WPF 中的双向功能概述
与其他任何开发平台不同,WPF 具有许多支持双向内容快速开发的功能,例如,同一文档中混合了从左到右和从右到左的数据。 同时,WPF 也为需要双向功能的用户(如阿拉伯语和希伯来语用户)带来了绝佳的体验。
以下各节结合一些示例阐释了如何获得双向内容的最佳显示效果,并对许多双向功能进行了说明。 大多数示例使用的是 XAML,但你可以轻松地将这些概念应用于 C# 或 Microsoft Visual Basic 代码。
FlowDirection
FlowDirection 是在 WPF 应用程序中定义内容流方向的基本属性。 此属性可设置为以下两个枚举值之一:LeftToRight 或 RightToLeft。 此属性可用于从 FrameworkElement 继承的所有 WPF 元素。
以下示例将设置 TextBox 元素的流方向。
从左向右的流方向
<TextBlock Background="DarkBlue" Foreground="LightBlue"
FontSize="20" FlowDirection="LeftToRight">
This is a left-to-right TextBlock
</TextBlock>
从右向左的流方向
<TextBlock Background="LightBlue" Foreground="DarkBlue"
FontSize="20" FlowDirection="RightToLeft">
This is a right-to-left TextBlock
</TextBlock>
下图显示了前面代码的呈现方式。
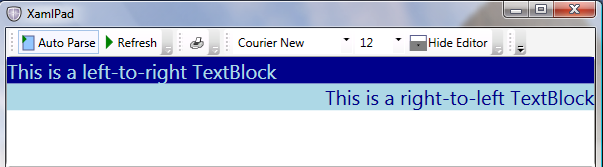
用户界面 (UI) 树内的元素将从其容器继承 FlowDirection。 在下面的示例中,TextBlock 位于 Grid 中,而后者位于 Window 中。 为 Window 设置 FlowDirection 意味着还将为 Grid 和 TextBlock 设置该属性。
以下示例演示如何设置 FlowDirection。
<Window
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
x:Class="FlowDirectionApp.Window1"
Title="BidiFeatures" Height="200" Width="700"
FlowDirection="RightToLeft">
<Grid>
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition/>
<ColumnDefinition/>
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<TextBlock Grid.Column="0" >
This is a right-to-left TextBlock
</TextBlock>
<TextBlock Grid.Column="1" FlowDirection="LeftToRight">
This is a left-to-right TextBlock
</TextBlock>
