Integrate Microsoft Defender for Cloud with Azure VMware Solution
Microsoft Defender for Cloud provides advanced threat protection across your Azure VMware Solution and on-premises virtual machines (VMs). It assesses the vulnerability of Azure VMware Solution VMs and raises alerts as needed. These security alerts can be forwarded to Azure Monitor for resolution. You can define security policies in Microsoft Defender for Cloud. For more information, see Working with security policies.
Microsoft Defender for Cloud offers many features, including:
- File integrity monitoring
- Fileless attack detection
- Operating system patch assessment
- Security misconfigurations assessment
- Endpoint protection assessment
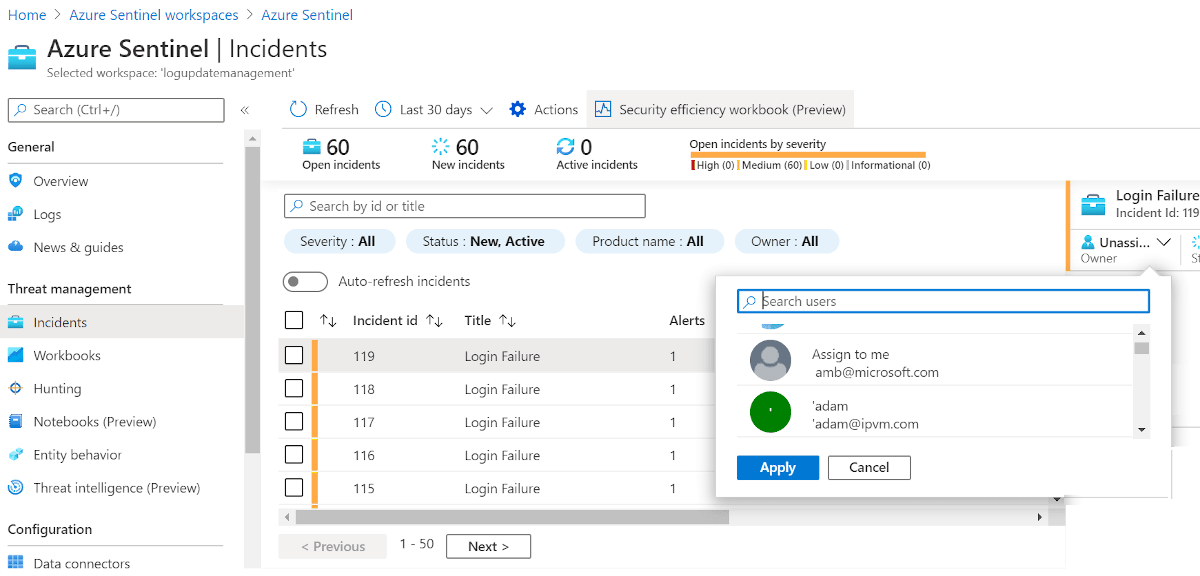
The diagram shows the integrated monitoring architecture of integrated security for Azure VMware Solution VMs.
Log Analytics agent collects log data from Azure, Azure VMware Solution, and on-premises VMs. The log data is sent to Azure Monitor Logs and stored in a Log Analytics Workspace. Each workspace has its own data repository and configuration to store data. Once the logs are collected, Microsoft Defender for Cloud assesses the vulnerability status of Azure VMware Solution VMs and raises an alert for any critical vulnerability. Once assessed, Microsoft Defender for Cloud forwards the vulnerability status to Microsoft Sentinel to create an incident and map with other threats. Microsoft Defender for Cloud is connected to Microsoft Sentinel using Microsoft Defender for Cloud Connector.
Create a Log Analytics workspace to collect data from various sources.
Enable Microsoft Defender for Cloud in your subscription.
Note
Microsoft Defender for Cloud is a pre-configured tool that doesn't require deployment, but you'll need to enable it.
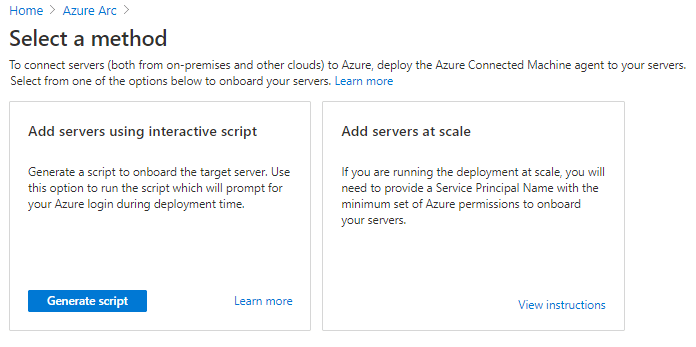
In the Azure portal, search on Azure Arc and select it.
Under Resources, select Servers and then +Add.
Select Generate script.
On the Prerequisites tab, select Next.
On the Resource details tab, fill in the following details and then select Next. Tags:
- Subscription
- Resource group
- Region
- Operating system
- Proxy Server details
On the Tags tab, select Next.
On the Download and run script tab, select Download.
