High availability for SAP NetWeaver on Azure VMs on Red Hat Enterprise Linux for SAP applications multi-SID
This article describes how to deploy multiple SAP NetWeaver highly available systems (multi-SID) in a two node cluster on Azure VMs with Red Hat Enterprise Linux for SAP applications.
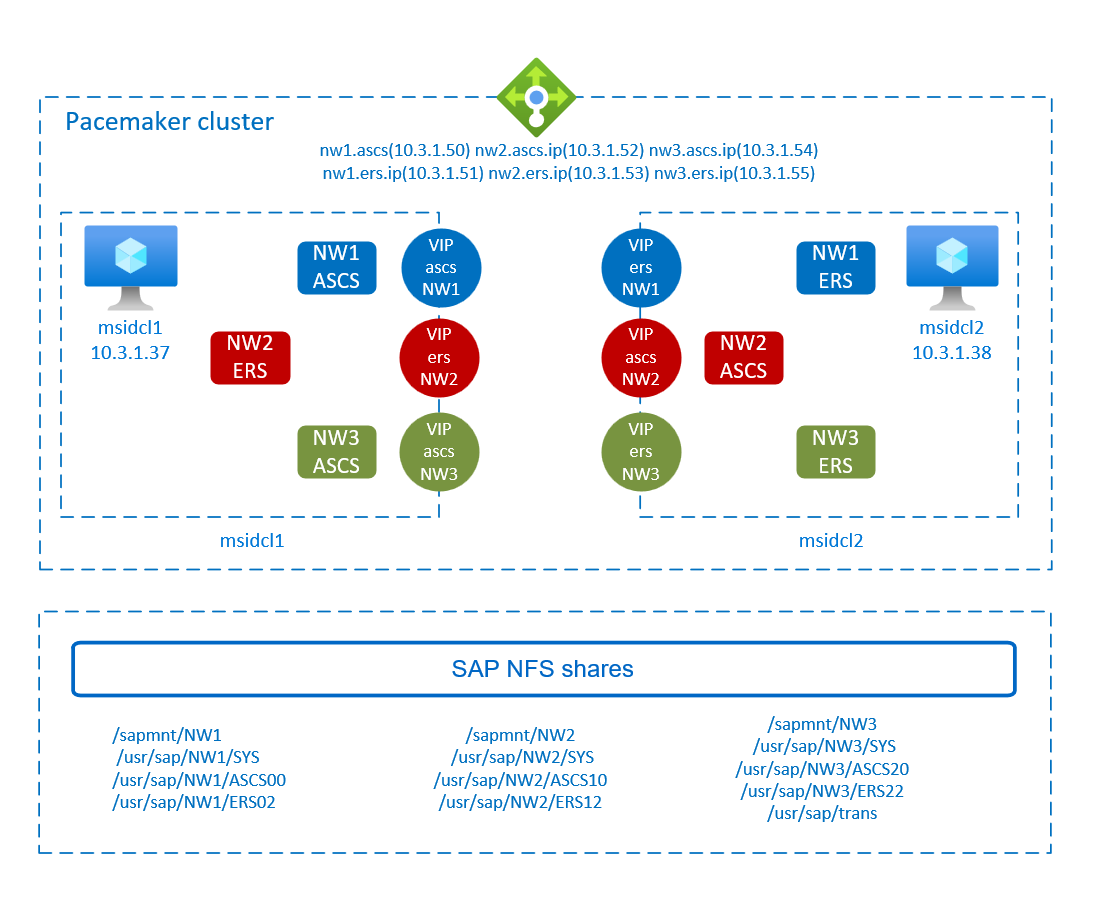
In the example configurations, three SAP NetWeaver 7.50 systems are deployed in a single, two node high availability cluster. The SAP systems SIDs are:
NW1: ASCS instance number 00 and virtual host namemsnw1ascs. ERS instance number 02 and virtual host namemsnw1ers.NW2: ASCS instance number 10 and virtual hostnamemsnw2ascs. ERS instance number 12 and virtual host namemsnw2ers.NW3: ASCS instance number 20 and virtual hostnamemsnw3ascs. ERS instance number 22 and virtual host namemsnw3ers.
The article doesn't cover the database layer and the deployment of the SAP NFS shares.