</Grid>
</Window>
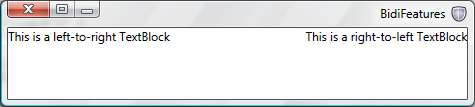
顶级 Window 包含 RightToLeftFlowDirection,因此其中包含的所有元素也都继承同一 FlowDirection。 对于要替代指定的 FlowDirection 的元素,必须添加显式方向更改,如上一示例中的第二个 TextBlock,该控件更改为 LeftToRight。 如果未定义 FlowDirection,将应用默认的 LeftToRight。
下图显示了上一个示例的输出:
FlowDocument
HTML、Win32 和 Java 等许多开发平台都对双向内容开发提供特殊支持。 标记语言(如 HTML)为内容编写器提供了在任意所需方向显示文本时必需的标记,如 HTML 4.0 标记、采用“rtl”或“ltr”作为值的“dir”等。 此标记类似于 FlowDirection 属性,但 FlowDirection 属性使用了一种更高级的方法来布局文本内容,并可用于除文本以外的内容。
在 UI 中,它是一种可以托管文本、表、图像和其他元素的组合的元素。 以下各节中的示例均使用此元素。
可通过多种方式将文本添加到 FlowDocument。 其中一种简单方法就是使用 Paragraph,它是用于对文本等内容进行分组的块级元素。 为了将文本添加到内联级元素,这些示例使用了 Span 和 Run。 Span 是用于对其他内联元素进行分组的内联级流内容元素,而 Run 是用于包含一系列无格式文本的内联级流内容元素。 一个 Span 可以包含多个 Run 元素。
第一个文档示例包含的文档具有很多个网络共享名,例如 \\server1\folder\file.ext。 无论此网络链接是包含在阿拉伯语文档还是英语文档中,建议始终以相同的方式显示它。 下图演示了如何使用 Span 元素,并显示了阿拉伯语 RightToLeft 文档中的链接:
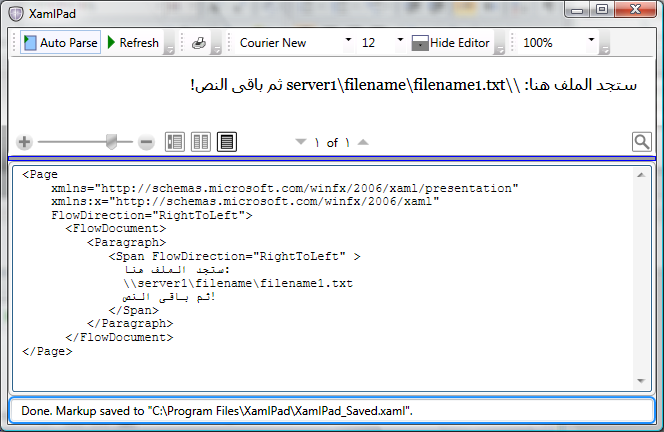
由于文本是 RightToLeft,因此所有特殊字符(如“\”)都按从右到左的顺序分隔文本。 这样会导致链接显示顺序不正确,因此,若要解决此问题,必须嵌入文本以保留按 LeftToRight 显示的单独的 Run。 除了为每种语言提供单独的 Run 之外,还可使用一种更好的方法来解决此问题,即,将不常用的英语文本嵌入到较大的阿拉伯语 Span 中。
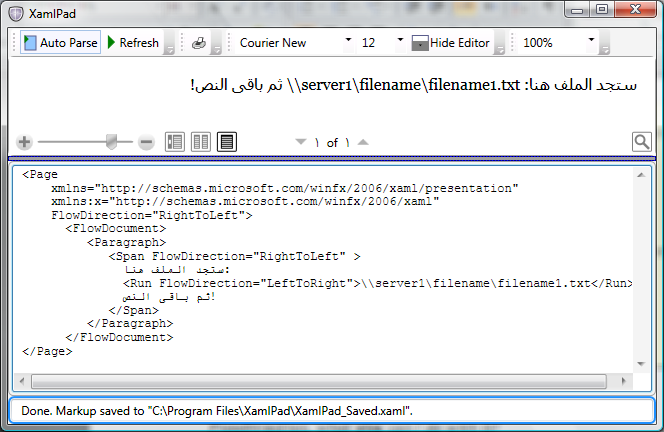
下图通过使用 Span 元素中嵌入的 Run 元素说明了这一点:
<Page
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
FlowDirection="RightToLeft">
<FlowDocument>
<Paragraph>
<Span FlowDirection="RightToLeft" >
ستجد الملف هنا:
<Run FlowDirection="LeftToRight">
\\server1\filename\filename1.txt</Run>
ثم باقى النص!
</Span>
</Paragraph>
</FlowDocument>
</Page>
Span 元素
Span 元素用作具有不同流方向的文本之间的边界分隔符。 甚至具有相同流方向的 Span 元素也被视为具有不同的双向范围,这意味着 Span 元素按容器的 FlowDirection 进行排序,只有 Span 元素内的内容才遵循 Span 的 FlowDirection。
下图显示了几个 TextBlock 元素的流方向。
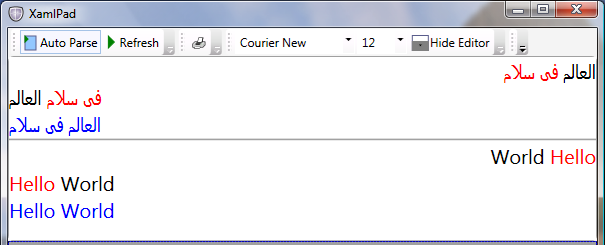
以下示例演示如何使用 Span 和 Run 元素生成上图中显示的结果。
<Page xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation">
<StackPanel >
<TextBlock FontSize="20" FlowDirection="RightToLeft">
<Run FlowDirection="LeftToRight">العالم</Run>
<Run FlowDirection="LeftToRight" Foreground="Red" >فى سلام</Run>
</TextBlock>
<TextBlock FontSize="20" FlowDirection="LeftToRight">
<Run FlowDirection="RightToLeft">العالم</Run>
<Run FlowDirection="RightToLeft" Foreground="Red" >فى سلام</Run>
</TextBlock>
<TextBlock FontSize="20" Foreground="Blue">العالم فى سلام</TextBlock>
<Separator/>
<TextBlock FontSize="20" FlowDirection="RightToLeft">
<Span Foreground="Red" FlowDirection="LeftToRight">Hello</Span>
<Span FlowDirection="LeftToRight">World</Span>
</TextBlock>
<TextBlock FontSize="20" FlowDirection="LeftToRight">
<Span Foreground="Red" FlowDirection="RightToLeft">Hello</Span>
<Span FlowDirection="RightToLeft">World</Span>
</TextBlock>
<TextBlock FontSize="20" Foreground="Blue">Hello World</TextBlock>
</StackPanel>
</Page>
在此示例的 TextBlock 元素中,Span 元素根据其父级的 FlowDirection 进行布局,但每个 Span 元素中的文本根据其自己的 FlowDirection 流动。 这适用于拉丁语和阿拉伯语,也适用于任何其他语言。
添加 xml:lang
下图显示了另一个示例,该示例使用数字和算术表达式,如 "200.0+21.4=221.4"。 请注意,仅设置了 FlowDirection。
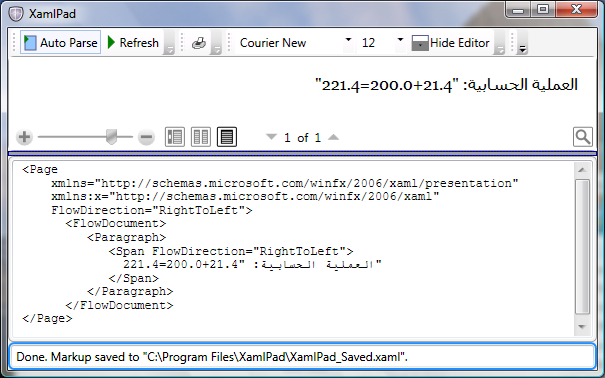
此应用程序的用户将对输出感到失望,即使 FlowDirection 正确,但数字的形状不是阿拉伯语数字应有的形状。
XAML 元素可以包括 XML 属性 (xml:lang),该属性用于定义每个元素的语言。 XAML 还支持 XML 语言原则,即,应用于树中父元素的 xml:lang 值将用于子元素。 在上面的示例中,由于未对 Run 元素或其任意顶级元素设置语言,因此使用了默认的 xml:lang(对于 XAML 为 en-US)。 Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF) 的内部数字整理算法选择对应语言(在本示例中为英语)中的数字。 若要正确呈现阿拉伯语数字,需要设置 xml:lang。
下图演示添加了 xml:lang 的示例。