Specify your operating system and run the script on your Azure VMware Solution VM.
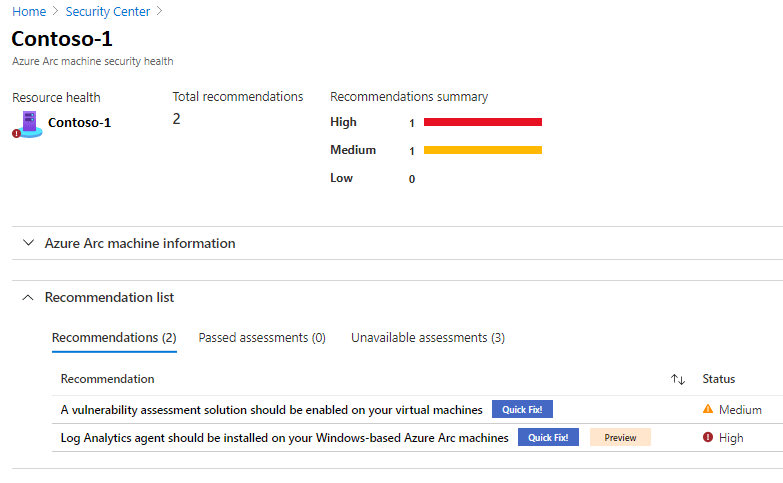
Recommendations and assessments provide you with the security health details of your resource.
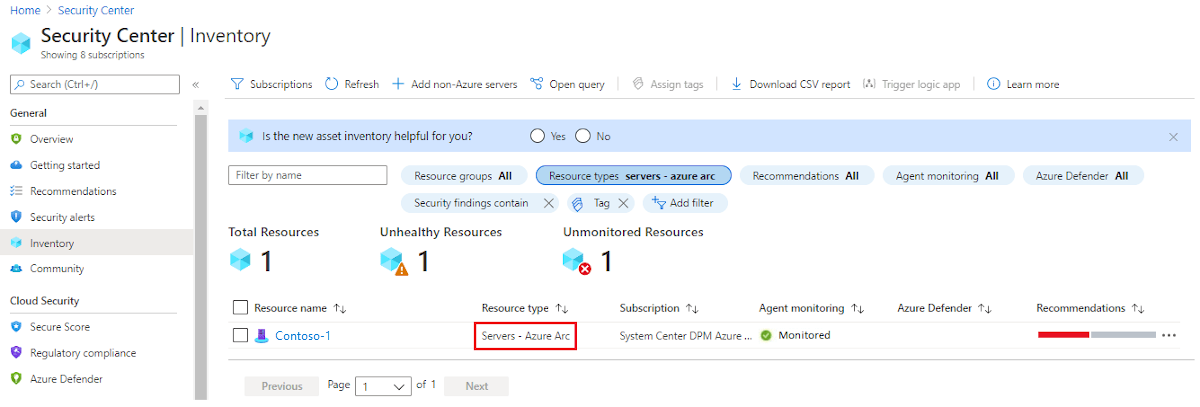
In Microsoft Defender for Cloud, select Inventory from the left pane.
For Resource type, select Servers - Azure Arc.
Select the name of your resource. A page opens showing the security health details of your resource.
Under Recommendation list, select the Recommendations, Passed assessments, and Unavailable assessments tabs to view these details.
Microsoft Sentinel provides security analytics, alert detection, and automated threat response across an environment. It's a cloud-native, security information event management (SIEM) solution built on top of a Log Analytics workspace.
Since Microsoft Sentinel is built on top of a Log Analytics workspace, you only need to select the workspace you want to use.
In the Azure portal, search for Microsoft Sentinel, and select it.
On the Microsoft Sentinel workspaces page, select +Add.
Select the Log Analytics workspace and select Add.
On the Microsoft Sentinel workspaces page, select the configured workspace.
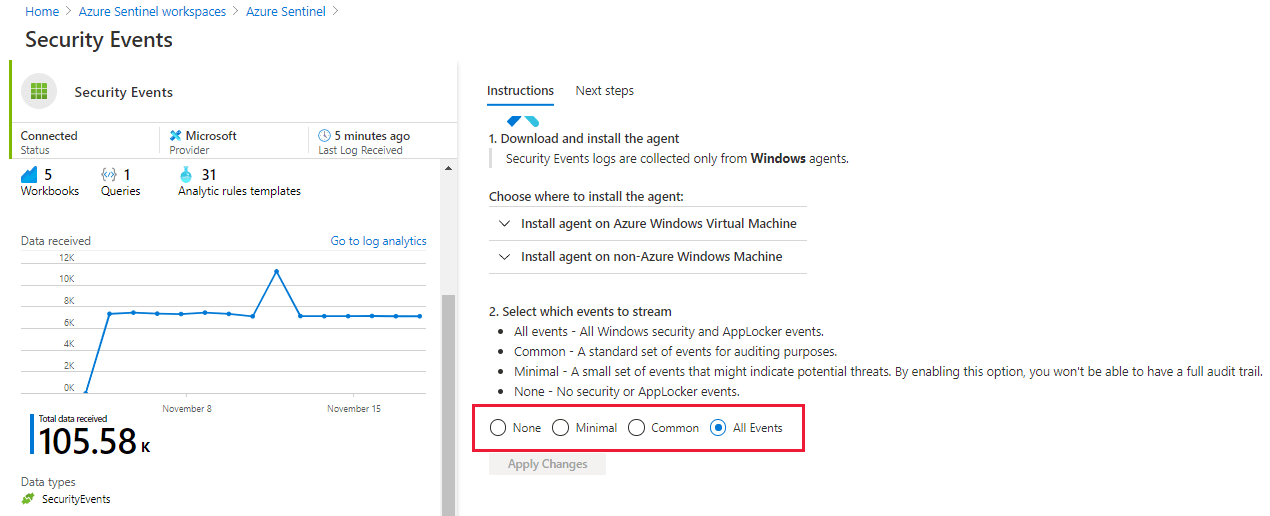
Under Configuration, select Data connectors.
