Connect to an existing database in SSDT
This article shows how a user can connect to an existing database in SQL Server Data Tools (SSDT). SSDT allows you to connect to an existing database, run queries with Transact-SQL (T-SQL), and view the results.
SSDT also offers you a plethora of features that you can use to work with your database. These are explained in detail in the following sections. Let us understand how we can connect to an existing database.
To Connect to an existing database, refer to the following steps:
- Connect using SQL Server Object Explorer
- Know about Authentication Types
- Encrypt and Trust Server Certificate
Connect to a database using SQL Server Object Explorer
SQL Server Object Explorer (SSOX) is a tool available in SSDT for Visual Studio. It allows you to connect to and manage SQL Server databases within Visual Studio. To connect to a database using SQL Server Object Explorer in SSDT, follow these steps:
Open Visual Studio: Make sure you have installed SSDT along with the appropriate version of Visual Studio. Launch Visual Studio.
Open SQL Server Object Explorer: Go to the View menu and select SQL Server Object Explorer. Alternatively, you can use the shortcut Ctrl + \ (backslash) and then type Ctrl + S.
Connect to a Database Server: In the SQL Server Object Explorer window, select the Add SQL Server button (it looks like a sheet with a + icon to its top left) or right-click on the SQL Server node and choose Add SQL Server.
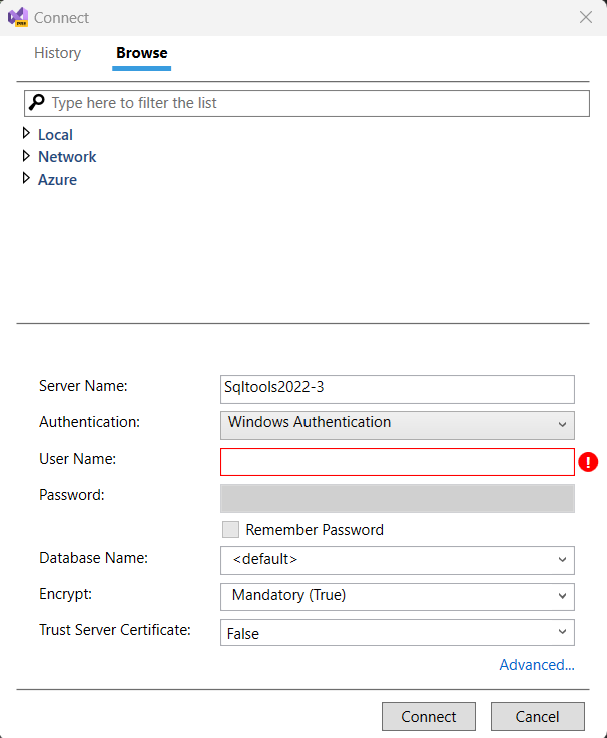
Enter Server Connection Details: In the Connect dialog box, enter the connection details for the SQL Server instance you want to connect to. This includes the server name, authentication method (for example, Windows Authentication or SQL Server Authentication), login credentials if applicable, and Encryption Details. Once a SQL Server instance is connected, it would automatically appear under the Recent Connection Option in the History tab.
Test Connection: After entering the connection details, you can select the Connect button to test the connection. If the connection is successful, you should see the instance and its databases listed in SQL Server Object Explorer.
Navigate and Manage Databases: Once connected, you can expand the server node to view all the databases hosted on that instance. You can further expand each database node to explore its tables, views, stored procedures, and other database objects.
Perform Actions: Right-click on a database or any object to perform various actions like querying data, creating new objects, editing existing ones, and more.
Authentication types
SSDT lets you connect to databases on your local machine, network, and Azure. Considering the variety of scenarios, we have multiple authentication types. They are as follows:

Windows Authentication: This authentication method uses Windows security to authenticate users to SQL Server.
SQL Server Authentication: This authentication method requires that a user has a SQL Server login and password.
Active Directory Password Authentication: This authentication method uses the user's Active Directory password to authenticate them to SQL Server. This is the simplest authentication method to configure, but it doesn't offer any additional security features.
Active Directory Integrated Authentication: This authentication method uses Kerberos to authenticate users to SQL Server. Kerberos is a more secure authentication protocol than Active Directory Password Authentication, but it requires that both the client and the server are joined to an Active Directory domain.
Active Directory Interactive Authentication: This authentication method allows users to authenticate to SQL Server by entering their Active Directory credentials in a dialog box. This is the most secure authentication method, but it can be inconvenient for users who must enter their credentials every time they connect to SQL Server.
Summary
| Authentication Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Windows Authentication | Uses the Windows security system to authenticate users. |
| SQL Server Authentication | Allows users to create a separate SQL Server login and password. |
| Active Directory Password Authentication | Uses the user's Active Directory password to authenticate them to SQL Server. |
| Active Directory Integrated Authentication | Uses Kerberos to authenticate users to SQL Server. |
| Active Directory Interactive Authentication | Allow users to authenticate to SQL Server by entering their Active Directory credentials in a dialog box. |
Encrypt and Trust Server Certificate
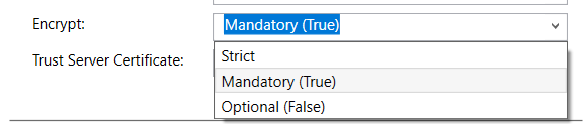
For SSDT in Visual Studio 17.8 and later versions, there's an important change to the Encrypt property, which is now enabled by default for all connections. SQL Server must be configured with a TLS certificate, signed by a trusted root certificate authority. In addition, if an initial connection attempt fails with encryption enabled (default), SSDT provides a notification prompt with an option to attempt the connection with Trust Server Certificate enabled. Both the Encrypt and Trust Server Certificate properties are also available for manual editing. The best practice is to support a trusted encrypted connection to the server.
For users connecting to Azure SQL Database, no changes to existing, saved connections are needed; Azure SQL Database supports encrypted connections and is configured with trusted certificates.
For users connecting to on-premises SQL Server instances, or SQL Server running on a virtual machine, if Encrypt is set to True, ensure that you have a certificate from a trusted certificate authority (for example, not a self-signed certificate). Alternatively, you might choose to connect without encryption (Encrypt set to False), or to trust the server certificate (Encrypt set to True and Trust Server Certificate set to True).
If SQL Server isn't configured with a trusted certificate, and you attempt to connect using Strict encryption, or with Encrypt set to True and Trust Server Certificate set to False, the following error message is displayed:
Encryption was enabled on this connection, review your SSL and certificate configuration for the target SQL Server, or enable 'Trust server certificate' in the connection dialog.
Additional information
A connection was successfully established with the server, but then an error occurred during the login process. (provider: SSL Provider, error: 0 - The certificate chain was issued by an authority that is not trusted.) (Microsoft SQL Server)
