Hello ComputerGladiator,
Thank you for posting here.
Here are the answers for your questions:
Q1: I have raised the domain level from Server 2003 to 2008 and when using Get-ADForest command the Forest Mode still shows as Windows2003Forest. This was raised to 2008 yesterday afternoon. Is it still propagating?
A1: As DSPatrick mentioned, the minimum requirement to add a Windows Server 2019 Domain Controller is a Windows Server 2008 forest functional level. The domain also has to use DFS-R as the engine to replicate SYSVOL.
According to the description, please check whether your domain function level is 2008 in ADUC (Active Directory Users and Computers) and whether the forest function level is 2003 in ADDT (Active Directory Domains and Trusts).
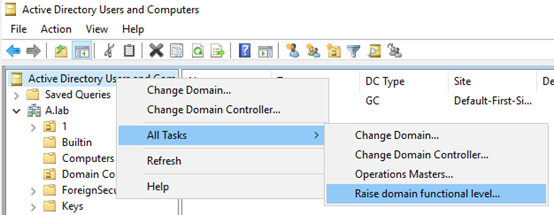
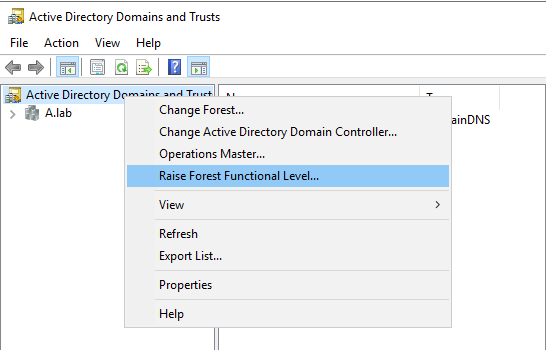
- If your forest function level is 2003 and your domain function level is 2008, we should raise forest function level from 2003 to 2008 first.
- Then check SYSVOL replication type.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\DFSR\Parameters\SysVols\Migrating Sysvols\LocalState registry subkey. If this registry subkey exists and its value is set to 3 (ELIMINATED), DFSR is being used. If the subkey does not exist, or if it has a different value, FRS is being used.
Before we do any change in existing AD domain environment, we had better do:
- Check if AD environment is healthy. Check all DCs in this domain is working fine by running Dcdiag /v. Check if AD replication works properly by running repadmin /showrepl and repadmin /replsum.
- Back up all domain controllers.
- Check both SYSVOL folder and Netlogon folder are shared by running net share on each DC.
- Check we can update gpupdate /force on each DC successfully.
After we ensure forest function level is 2008 and SYSVOL replication is DFSR replication type, we can add one Windows server 2019 to the existing domain and promote is as a domain controller.
Q2: I understand that the 2019 server schema needs to be upgraded. Is there a set of steps in achieving this?
A2: For upgrading domain controller from lower operating system to higher operating system, there are two methods:
Method 1 Perform an in-place upgrade of an existing domain controller to higher operating system, in this way, we will need to run adprep /forestprep and adprep /domainprep manually.
Method 2 Promote a new higher operating system of Windows server in the existing domain, you do not need to run these manually.
However, we recommend we add new domain controller to the existing domain.
Adprep and Domainprep
If you are doing an in-place upgrade of an existing domain controller to the Windows Server 2016 operating system, you will need to run adprep /forestprep and adprep /domainprep manually. Adprep /forestprep needs to be run only once in the forest. Adprep /domainprep needs to be run once in each domain in which you have domain controllers that you are upgrading to Windows Server 2016.
If you are promoting a new Windows Server 2016 server you do not need to run these manually. These are integrated into the PowerShell and Server Manager experiences.
We can follow steps below to upgrade Window server 2008 R2 DC to Window server 2019 DC after you raise forest functional level to 2008 successfully:
- Check if AD environment is healthy. Check all DCs in this domain is working fine by running Dcdiag /v. Check if AD replication works properly by running repadmin /showrepl and repadmin /replsum.
- Add the new Window server 2019 to this existing domain.
- Add AD DS and DNS roles and promote this Windows server 2019 as a DC (as a GC).
- Check if AD environment is healthy again based on step 1.
- If step 1-step 4 is OK without any error. We can transfer FSMO roles to new 2019 DC if needed.
- Based on “The 2008 R2 DC has DHCP on it as well.”, migrate DHCP to new server if needed.
- Demote Windows server 2008 R2 after migrating AD DS and DHCP role if needed. Before we demote 2008 R2 DC, we should check:
If the removed DC was a DNS server, update the DNS client configuration on all member workstations, member servers, and other DCs that might have used this DNS server for name resolution. If it is required, modify the DHCP scope to reflect the removal of the DNS server.
If the removed DC was a DNS server, update the Forwarder settings and the Delegation settings on any other DNS servers that might have pointed to the removed DC for name resolution.
References:
Forest and Domain Functional Levels
https://video2.skills-academy.com/en-us/windows-server/identity/ad-ds/active-directory-functional-levels
Upgrade Domain Controllers to Windows Server 2016
https://video2.skills-academy.com/en-us/windows-server/identity/ad-ds/deploy/upgrade-domain-controllers
How to Migrate DHCP from Windows Server 2008 to 2012/2016
https://brycematheson.io/how-to-migrate-dhcp-from-windows-server-2008-to-2012-2016/
How to Migrate DHCP from Windows Server 2012 R2 to Server 2016
https://www.faqforge.com/windows-server-2016/migrate-dhcp-windows-server-2012-r2-server-2016/
Hope the information above is helpful. If anything is unclear, please feel free to let us know.
Best Regards,
Stephanie Yu