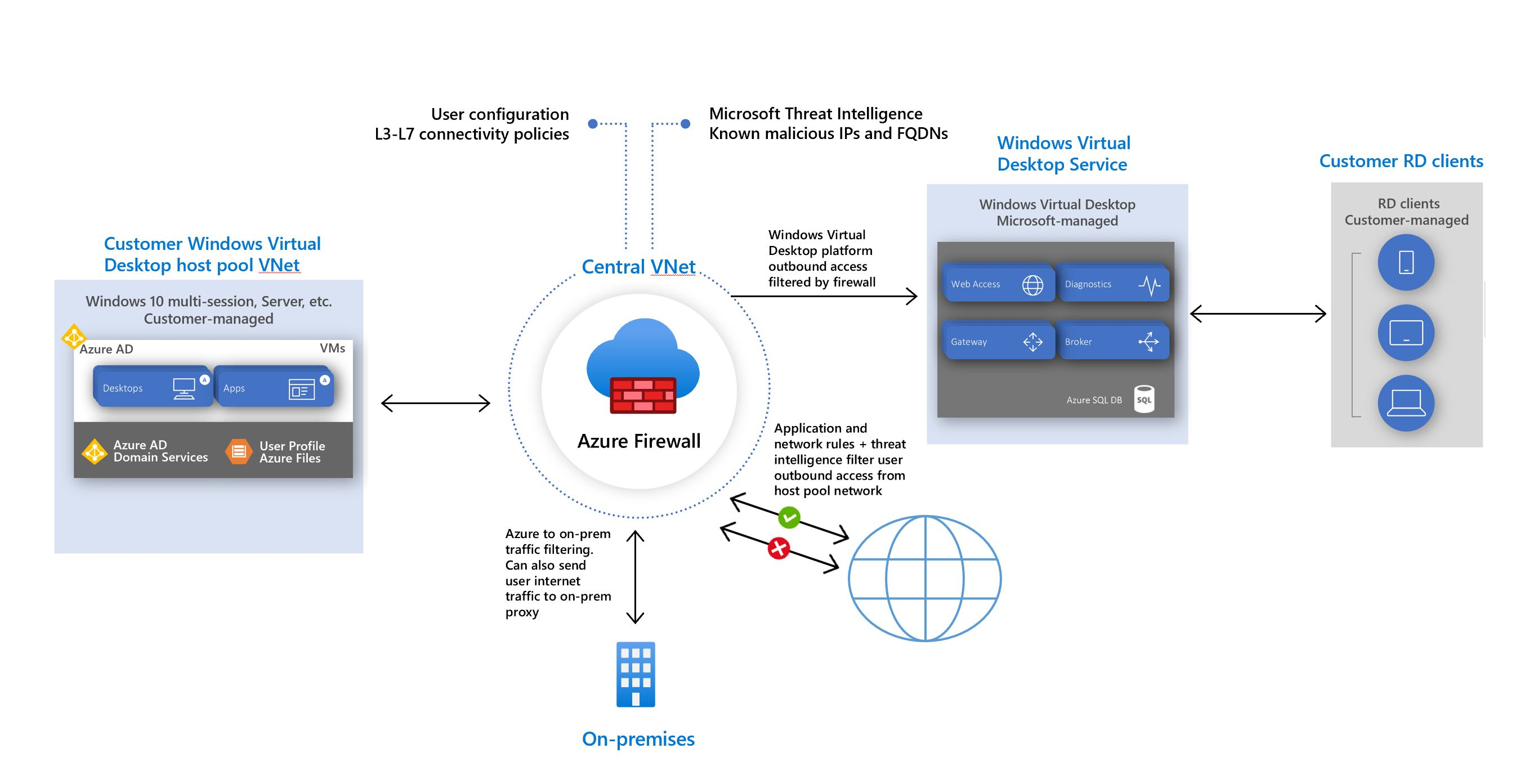
Use Azure Firewall to protect Azure Virtual Desktop deployments
Azure Virtual Desktop is a cloud virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) service that runs on Azure. When an end user connects to Azure Virtual Desktop, their session comes from a session host in a host pool. A host pool is a collection of Azure virtual machines that register to Azure Virtual Desktop as session hosts. These virtual machines run in your virtual network and are subject to the virtual network security controls. They need outbound internet access to the Azure Virtual Desktop service to operate properly and might also need outbound internet access for end users. Azure Firewall can help you lock down your environment and filter outbound traffic.
Follow the guidelines in this article to provide extra protection for your Azure Virtual Desktop host pool using Azure Firewall.
- A deployed Azure Virtual Desktop environment and host pool. For more information, see Deploy Azure Virtual Desktop.
- An Azure Firewall deployed with at least one Firewall Manager Policy.
- DNS and DNS Proxy enabled in the Firewall Policy to use FQDN in Network Rules.
To learn more about Azure Virtual Desktop terminology, see Azure Virtual Desktop terminology.
The Azure virtual machines you create for Azure Virtual Desktop must have access to several Fully Qualified Domain Names (FQDNs) to function properly. Azure Firewall uses the Azure Virtual Desktop FQDN tag WindowsVirtualDesktop to simplify this configuration. You'll need to create an Azure Firewall Policy and create Rule Collections for Network Rules and Applications Rules. Give the Rule Collection a priority and an allow or deny action.
You need to create rules for each of the required FQDNs and endpoints. The list is available at Required FQDNs and endpoints for Azure Virtual Desktop. In order to identify a specific host pool as Source, you can create an IP Group with each session host to represent it.
Important
We recommend that you don't use TLS inspection with Azure Virtual Desktop. For more information, see the proxy server guidelines.
All the mandatory and optional rules mentioned above can be easily deployed in a single Azure Firewall Policy using the template published at https://github.com/Azure/RDS-Templates/tree/master/AzureFirewallPolicyForAVD. Before deploying into production, we recommended reviewing all the network and application rules defined, ensure alignment with Azure Virtual Desktop official documentation and security requirements.
Depending on your organization needs, you might want to enable secure outbound internet access for your end users. If the list of allowed destinations is well-defined (for example, for Microsoft 365 access), you can use Azure Firewall application and network rules to configure the required access. This routes end-user traffic directly to the internet for best performance. If you need to allow network connectivity for Windows 365 or Intune, see Network requirements for Windows 365 and Network endpoints for Intune.
If you want to filter outbound user internet traffic by using an existing on-premises secure web gateway, you can configure web browsers or other applications running on the Azure Virtual Desktop host pool with an explicit proxy configuration. For example, see How to use Microsoft Edge command-line options to configure proxy settings. These proxy settings only influence your end-user internet access, allowing the Azure Virtual Desktop platform outbound traffic directly via Azure Firewall.
Admins can allow or deny user access to different website categories. Add a rule to your Application Collection from your specific IP address to web categories you want to allow or deny. Review all the web categories.
- Learn more about Azure Virtual Desktop: What is Azure Virtual Desktop?