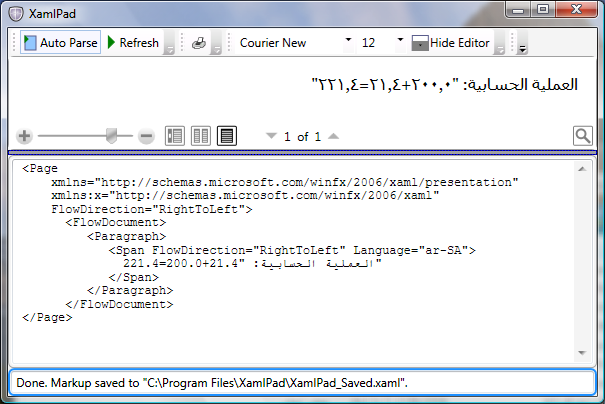
以下示例将向应用程序添加 xml:lang。
<Page
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
FlowDirection="RightToLeft">
<FlowDocument>
<Paragraph>
<Span FlowDirection="RightToLeft" Language="ar-SA">
العملية الحسابية: "200.0+21.4=221.4"
</Span>
</Paragraph>
</FlowDocument>
</Page>
请注意,根据目标区域的不同,许多语言具有不同的 xml:lang 值,例如,"ar-SA" 和 "ar-EG" 表示阿拉伯语的两个变体。 上述示例说明你需要同时定义 xml:lang 和 FlowDirection 值。
非文本元素的 FlowDirection
FlowDirection 不仅定义文本在文本元素中的流动方式,还定义几乎所有其他 UI 元素的流方向。 下图显示了一个 ToolBar,该控件使用水平 LinearGradientBrush 以从左到右渐变绘制其背景。
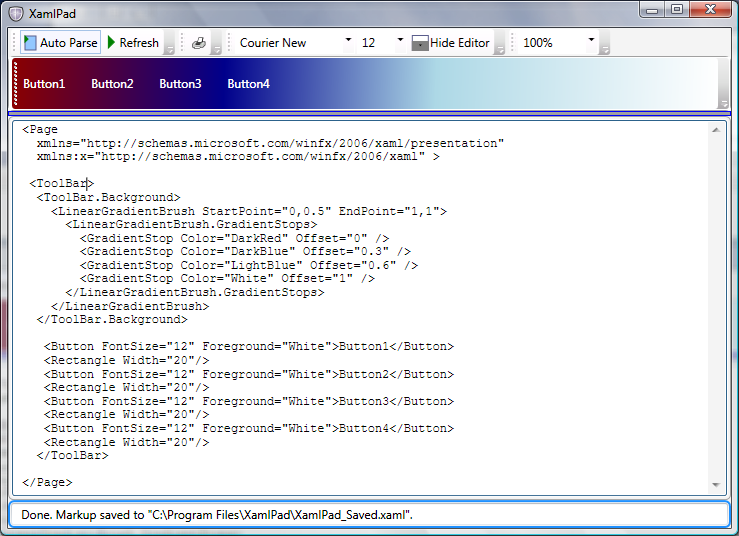
将 FlowDirection 设置为 RightToLeft 后,不仅 ToolBar 按钮是从右到左排列的,甚至 LinearGradientBrush 也将其偏移量重新调整为从右到左流动。
下图显示了 LinearGradientBrush 的重新排列。
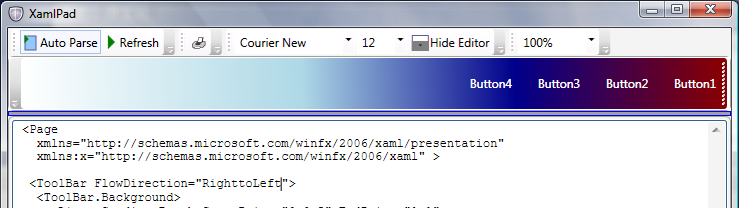
以下示例绘制了一个 RightToLeftToolBar。 若要从左到右绘制,请删除 ToolBar 的 FlowDirection 属性。
<Page
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml">
<ToolBar FlowDirection="RightToLeft" Height="50" DockPanel.Dock="Top">
<ToolBar.Background>
<LinearGradientBrush StartPoint="0,0.5" EndPoint="1,1">
<LinearGradientBrush.GradientStops>
<GradientStop Color="DarkRed" Offset="0" />
<GradientStop Color="DarkBlue" Offset="0.3" />
<GradientStop Color="LightBlue" Offset="0.6" />
<GradientStop Color="White" Offset="1" />
</LinearGradientBrush.GradientStops>
</LinearGradientBrush>
</ToolBar.Background>
<Button FontSize="12" Foreground="White">Button1</Button>
<Rectangle Width="20"/>
<Button FontSize="12" Foreground="White">Button2</Button>
<Rectangle Width="20"/>
<Button FontSize="12" Foreground="White">Button3</Button>
<Rectangle Width="20"/>
<Button FontSize="12" Foreground="White">Button4</Button>
<Rectangle Width="20"/>
</ToolBar>
</Page>
FlowDirection 异常
在少数情况下,FlowDirection 会不按预期方式运行。 本部分介绍其中两种异常。
Image
Image 表示用于显示图像的控件。 在 XAML 中,该控件可与 Source 属性一起使用,后者用于定义要显示的 Image 的统一资源标识符 (URI)。
与其他 UI 元素不同,Image 不会从容器继承 FlowDirection。 但是,如果将 FlowDirection 显式设置为 RightToLeft,则会以水平翻转方式显示 Image。 这可作为一种便捷功能提供给双向内容的开发人员,因为在某些情况下,水平翻转图像会达到所需的效果。
下图显示翻转后的 Image。
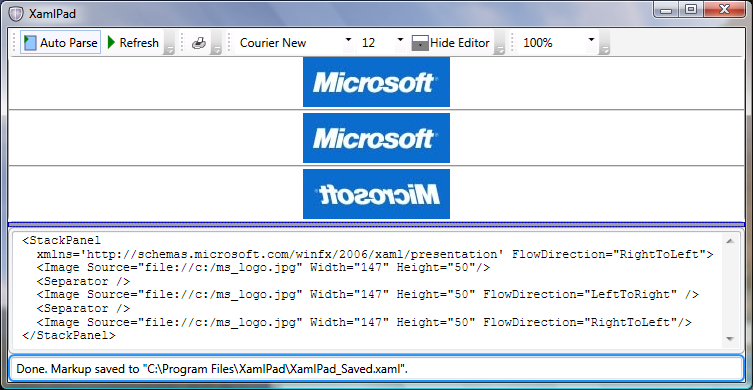
以下示例演示 Image 未能从包含它的 StackPanel 中继承 FlowDirection。
注意
C:\ 驱动器上必须具有名为 ms_logo.jpg 的文件才能运行此示例。
<StackPanel
xmlns='http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation'
FlowDirection="RightToLeft">
<Image Source="file://c:/ms_logo.jpg"
Width="147" Height="50"/>
<Separator Height="10"/>
<Image Source="file://c:/ms_logo.jpg"
Width="147" Height="50" FlowDirection="LeftToRight" />
<Separator Height="10"/>
<Image Source="file://c:/ms_logo.jpg"
Width="147" Height="50" FlowDirection="RightToLeft"/>
</StackPanel>
注意
下载文件中包含的内容是 ms_logo.jpg 文件。 该代码假定 .jpg 文件不在项目中,而是位于 C:\ 驱动器中的某个位置。 必须将 .jpg 从项目文件复制到 C:\ 驱动器或更改代码才能在项目内查找该文件。 为此,请将 Source="file://c:/ms_logo.jpg" 更改为 Source="ms_logo.jpg"。
路径
除 Image 外,另一个值得关注的元素是 Path。 Path 是可用于绘制一系列连接的直线和曲线的对象。 就其 FlowDirection 而言,它的行为方式类似于 Image,例如它的 RightToLeftFlowDirection 是其 LeftToRight 的水平镜像。 但是,与 Image 不同的是,Path 从容器中继承其 FlowDirection,因此用户无需显式指定它。
下面的示例使用 3 条线绘制简单的箭头。 第一个箭头从 StackPanel 继承 RightToLeft 流方向,以便从右侧的根测量其起点和终点。 第二个箭头具有显式的 RightToLeftFlowDirection,也从右侧开始。 但第三个箭头的起始根位于左侧。 有关绘图的详细信息,请参阅 LineGeometry 和 GeometryGroup。
<StackPanel
xmlns='http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation'
FlowDirection="RightToLeft">
<Path Stroke="Blue" StrokeThickness="4">
<Path.Data>
<GeometryGroup >
<LineGeometry StartPoint="300,10" EndPoint="350,30" />
<LineGeometry StartPoint="10,30" EndPoint="352,30" />
<LineGeometry StartPoint="300,50" EndPoint="350,30" />
</GeometryGroup>
</Path.Data>
</Path>
<Path Stroke="Red" StrokeThickness="4" FlowDirection="RightToLeft">
<Path.Data>
<GeometryGroup >
<LineGeometry StartPoint="300,10" EndPoint="350,30" />
<LineGeometry StartPoint="10,30" EndPoint="352,30" />