The examples in this article use the Azure NetApp Files volume sapMSID for the NFS shares, assuming that the volume is already deployed. The examples assume that the Azure NetApp Files volume is deployed with NFSv3 protocol. They use the following file paths for the cluster resources for the ASCS and ERS instances of SAP systems NW1, NW2, and NW3:
- volume sapMSID (nfs://10.42.0.4/sapmntNW1)
- volume sapMSID (nfs://10.42.0.4/usrsapNW1ascs)
- volume sapMSID (nfs://10.42.0.4/usrsapNW1sys)
- volume sapMSID (nfs://10.42.0.4/usrsapNW1ers)
- volume sapMSID (nfs://10.42.0.4/sapmntNW2)
- volume sapMSID (nfs://10.42.0.4/usrsapNW2ascs)
- volume sapMSID (nfs://10.42.0.4/usrsapNW2sys)
- volume sapMSID (nfs://10.42.0.4/usrsapNW2ers)
- volume sapMSID (nfs://10.42.0.4/sapmntNW3)
- volume sapMSID (nfs://10.42.0.4/usrsapNW3ascs)
- volume sapMSID (nfs://10.42.0.4/usrsapNW3sys)
- volume sapMSID (nfs://10.42.0.4/usrsapNW3ers)
Before you begin, refer to the following SAP Notes and papers:
- SAP Note 1928533, which has:
- List of Azure VM sizes that are supported for the deployment of SAP software.
- Important capacity information for Azure VM sizes.
- Supported SAP software, and operating system (OS) and database combinations.
- Required SAP kernel version for Windows and Linux on Microsoft Azure.
- Azure NetApp Files documentation.
- SAP Note 2015553 has prerequisites for SAP-supported SAP software deployments in Azure.
- SAP Note 2002167 has recommended OS settings for Red Hat Enterprise Linux.
- SAP Note 2009879 has SAP HANA Guidelines for Red Hat Enterprise Linux.
- SAP Note 2178632 has detailed information about all monitoring metrics reported for SAP in Azure.
- SAP Note 2191498 has the required SAP Host Agent version for Linux in Azure.
- SAP Note 2243692 has information about SAP licensing on Linux in Azure.
- SAP Note 1999351 has more troubleshooting information for the Azure Enhanced Monitoring Extension for SAP.
- SAP Community WIKI has all required SAP Notes for Linux.
- Azure Virtual Machines planning and implementation for SAP on Linux.
- Azure Virtual Machines deployment for SAP on Linux.
- Azure Virtual Machines DBMS deployment for SAP on Linux.
- SAP Netweaver in pacemaker cluster.
- General RHEL documentation:
- Azure-specific RHEL documentation:
- NetApp SAP Applications on Microsoft Azure using Azure NetApp Files
The virtual machines that participate in the cluster must be sized to be able to run all resources in case failover occurs. Each SAP SID can fail over independently from each other in the multi-SID high availability cluster.
To achieve high availability, SAP NetWeaver requires highly available shares. This article shows examples with the SAP shares deployed on Azure NetApp Files NFS volumes. You could instead host the shares on highly available GlusterFS cluster, which can be used by multiple SAP systems.
Important
The support for multi-SID clustering of SAP ASCS/ERS with Red Hat Linux as guest operating system in Azure VMs is limited to five SAP SIDs on the same cluster. Each new SID increases the complexity. A mix of SAP Enqueue Replication Server 1 and Enqueue Replication Server 2 on the same cluster is not supported. Multi-SID clustering describes the installation of multiple SAP ASCS/ERS instances with different SIDs in one Pacemaker cluster. Currently multi-SID clustering is only supported for ASCS/ERS.
Tip
The multi-SID clustering of SAP ASCS/ERS is a solution with higher complexity. It is more complex to implement. It also involves higher administrative effort, when executing maintenance activities, like OS patching. Before you start the actual implementation, take time to carefully plan out the deployment and all involved components like VMs, NFS mounts, VIPs, load balancer configurations and so on.
SAP NetWeaver ASCS, SAP NetWeaver SCS, and SAP NetWeaver ERS use virtual hostname and virtual IP addresses. On Azure, a load balancer is required to use a virtual IP address. We recommend using Standard load balancer.
- Frontend IP addresses for ASCS: 10.3.1.50 (NW1), 10.3.1.52 (NW2), and 10.3.1.54 (NW3)
- Frontend IP addresses for ERS: 10.3.1.51 (NW1), 10.3.1.53 (NW2), and 10.3.1.55 (NW3)
- Probe port 62000 for NW1 ASCS, 62010 for NW2 ASCS, and 62020 for NW3 ASCS
- Probe port 62102 for NW1 ASCS, 62112 for NW2 ASCS, and 62122 for NW3 ASCS
Note
When VMs without public IP addresses are placed in the backend pool of internal (no public IP address) Standard Azure load balancer, there is no outbound internet connectivity, unless additional configuration is performed to allow routing to public end points. For details on how to achieve outbound connectivity see Public endpoint connectivity for Virtual Machines using Azure Standard Load Balancer in SAP high-availability scenarios.
Important
Do not enable TCP timestamps on Azure VMs placed behind Azure Load Balancer. Enabling TCP timestamps causes the health probes to fail. Set parameter net.ipv4.tcp_timestamps to 0. For more information, see Load Balancer health probes.
SAP NetWeaver requires shared storage for the transport, profile directory, and so on. For highly available SAP system, it's important to have highly available shares. You need to decide on the architecture for your SAP shares. One option is to deploy the shares on Azure NetApp Files NFS volumes. With Azure NetApp Files, you get built-in high availability for the SAP NFS shares.
Another option is to build GlusterFS on Azure VMs on Red Hat Enterprise Linux for SAP NetWeaver, which can be shared between multiple SAP systems.
After you decide on the architecture for the SAP shares, deploy the first SAP system in the cluster, following the corresponding documentation.
- If you use Azure NetApp Files NFS volumes, follow Azure VMs high availability for SAP NetWeaver on Red Hat Enterprise Linux with Azure NetApp Files for SAP applications.
- If you use GlusterFS cluster, follow GlusterFS on Azure VMs on Red Hat Enterprise Linux for SAP NetWeaver.
These articles guide you through the steps to prepare the necessary infrastructure, build the cluster, prepare the OS for running the SAP application.
Tip
Always test the failover functionality of the cluster after the first system is deployed, before adding the additional SAP SIDs to the cluster. That way, you know that the cluster functionality works, before adding the complexity of additional SAP systems to the cluster.
This example assumes that system NW1 was already deployed in the cluster. This example shows how to deploy SAP systems NW2 and NW3 in the cluster.
The following items are prefixed with:
- [A] Applicable to all nodes
- [1] Only applicable to node 1
- [2] Only applicable to node 2
Important
Before following the instructions to deploy additional SAP systems in the cluster, deploy the first SAP system in the cluster. There are steps which are only necessary during the first system deployment.
This article assumes that:
- The Pacemaker cluster is already configured and running.
- At least one SAP system (ASCS / ERS instance) is already deployed and is running in the cluster.
- The cluster failover functionality has been tested.
- The NFS shares for all SAP systems are deployed.
Add configuration for the newly deployed system (that is,
NW2andNW3) to the existing Azure Load Balancer, following the instructions Deploy Azure Load Balancer manually via Azure portal. Adjust the IP addresses, health probe ports, and load-balancing rules for your configuration.[A] Set up name resolution for the more SAP systems. You can either use DNS server or modify /etc/hosts on all nodes. This example shows how to use the /etc/hosts file. Adapt the IP addresses and the host names to your environment.
sudo vi /etc/hosts # IP address of the load balancer frontend configuration for NW2 ASCS 10.3.1.52 msnw2ascs # IP address of the load balancer frontend configuration for NW3 ASCS 10.3.1.54 msnw3ascs # IP address of the load balancer frontend configuration for NW2 ERS 10.3.1.53 msnw2ers # IP address of the load balancer frontend configuration for NW3 ERS 10.3.1.55 msnw3ers[A] Create the shared directories for the
NW2andNW3SAP systems to deploy to the cluster.sudo mkdir -p /sapmnt/NW2 sudo mkdir -p /usr/sap/NW2/SYS sudo mkdir -p /usr/sap/NW2/ASCS10 sudo mkdir -p /usr/sap/NW2/ERS12 sudo mkdir -p /sapmnt/NW3 sudo mkdir -p /usr/sap/NW3/SYS sudo mkdir -p /usr/sap/NW3/ASCS20 sudo mkdir -p /usr/sap/NW3/ERS22 sudo chattr +i /sapmnt/NW2 sudo chattr +i /usr/sap/NW2/SYS sudo chattr +i /usr/sap/NW2/ASCS10 sudo chattr +i /usr/sap/NW2/ERS12 sudo chattr +i /sapmnt/NW3 sudo chattr +i /usr/sap/NW3/SYS sudo chattr +i /usr/sap/NW3/ASCS20 sudo chattr +i /usr/sap/NW3/ERS22[A] Add the mount entries for the /sapmnt/SID and /usr/sap/SID/SYS file systems for the other SAP systems that you're deploying to the cluster. In this example, it's
NW2andNW3.Update file
/etc/fstabwith the file systems for the other SAP systems that you're deploying to the cluster.- If using Azure NetApp Files, follow the instructions in Azure VMs high availability for SAP NW on RHEL with Azure NetApp Files.
- If using GlusterFS cluster, follow the instructions in Azure VMs high availability for SAP NW on RHEL.
Create the virtual IP and health probe cluster resources for the ASCS instances of the other SAP systems you're deploying to the cluster. This example uses
NW2andNW3ASCS, using NFS on Azure NetApp Files volumes with NFSv3 protocol.sudo pcs resource create fs_NW2_ASCS Filesystem device='10.42.0.4:/sapMSIDR/usrsapNW2ascs' \ directory='/usr/sap/NW2/ASCS10' fstype='nfs' force_unmount=safe \ op start interval=0 timeout=60 op stop interval=0 timeout=120 op monitor interval=200 timeout=40 \ --group g-NW2_ASCS sudo pcs resource create vip_NW2_ASCS IPaddr2 \ ip=10.3.1.52 \ --group g-NW2_ASCS sudo pcs resource create nc_NW2_ASCS azure-lb port=62010 \ --group g-NW2_ASCS sudo pcs resource create fs_NW3_ASCS Filesystem device='10.42.0.4:/sapMSIDR/usrsapNW3ascs' \ directory='/usr/sap/NW3/ASCS20' fstype='nfs' force_unmount=safe \ op start interval=0 timeout=60 op stop interval=0 timeout=120 op monitor interval=200 timeout=40 \ --group g-NW3_ASCS sudo pcs resource create vip_NW3_ASCS IPaddr2 \ ip=10.3.1.54 \ --group g-NW3_ASCS sudo pcs resource create nc_NW3_ASCS azure-lb port=62020 \ --group g-NW3_ASCSMake sure the cluster status is ok and that all resources are started. It's not important on which node the resources are running.
[1] Install SAP NetWeaver ASCS.
Install SAP NetWeaver ASCS as root, using a virtual hostname that maps to the IP address of the load balancer frontend configuration for the ASCS. For example, for system
NW2, the virtual hostname ismsnw2ascs,10.3.1.52, and the instance number that you used for the probe of the load balancer, for example10. For systemNW3, the virtual hostname ismsnw3ascs,10.3.1.54, and the instance number that you used for the probe of the load balancer, for example20. Note down on which cluster node you installed ASCS for each SAP SID.You can use the
sapinstparameterSAPINST_REMOTE_ACCESS_USERto allow a non-root user to connect to sapinst. You can use parameterSAPINST_USE_HOSTNAMEto install SAP, using virtual host name.# Allow access to SWPM. This rule is not permanent. If you reboot the machine, you have to run the command again sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=4237/tcp sudo swpm/sapinst SAPINST_REMOTE_ACCESS_USER=sapadmin SAPINST_USE_HOSTNAME=virtual_hostnameIf the installation fails to create a subfolder in /usr/sap/<SID>/ASCS<Instance#>, try setting the owner to <sid>adm and group to sapsys of the ASCS<Instance#> and retry.
[1] Create a virtual IP and health-probe cluster resources for the ERS instance of the other SAP system you're deploying to the cluster. This example is for
NW2andNW3ERS, using NFS on Azure NetApp Files volumes with NFSv3 protocol.sudo pcs resource create fs_NW2_AERS Filesystem device='10.42.0.4:/sapMSIDR/usrsapNW2ers' \ directory='/usr/sap/NW2/ERS12' fstype='nfs' force_unmount=safe \ op start interval=0 timeout=60 op stop interval=0 timeout=120 op monitor interval=200 timeout=40 \ --group g-NW2_AERS sudo pcs resource create vip_NW2_AERS IPaddr2 \ ip=10.3.1.53 \ --group g-NW2_AERS sudo pcs resource create nc_NW2_AERS azure-lb port=62112 \ --group g-NW2_AERS sudo pcs resource create fs_NW3_AERS Filesystem device='10.42.0.4:/sapMSIDR/usrsapNW3ers' \ directory='/usr/sap/NW3/ERS22' fstype='nfs' force_unmount=safe \ op start interval=0 timeout=60 op stop interval=0 timeout=120 op monitor interval=200 timeout=40 \ --group g-NW3_AERS sudo pcs resource create vip_NW3_AERS IPaddr2 \ ip=10.3.1.55 \ --group g-NW3_AERS sudo pcs resource create nc_NW3_AERS azure-lb port=62122 \ --group g-NW3_AERSMake sure the cluster status is ok and that all resources are started.
Next, make sure that the resources of the newly created ERS group are running on the cluster node, opposite to the cluster node where the ASCS instance for the same SAP system was installed. For example, if NW2 ASCS was installed on
rhelmsscl1, then make sure the NW2 ERS group is running onrhelmsscl2. You can migrate the NW2 ERS group torhelmsscl2by running the following command for one of the cluster resources in the group:pcs resource move fs_NW2_AERS rhelmsscl2[2] Install SAP NetWeaver ERS.
Install SAP NetWeaver ERS as root on the other node, using a virtual hostname that maps to the IP address of the load balancer frontend configuration for the ERS. For example, for system
NW2, the virtual host name ismsnw2ers,10.3.1.53, and the instance number that you used for the probe of the load balancer, for example12. For systemNW3, the virtual host namemsnw3ers,10.3.1.55, and the instance number that you used for the probe of the load balancer, for example22.You can use the
sapinstparameterSAPINST_REMOTE_ACCESS_USERto allow a non-root user to connect to sapinst. You can use parameterSAPINST_USE_HOSTNAMEto install SAP, using virtual host name.# Allow access to SWPM. This rule is not permanent. If you reboot the machine, you have to run the command again sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=4237/tcp sudo swpm/sapinst SAPINST_REMOTE_ACCESS_USER=sapadmin SAPINST_USE_HOSTNAME=virtual_hostnameNote
Use SWPM SP 20 PL 05 or higher. Lower versions do not set the permissions correctly and the installation fails.
If the installation fails to create a subfolder in /usr/sap/<NW2>/ERS<Instance#>, try setting the owner to <sid>adm and the group to sapsys of the ERS<Instance#> folder and retry.
If it was necessary for you to migrate the ERS group of the newly deployed SAP system to a different cluster node, don't forget to remove the location constraint for the ERS group. You can remove the constraint by running the following command. This example is given for SAP systems
NW2andNW3. Make sure to remove the temporary constraints for the same resource you used in the command to move the ERS cluster group.pcs resource clear fs_NW2_AERS pcs resource clear fs_NW3_AERS[1] Adapt the ASCS/SCS and ERS instance profiles for the newly installed SAP systems. The example shown below is for
NW2. You need to adapt the ASCS/SCS and ERS profiles for all SAP instances added to the cluster.ASCS/SCS profile
sudo vi /sapmnt/NW2/profile/NW2_ASCS10_msnw2ascs # Change the restart command to a start command #Restart_Program_01 = local $(_EN) pf=$(_PF) Start_Program_01 = local $(_EN) pf=$(_PF) # Add the keep alive parameter, if using ENSA1 enque/encni/set_so_keepalive = TRUEFor both ENSA1 and ENSA2, make sure that the
keepaliveOS parameters are set as described in SAP note 1410736.ERS profile
sudo vi /sapmnt/NW2/profile/NW2_ERS12_msnw2ers # Change the restart command to a start command #Restart_Program_00 = local $(_ER) pf=$(_PFL) NR=$(SCSID) Start_Program_00 = local $(_ER) pf=$(_PFL) NR=$(SCSID) # remove Autostart from ERS profile # Autostart = 1
[A] Update the /usr/sap/sapservices file.
To prevent the start of the instances by the sapinit startup script, all instances managed by Pacemaker must be commented out from /usr/sap/sapservices file. The example shown below is for SAP systems
NW2andNW3.# Depending on whether the SAP Startup framework is integrated with systemd, you may observe below entries on the node for ASCS instances. You should comment out the line(s). # LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/usr/sap/NW2/ASCS10/exe:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH; export LD_LIBRARY_PATH; /usr/sap/NW2/ASCS10/exe/sapstartsrv pf=/usr/sap/NW2/SYS/profile/NW2_ASCS10_msnw2ascs -D -u nw2adm # LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/usr/sap/NW3/ASCS20/exe:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH; export LD_LIBRARY_PATH; /usr/sap/NW3/ASCS20/exe/sapstartsrv pf=/usr/sap/NW3/SYS/profile/NW3_ASCS20_msnw3ascs -D -u nw3adm # systemctl --no-ask-password start SAPNW2_10 # sapstartsrv pf=/usr/sap/NW2/SYS/profile/NW2_ASCS10_msnw2ascs # systemctl --no-ask-password start SAPNW3_20 # sapstartsrv pf=/usr/sap/NW3/SYS/profile/NW3_ASCS20_msnw3ascs # Depending on whether the SAP Startup framework is integrated with systemd, you may observe below entries on the node for ERS instances. You should comment out the line(s). #LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/usr/sap/NW2/ERS12/exe:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH; export LD_LIBRARY_PATH; /usr/sap/NW2/ERS12/exe/sapstartsrv pf=/usr/sap/NW2/ERS12/profile/NW2_ERS12_msnw2ers -D -u nw2adm #LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/usr/sap/NW3/ERS22/exe:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH; export LD_LIBRARY_PATH; /usr/sap/NW3/ERS22/exe/sapstartsrv pf=/usr/sap/NW3/ERS22/profile/NW3_ERS22_msnw3ers -D -u nw3adm # systemctl --no-ask-password start SAPNW2_12 # sapstartsrv pf=/usr/sap/NW2/ERS12/profile/NW2_ERS12_msnw2ers # systemctl --no-ask-password start SAPNW3_22 # sapstartsrv pf=/usr/sap/NW3/ERS22/profile/NW3_ERS22_msnw3ersImportant
With the systemd based SAP Startup Framework, SAP instances can now be managed by systemd. The minimum required Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) version is RHEL 8 for SAP. As described in SAP Note 3115048, a fresh installation of a SAP kernel with integrated systemd based SAP Startup Framework support will always result in a systemd controlled SAP instance. After an SAP kernel upgrade of an existing SAP installation to a kernel which has systemd based SAP Startup Framework support, however, some manual steps have to be performed as documented in SAP Note 3115048 to convert the existing SAP startup environment to one which is systemd controlled.
When utilizing Red Hat HA services for SAP (cluster configuration) to manage SAP application server instances such as SAP ASCS and SAP ERS, additional modifications will be necessary to ensure compatibility between the SAPInstance resource agent and the new systemd-based SAP startup framework. So once the SAP application server instances has been installed or switched to a systemd enabled SAP Kernel as per SAP Note 3115048, the steps mentioned in Red Hat KBA 6884531 must be completed successfully on all cluster nodes.
[1] Create the SAP cluster resources for the newly installed SAP system.
Depending on whether you are running an ENSA1 or ENSA2 system, select respective tab to define the resources for SAP systems
NW2andNW3as follows. SAP introduced support for ENSA2, including replication, in SAP NetWeaver 7.52. Starting with ABAP Platform 1809, ENSA2 is installed by default. For ENSA2 support, see SAP Note 2630416 for enqueue server 2 support.If you use enqueue server 2 architecture (ENSA2), install resource agent resource-agents-sap-4.1.1-12.el7.x86_64 or newer and define the resources for SAP systems
NW2andNW3as follows:sudo pcs property set maintenance-mode=true sudo pcs resource create rsc_sap_NW2_ASCS10 SAPInstance \ InstanceName=NW2_ASCS10_msnw2ascs START_PROFILE="/sapmnt/NW2/profile/NW2_ASCS10_msnw2ascs" \ AUTOMATIC_RECOVER=false \ meta resource-stickiness=5000 migration-threshold=1 failure-timeout=60 \ op monitor interval=20 on-fail=restart timeout=60 \ op start interval=0 timeout=600 op stop interval=0 timeout=600 \ --group g-NW2_ASCS sudo pcs resource meta g-NW2_ASCS resource-stickiness=3000 sudo pcs resource create rsc_sap_NW2_ERS12 SAPInstance \ InstanceName=NW2_ERS12_msnw2ers START_PROFILE="/sapmnt/NW2/profile/NW2_ERS12_msnw2ers" \ AUTOMATIC_RECOVER=false IS_ERS=true \ op monitor interval=20 on-fail=restart timeout=60 op start interval=0 timeout=600 op stop interval=0 timeout=600 \ --group g-NW2_AERS sudo pcs constraint colocation add g-NW2_AERS with g-NW2_ASCS -5000 sudo pcs constraint location rsc_sap_NW2_ASCS10 rule score=2000 runs_ers_NW2 eq 1 sudo pcs constraint order start g-NW2_ASCS then stop g-NW2_AERS kind=Optional symmetrical=false sudo pcs resource create rsc_sap_NW3_ASCS20 SAPInstance \ InstanceName=NW3_ASCS20_msnw3ascs START_PROFILE="/sapmnt/NW3/profile/NW3_ASCS20_msnw3ascs" \ AUTOMATIC_RECOVER=false \ meta resource-stickiness=5000 migration-threshold=1 failure-timeout=60 \ op monitor interval=20 on-fail=restart timeout=60 \ op start interval=0 timeout=600 op stop interval=0 timeout=600 \ --group g-NW3_ASCS sudo pcs resource meta g-NW3_ASCS resource-stickiness=3000 sudo pcs resource create rsc_sap_NW3_ERS22 SAPInstance \ InstanceName=NW3_ERS22_msnw3ers START_PROFILE="/sapmnt/NW3/profile/NW2_ERS22_msnw3ers" \ AUTOMATIC_RECOVER=false IS_ERS=true \ op monitor interval=20 on-fail=restart timeout=60 op start interval=0 timeout=600 op stop interval=0 timeout=600 \ --group g-NW3_AERS sudo pcs constraint colocation add g-NW3_AERS with g-NW3_ASCS -5000 sudo pcs constraint location rsc_sap_NW3_ASCS20 rule score=2000 runs_ers_NW3 eq 1 sudo pcs constraint order start g-NW3_ASCS then stop g-NW3_AERS kind=Optional symmetrical=false sudo pcs property set maintenance-mode=falseIf you're upgrading from an older version and switching to enqueue server 2, see SAP note 2641019.
Note
The timeouts in the above configuration are just examples and might need to be adapted to the specific SAP setup.
