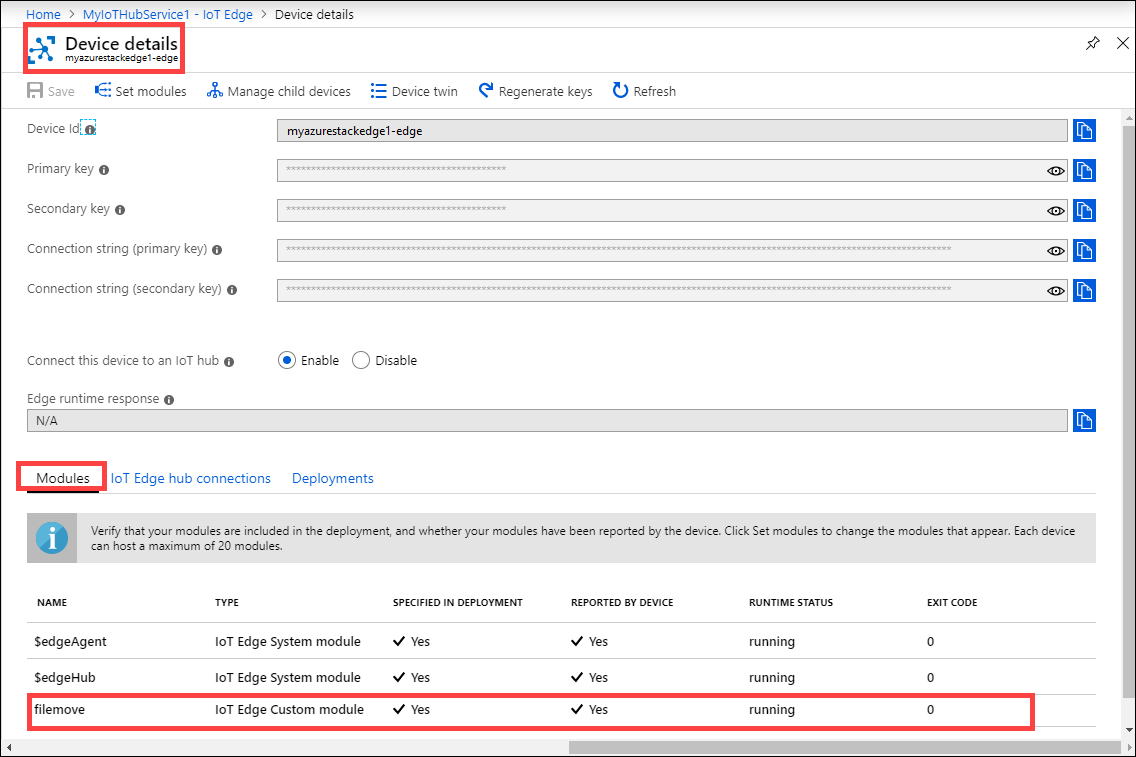
Verify data transform, transfer
The final step is to ensure that the module is connected and running as expected. The run-time status of the module should be running for your IoT Edge device in the IoT Hub resource.
Take the following steps to verify data transform and transfer to Azure.
In File Explorer, connect to both the Edge local and Edge shares you created previously.
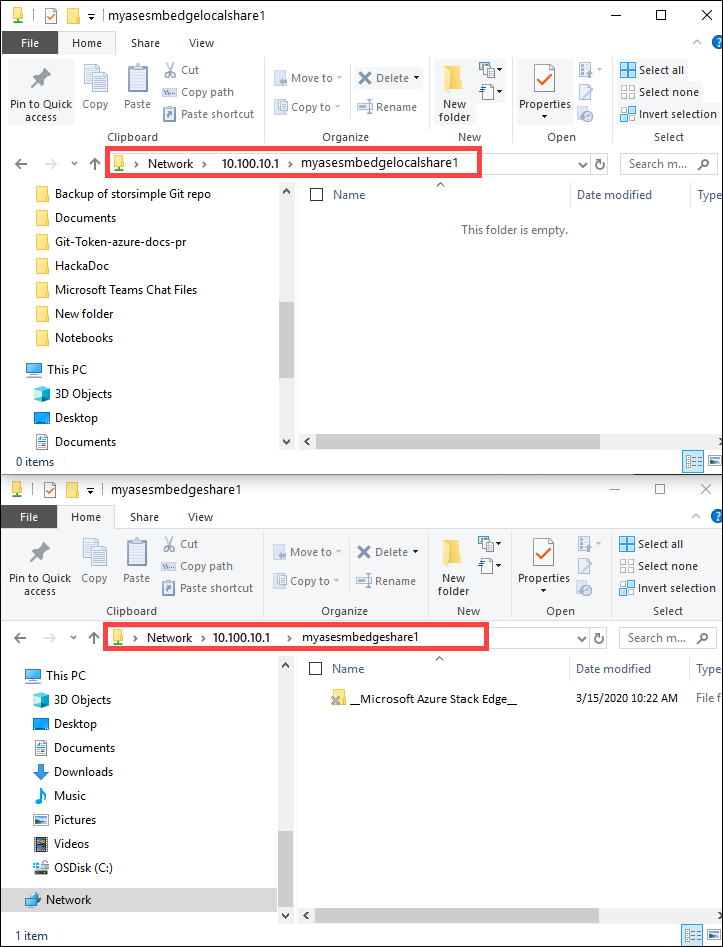
Add data to the local share.
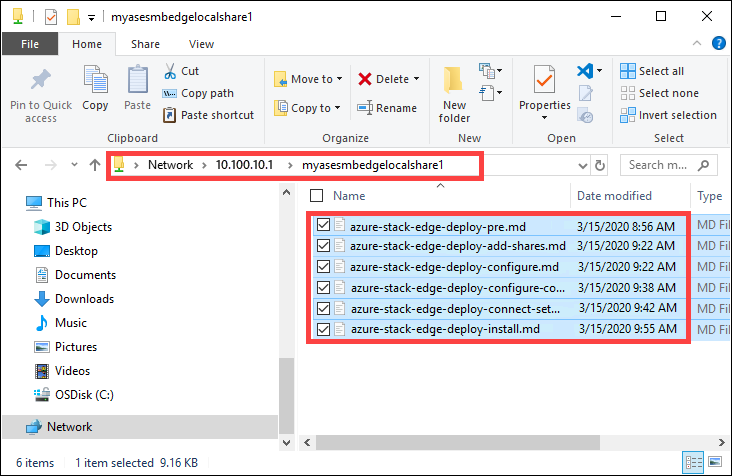
The data gets moved to the cloud share.
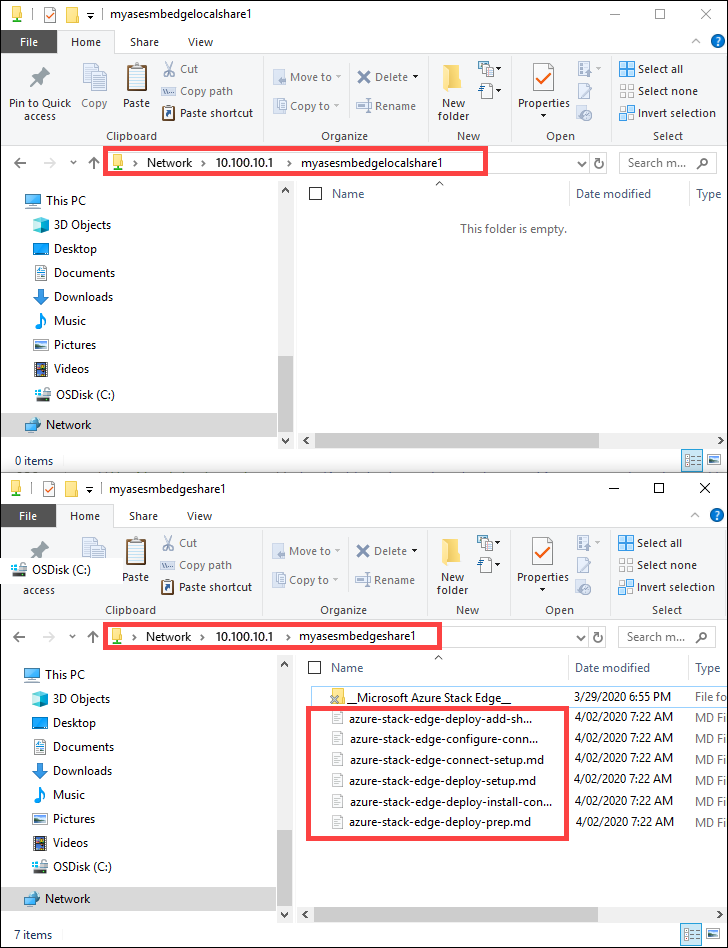
The data is then pushed from the cloud share to the storage account. To view the data, go to your storage account and then select Storage Explorer. You can view the uploaded data in your storage account.