<LineGeometry StartPoint="300,50" EndPoint="350,30" />
</GeometryGroup>
</Path.Data>
</Path>
<Path Stroke="Green" StrokeThickness="4" FlowDirection="LeftToRight">
<Path.Data>
<GeometryGroup >
<LineGeometry StartPoint="300,10" EndPoint="350,30" />
<LineGeometry StartPoint="10,30" EndPoint="352,30" />
<LineGeometry StartPoint="300,50" EndPoint="350,30" />
</GeometryGroup>
</Path.Data>
</Path>
</StackPanel>
下图显示了上一个示例的输出,其中使用 Path 元素绘制了箭头:
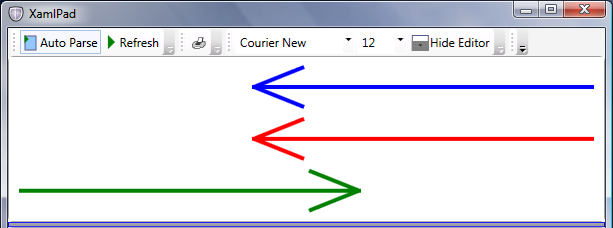
Image 和 Path 这两个示例展示了 WPF 如何使用 FlowDirection。 除了在容器内按特定方向布局 UI 元素外,FlowDirection 还可与 InkPresenter(在图面上呈现墨迹)、LinearGradientBrush、RadialGradientBrush 等元素一起使用。 每当模拟从左到右行为的内容需要从右到左行为(反之亦然)时,Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF) 就会提供该功能。
数字替换
一直以来,Windows 始终通过以下方式支持数字替换:允许对相同数字使用不同区域性形状的表示形式,但同时使这些数字的内部存储形式在不同区域设置之间保持统一;例如,数字虽然以其常见的十六进制值(如 0x40、0x41)存储,但却根据所选的语言进行显示。
这使应用程序无需将数值从一种语言转换为另一种语言,就可对它们进行处理;例如,用户可以在本地化的阿拉伯语 Windows 中打开 Microsoft Excel 电子表格,并会看到阿拉伯语形状的数字,但在欧洲版 Windows 中打开它时,会看到相同数字的欧洲表示形式。 这对其他符号(如逗号分隔符和百分比符号)来说也是必需的,因为在同一文档中它们通常随数字一起出现。
Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF) 沿承了这一传统,并为此功能提供了进一步支持,以允许用户更好地控制何时以及如何使用替换。 虽然此功能适用于任何语言,但它对双向内容尤其有用;由于应用程序可能会在各种区域性下运行,因此针对特定语言来设置数字形状通常是应用程序开发人员所面临的难题。
控制 Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF) 中的数字替换方式的核心属性是 Substitution 依赖属性。 NumberSubstitution 类指定如何显示文本中的数字。 它有三个定义其行为的公共属性。 下面概括了其中的每个属性:
CultureSource:
此属性指定如何确定数字的区域性。 它使用三个 NumberCultureSource 枚举值之一。
Override:数字区域性是 CultureOverride 属性的区域性。
Text:数字区域性是文本运行的区域性。 在标记中,这将是
xml:lang,或其别名Language属性(Language 或 Language)。 此外,它还是派生自 FrameworkContentElement 的类的默认值。 这种类包括 System.Windows.Documents.Paragraph、System.Windows.Documents.Table、System.Windows.Documents.TableCell 等。User:数字区域性是当前线程的区域性。 该属性是 FrameworkElement 的所有子类(如 Page、Window 和 TextBlock)的默认值。
CultureOverride:
仅当 CultureSource 属性设置为 Override 时才使用 CultureOverride 属性,否则将忽略。 该属性指定数字区域性。 默认值 null 被解释为 en-US。
Substitution:
此属性指定要执行的数字替换类型。 它使用以下 NumberSubstitutionMethod 枚举值之一:
AsCulture:替换方法根据数字区域性的 NumberFormatInfo.DigitSubstitution 属性决定。 这是默认情况。
Context:如果数字区域性为阿拉伯语或波斯语区域性,则指定数字取决于上下文。
European:数字始终呈现为欧洲数字。
NativeNational:使用数字区域性的民族数字(由区域性的 NumberFormat 指定)呈现数字。
Traditional:使用数字区域性的传统数字呈现数字。 对于大多数区域性,这与 NativeNational 相同。 但是,NativeNational 对某些阿拉伯语区域性会产生拉丁数字,而此值对所有阿拉伯语区域性产生阿拉伯数字。
这些值对双向内容开发人员意味着什么? 在大多数情况下,开发人员可能只需要定义 FlowDirection 和每个文本 UI 元素的语言,例如 Language="ar-SA" 和 NumberSubstitution 逻辑负责根据正确的 UI 显示数字。 以下示例演示如何在阿拉伯语版 Windows 中运行的 Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF) 应用程序中使用阿拉伯语和英语数字。
<Page
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml" >
<StackPanel>
<TextBlock Background="LightGreen" FontSize="32"
Language="ar-SA" FlowDirection="RightToLeft">1+2=3</TextBlock>
<TextBox Background="LightGreen" FontSize="32"
Language="ar-SA" FlowDirection="RightToLeft">1+2=3</TextBox>
<TextBlock Background="LightBlue" FontSize="32">1+2=3</TextBlock>
<TextBox Background="LightBlue" FontSize="32">1+2=3</TextBox>
</StackPanel>
</Page>
下图演示了在阿拉伯语版的 Windows 中运行并显示阿拉伯语和英语数字时上一示例的输出:
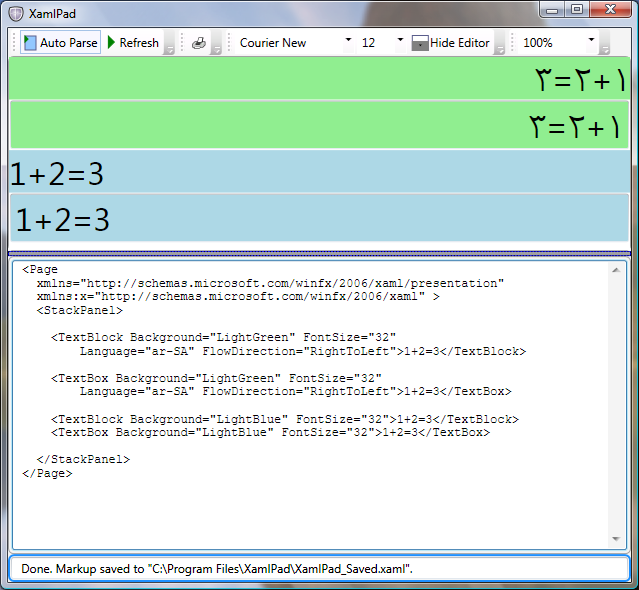
在此示例中,FlowDirection 很重要,因为将 FlowDirection 改为设置成 LeftToRight 时会产生欧洲数字。 以下各节介绍如何在整个文档内统一显示数字。 如果未在阿拉伯语版 Windows 上运行此示例,所有数字都将显示为欧洲数字。
定义替换规则
在实际的应用程序中,可能需要以编程方式设置语言。 例如,希望将 xml:lang 属性设置为系统 UI 所用的相同属性,或根据应用程序具体状态更改语言。
如果希望根据应用程序状态进行更改,请利用 Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF) 提供的其他功能。
首先,设置应用程序组件的 NumberSubstitution.CultureSource="Text"。 使用此设置可确保对于将“User”用作默认值的文本元素(如 TextBlock),设置不会来自 UI。
例如:
<TextBlock
Name="text1" NumberSubstitution.CultureSource="Text">
1234+5679=6913
</TextBlock>
例如,在对应的 C# 代码中,将 Language 属性设置为 "ar-SA"。
text1.Language = System.Windows.Markup.XmlLanguage.GetLanguage("ar-SA");
如果需要将 Language 属性设置为当前用户的 UI 语言,请使用下面的代码。
text1.Language = System.Windows.Markup.XmlLanguage.GetLanguage(System.Globalization.CultureInfo.CurrentUICulture.IetfLanguageTag);
CultureInfo.CurrentCulture 表示当前线程在运行时所用的当前区域性。
最后的 XAML 示例应与下面的示例类似。
<Page x:Class="WindowsApplication.Window1"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
Title="Code Sample" Height="300" Width="300"
>
<StackPanel>
<TextBlock Language="ar-SA"
FlowDirection="RightToLeft">عربى: 1+2=3
</TextBlock>
<TextBlock Language="ar-SA"
FlowDirection="RightToLeft"
NumberSubstitution.Substitution="European">عربى: 1+2=3
</TextBlock>
</StackPanel>
</Page>
最后的 C# 示例应与下面的示例类似。
namespace BidiTest
{
public partial class Window1 : Window
{
public Window1()
{
InitializeComponent();
string currentLanguage =
System.Globalization.CultureInfo.CurrentCulture.IetfLanguageTag;
text1.Language = System.Windows.Markup.XmlLanguage.GetLanguage(currentLanguage);
if (currentLanguage.ToLower().StartsWith("ar"))
{
text1.FlowDirection = FlowDirection.RightToLeft;
}
else
{
text1.FlowDirection = FlowDirection.LeftToRight;
}
}
}
}
下图显示了任一编程语言的窗口外观,该窗口显示阿拉伯语数字:

使用 Substitution 属性
Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF) 中的数字替换方式同时取决于文本元素的语言及其 FlowDirection。 如果 FlowDirection 为从左到右,则会呈现欧洲数字。 但是,如果数字的前面为阿拉伯语文本或者具有设置为“ar”的语言,且 FlowDirection 为 RightToLeft,则会改为呈现阿拉伯语数字。
但在某些情况下,建议创建统一的应用程序,例如适用于所有用户的欧洲数字。 或者在具有特定 Style 的 Table 单元格中呈现阿拉伯语数字。 执行此操作的一种简单方法是使用 Substitution 属性。
在下面的示例中,第一个 TextBlock 未设置 Substitution 属性,因此算法将按预期方式显示阿拉伯语数字。 但是,在第二个 TextBlock 中,替换设置为欧洲,替代了默认的阿拉伯语数字替换,此时将显示欧洲数字。
<Page x:Class="WindowsApplication.Window1"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
Title="Code Sample" Height="300" Width="300"
>
<StackPanel>
<TextBlock Language="ar-SA"
FlowDirection="RightToLeft">عربى: 1+2=3
</TextBlock>
<TextBlock Language="ar-SA"
FlowDirection="RightToLeft"
NumberSubstitution.Substitution="European">عربى: 1+2=3
</TextBlock>
</StackPanel>
</Page>