Make sure that the cluster status is ok and that all resources are started. It's not important on which node the resources are running. The following example shows the cluster resources status, after SAP systems
NW2andNW3were added to the cluster.sudo pcs status # Online: [ rhelmsscl1 rhelmsscl2 ] # Full list of resources: # rsc_st_azure (stonith:fence_azure_arm): Started rhelmsscl1 # Resource Group: g-NW1_ASCS # fs_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started rhelmsscl1 # vip_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started rhelmsscl1 # nc_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started rhelmsscl1 # rsc_sap_NW1_ASCS00 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started rhelmsscl1 # Resource Group: g-NW1_AERS # fs_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started rhelmsscl2 # vip_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started rhelmsscl2 # nc_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started rhelmsscl2 # rsc_sap_NW1_ERS02 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started rhelmsscl2 # Resource Group: g-NW2_ASCS # fs_NW2_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started rhelmsscl1 # vip_NW2_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started rhelmsscl1 # nc_NW2_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started rhelmsscl1 # rsc_sap_NW2_ASCS10 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started rhelmsscl1 # Resource Group: g-NW2_AERS # fs_NW2_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started rhelmsscl1 # vip_NW2_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started rhelmsscl1 # nc_NW2_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started rhelmsscl1 # rsc_sap_NW2_ERS12 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started rhelmsscl1 # Resource Group: g-NW3_ASCS # fs_NW3_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started rhelmsscl1 # vip_NW3_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started rhelmsscl1 # nc_NW3_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started rhelmsscl1 # rsc_sap_NW3_ASCS20 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started rhelmsscl1 # Resource Group: g-NW3_AERS # fs_NW3_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started rhelmsscl1 # vip_NW3_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started rhelmsscl1 # nc_NW3_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started rhelmsscl1 # rsc_sap_NW3_ERS22 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started rhelmsscl1[A] Add firewall rules for ASCS and ERS on both nodes. The example below shows the firewall rules for both SAP systems
NW2andNW3.# NW1 - ASCS sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port={62010,3210,3610,3910,8110,51013,51014,51016}/tcp --permanent sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port={62010,3210,3610,3910,8110,51013,51014,51016}/tcp # NW2 - ERS sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port={62112,3212,3312,51213,51214,51216}/tcp --permanent sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port={62112,3212,3312,51213,51214,51216}/tcp # NW3 - ASCS sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port={62020,3220,3620,3920,8120,52013,52014,52016}/tcp --permanent sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port={62020,3220,3620,3920,8120,52013,52014,52016}/tcp # NW3 - ERS sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port={62122,3222,3322,52213,52214,52216}/tcp --permanent sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port={62122,3222,3322,52213,52214,52216}/tcp
Complete your SAP installation by:
- Preparing your SAP NetWeaver application servers.
- Installing a DBMS instance.
- Installing A primary SAP application server.
- Installing one or more other SAP application instances.
The following tests are a subset of the test cases in the best practices guides of Red Hat. They're included for your convenience. For the full list of cluster tests, reference the following documentation:
- If you use Azure NetApp Files NFS volumes, follow Azure VMs high availability for SAP NetWeaver on RHEL with Azure NetApp Files for SAP applications
- If you use highly available
GlusterFS, follow Azure VMs high availability for SAP NetWeaver on RHEL for SAP applications.
Always read the Red Hat best practices guides and perform all other tests that might have been added. The tests that are presented are in a two-node, multi-SID cluster with three SAP systems installed.
Manually migrate the ASCS instance. The example shows migrating the ASCS instance for SAP system NW3.
Resource state before starting the test:
Online: [ rhelmsscl1 rhelmsscl2 ] Full list of resources: rsc_st_azure (stonith:fence_azure_arm): Started rhelmsscl1 Resource Group: g-NW1_ASCS fs_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started rhelmsscl1 vip_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started rhelmsscl1 nc_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started rhelmsscl1 rsc_sap_NW1_ASCS00 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started rhelmsscl1 Resource Group: g-NW1_AERS fs_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started rhelmsscl2 vip_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started rhelmsscl2 nc_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started rhelmsscl2 rsc_sap_NW1_ERS02 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started rhelmsscl2 Resource Group: g-NW2_ASCS fs_NW2_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started rhelmsscl2 vip_NW2_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started rhelmsscl2 nc_NW2_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started rhelmsscl2 rsc_sap_NW2_ASCS10 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started rhelmsscl2 Resource Group: g-NW2_AERS fs_NW2_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started rhelmsscl1 vip_NW2_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started rhelmsscl1 nc_NW2_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started rhelmsscl1 rsc_sap_NW2_ERS12 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started rhelmsscl1 Resource Group: g-NW3_ASCS fs_NW3_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started rhelmsscl2 vip_NW3_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started rhelmsscl2 nc_NW3_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started rhelmsscl2 rsc_sap_NW3_ASCS20 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started rhelmsscl2 Resource Group: g-NW3_AERS fs_NW3_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started rhelmsscl1 vip_NW3_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started rhelmsscl1 nc_NW3_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started rhelmsscl1 rsc_sap_NW3_ERS22 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started rhelmsscl1Run the following commands as root to migrate the NW3 ASCS instance.
pcs resource move rsc_sap_NW3_ASCS200 # Clear temporary migration constraints pcs resource clear rsc_sap_NW3_ASCS20 # Remove failed actions for the ERS that occurred as part of the migration pcs resource cleanup rsc_sap_NW3_ERS22Resource state after the test:
Online: [ rhelmsscl1 rhelmsscl2 ] Full list of resources: rsc_st_azure (stonith:fence_azure_arm): Started rhelmsscl1 Resource Group: g-NW1_ASCS fs_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started rhelmsscl1 vip_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started rhelmsscl1 nc_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started rhelmsscl1 rsc_sap_NW1_ASCS00 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started rhelmsscl1 Resource Group: g-NW1_AERS fs_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started rhelmsscl2 vip_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started rhelmsscl2 nc_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started rhelmsscl2 rsc_sap_NW1_ERS02 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started rhelmsscl2 Resource Group: g-NW2_ASCS fs_NW2_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started rhelmsscl2 vip_NW2_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started rhelmsscl2 nc_NW2_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started rhelmsscl2 rsc_sap_NW2_ASCS10 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started rhelmsscl2 Resource Group: g-NW2_AERS fs_NW2_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started rhelmsscl1 vip_NW2_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started rhelmsscl1 nc_NW2_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started rhelmsscl1 rsc_sap_NW2_ERS12 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started rhelmsscl1 Resource Group: g-NW3_ASCS fs_NW3_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started rhelmsscl1 vip_NW3_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started rhelmsscl1 nc_NW3_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started rhelmsscl1 rsc_sap_NW3_ASCS20 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started rhelmsscl1 Resource Group: g-NW3_AERS fs_NW3_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started rhelmsscl2 vip_NW3_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started rhelmsscl2 nc_NW3_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started rhelmsscl2 rsc_sap_NW3_ERS22 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started rhelmsscl2Simulate node crash.
Resource state before starting the test:
Online: [ rhelmsscl1 rhelmsscl2 ] Full list of resources: rsc_st_azure (stonith:fence_azure_arm): Started rhelmsscl1 Resource Group: g-NW1_ASCS fs_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started rhelmsscl1 vip_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started rhelmsscl1 nc_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started rhelmsscl1 rsc_sap_NW1_ASCS00 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started rhelmsscl1 Resource Group: g-NW1_AERS fs_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started rhelmsscl2 vip_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started rhelmsscl2 nc_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started rhelmsscl2 rsc_sap_NW1_ERS02 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started rhelmsscl2 Resource Group: g-NW2_ASCS fs_NW2_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started rhelmsscl1 vip_NW2_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started rhelmsscl1 nc_NW2_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started rhelmsscl1 rsc_sap_NW2_ASCS10 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started rhelmsscl1 Resource Group: g-NW2_AERS fs_NW2_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started rhelmsscl2 vip_NW2_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started rhelmsscl2 nc_NW2_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started rhelmsscl2 rsc_sap_NW2_ERS12 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started rhelmsscl2 Resource Group: g-NW3_ASCS fs_NW3_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started rhelmsscl1 vip_NW3_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started rhelmsscl1 nc_NW3_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started rhelmsscl1 rsc_sap_NW3_ASCS20 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started rhelmsscl1 Resource Group: g-NW3_AERS fs_NW3_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started rhelmsscl2 vip_NW3_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started rhelmsscl2 nc_NW3_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started rhelmsscl2 rsc_sap_NW3_ERS22 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started rhelmsscl2Run the following command as root on a node where at least one ASCS instance is running. This example runs the command on
rhelmsscl1, where the ASCS instances forNW1,NW2, andNW3are running.echo c > /proc/sysrq-triggerThe status after the test and after the node that was crashed has started again, should look like these results:
Full list of resources: rsc_st_azure (stonith:fence_azure_arm): Started rhelmsscl2 Resource Group: g-NW1_ASCS fs_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started rhelmsscl2 vip_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started rhelmsscl2 nc_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started rhelmsscl2 rsc_sap_NW1_ASCS00 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started rhelmsscl2 Resource Group: g-NW1_AERS fs_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started rhelmsscl1 vip_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started rhelmsscl1 nc_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started rhelmsscl1 rsc_sap_NW1_ERS02 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started rhelmsscl1 Resource Group: g-NW2_ASCS fs_NW2_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started rhelmsscl2 vip_NW2_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started rhelmsscl2 nc_NW2_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started rhelmsscl2 rsc_sap_NW2_ASCS10 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started rhelmsscl2 Resource Group: g-NW2_AERS fs_NW2_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started rhelmsscl1 vip_NW2_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started rhelmsscl1 nc_NW2_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started rhelmsscl1 rsc_sap_NW2_ERS12 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started rhelmsscl1 Resource Group: g-NW3_ASCS fs_NW3_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started rhelmsscl2 vip_NW3_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started rhelmsscl2 nc_NW3_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started rhelmsscl2 rsc_sap_NW3_ASCS20 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started rhelmsscl2 Resource Group: g-NW3_AERS fs_NW3_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started rhelmsscl1 vip_NW3_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started rhelmsscl1 nc_NW3_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started rhelmsscl1 rsc_sap_NW3_ERS22 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started rhelmsscl1If there are messages for failed resources, clean the status of the failed resources. For example:
pcs resource cleanup rsc_sap_NW1_ERS02
- Azure Virtual Machines planning and implementation for SAP
- Azure Virtual Machines deployment for SAP
- Azure Virtual Machines DBMS deployment for SAP
To learn how to establish high availability and plan for disaster recovery of SAP HANA on Azure VMs, see High Availability of SAP HANA on Azure Virtual Machines (VMs).