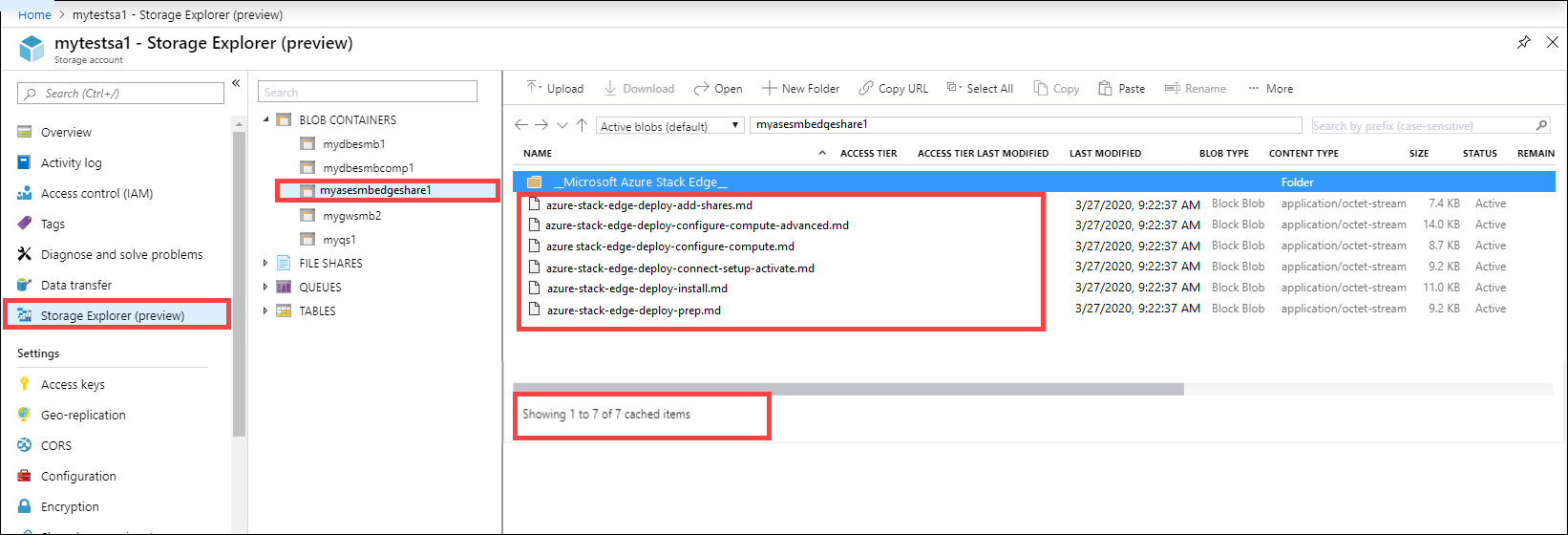
You have completed the validation process.
Next steps
In this tutorial, you learned how to:
- Configure compute
- Add shares
- Add a trigger
- Add a compute module
- Verify data transform and transfer
To learn how to administer your Azure Stack Edge Pro FPGA device, see: