transform_view 类(C++ 标准库)
元素视图,每个元素都是指定区域中元素的转换。
语法
template<input_range V, move_constructible F>
requires view<V> && is_object_v<F> &&
regular_invocable<F&, range_reference_t<V>> &&
can-reference<invoke_result_t<F&, range_reference_t<V>>>
class transform_view : public view_interface<transform_view<V, F>>;
模板参数
F
转换元素的函数对象的类型。
V
基础视图的类型。
视图特征
有关下列条目的说明,请参阅视图类特征
| 特征 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 范围适配器 | views::transform |
| 基础范围 | 必须满足 input_range 或更高范围 |
| 元素类型 | 与转换函数的返回类型相同。 |
| 视图枚举器类别 | 支持最多 random_access_range 的 input_range,具体取决于基础范围 |
| 已设置大小 | 仅当基础范围满足 sized_range 要求时 |
是 const 可迭代 |
仅当基础范围 const 可迭代且转换适用于 const 引用时。 |
| 常见范围 | 仅当基础范围满足 common_range 要求时 |
| 借入范围 | 否 |
成员
| 成员函数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 构造函数C++20 | 构造视图。 |
baseC++20 |
获取基础范围。 |
beginC++20 |
获取指向第一个元素的迭代器。 |
endC++20 |
获取视图末尾的 sentinel。 |
sizeC++20 |
获取元素数。 基础范围必须满足 sized_range。 |
从 view_interface 继承 |
描述 |
backC++20 |
获取最后一个元素。 |
emptyC++20 |
测试视图是否为空。 |
frontC++20 |
获取第一个元素。 |
operator boolC++20 |
测试视图是否不为空。 |
operator[]C++20 |
获取指定位置的元素。 |
要求
标头: <ranges> (自C++20以来)
命名空间:std::ranges
编译器选项:/std:c++20或更高版本是必需的。
构造函数
构造 transform_view 的实例
1) transform_view() requires default_initializable<V>
&& default_initializable<F> = default;
2) constexpr transform_view(V base, F func);
参数
base
基础视图。
func
转换每个元素的函数。
有关模板参数类型的信息,请参阅模板参数。
返回值
一个 transform_view 实例。
注解
创建 transform_view 的最佳方法是使用 views::transform 范围适配器。 范围适配器是创建视图类的预期方法。 如果要创建自己的自定义视图类型,会公开视图类型。
1) 创建值初始化的 transform_view。 转换函数和基础视图必须是可默认初始化的。
2) 从 base 视图和转换函数 func 移动构造 transform_view。 通过 std::move() 移动 base 和 func。
示例: transform_view
// requires /std:c++20 or later
#include <ranges>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <chrono>
using namespace std;
using namespace chrono;
void print(auto v)
{
for (auto x : v)
{
cout << x << ' ';
}
cout << '\n';
}
struct classes
{
string className;
weekday startDay;
};
int main()
{
std::vector<int> v{0, 1, 2, 3, -4, 5, 6};
// outputs 0 2 4 6 -8 10 12
print(v | std::views::transform([](int i) {return i * 2; }));
// ---- Modify the elements in the collection by returning a reference to the element to transform
std::vector<classes> theClasses = {
{"Math", Monday},
{"English", Wednesday},
{"History", Monday},
{"Science", Wednesday},
{"Art", Friday},
{"Music", Thursday}
};
// lambda to get a reference to the day of the week for a class
auto getDay = [](classes& c) -> weekday&
{
return c.startDay;
};
// If a class starts on Monday, change it to Tuesday
for (auto&& startDay : theClasses | std::views::transform(getDay))
{
// modify the startDay in the collection
if (startDay == Monday)
{
startDay = Tuesday;
}
}
// output classes and start times
for (auto c : theClasses)
{
std::cout << c.className << " : " << c.startDay << '\n';
}
}
0 2 4 6 -8 10 12
Math : Tue
English : Wed
History : Tue
Science : Wed
Art : Fri
Music : Thu
base
获取基础视图。
// Uses a copy constructor to return the underlying view
constexpr V base() const& requires std::copy_constructible<V>;
// Uses std::move() to return the underlying view
constexpr V base() &&;
参数
无。
返回
基础视图。
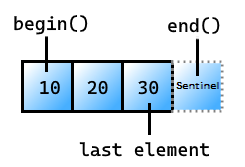
begin
获取指向视图中第一个元素的迭代器。
constexpr auto begin();
返回值
指向视图中第一个元素的迭代器。 如果视图没有谓词,则没有定义行为。
end
获取视图末尾的 sentinel。
constexpr auto end()
返回值
视图中最后一个元素后面的 sentinel:

size
获取视图中的元素数。
constexpr auto size() requires ranges::sized_range<V>;
constexpr auto size() const requires ranges::sized_range<const V>;
参数
无。
返回值
视图中的元素数。