Under the Connector Name column, select Security Events from the list, then select Open connector page.
On the connector page, select the events you wish to stream, then select Apply Changes.
On the Microsoft Sentinel workspace page, select the configured workspace.
Under Configuration, select Data connectors.
Select Microsoft Defender for Cloud from the list, then select Open connector page.
Select Connect to connect the Microsoft Defender for Cloud with Microsoft Sentinel.
Enable Create incident to generate an incident for Microsoft Defender for Cloud.
After connecting data sources to Microsoft Sentinel, you can create rules to generate alerts for detected threats. In the following example, we create a rule for attempts to sign in to Windows server with the wrong password.
On the Microsoft Sentinel overview page, under Configurations, select Analytics.
Under Configurations, select Analytics.
Select +Create and on the drop-down, select Scheduled query rule.
On the General tab, enter the required information and then select Next: Set rule logic.
- Name
- Description
- Tactics
- Severity
- Status
On the Set rule logic tab, enter the required information, then select Next.
Rule query (here showing our example query)
SecurityEvent |where Activity startswith '4625' |summarize count () by IpAddress,Computer |where count_ > 3Map entities
Query scheduling
Alert threshold
Event grouping
Suppression
On the Incident settings tab, enable Create incidents from alerts triggered by this analytics rule and select Next: Automated response.
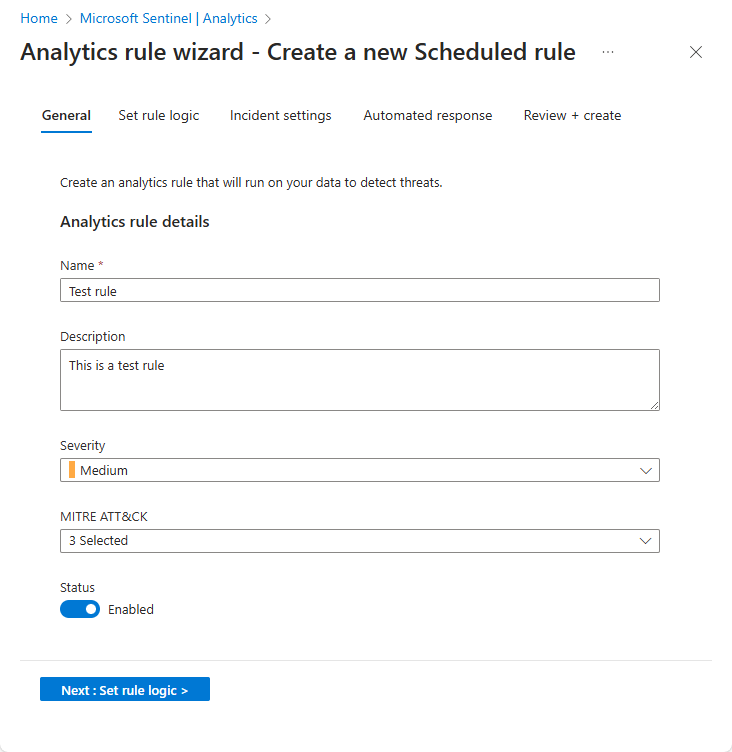
Select Next: Review.
On the Review and create tab, review the information, and select Create.
Tip
After the third failed attempt to sign in to Windows server, the created rule triggers an incident for every unsuccessful attempt.
You can view generated incidents with Microsoft Sentinel. You can also assign incidents and close them once they're resolved, all from within Microsoft Sentinel.
Go to the Microsoft Sentinel overview page.
Under Threat Management, select Incidents.
Select an incident and then assign it to a team for resolution.
Tip
After resolving the issue, you can close it.
You can create queries or use the available predefined query in Microsoft Sentinel to identify threats in your environment. The following steps run a predefined query.
On the Microsoft Sentinel overview page, under Threat management, select Hunting. A list of predefined queries is displayed.
Tip
You can also create a new query by selecting New Query.
Select a query and then select Run Query.
Select View Results to check the results.
Now that you covered how to protect your Azure VMware Solution VMs, you can learn more about: