Tutorial: Load data to Azure Synapse Analytics SQL pool
This tutorial uses PolyBase to load the WideWorldImportersDW data warehouse from Azure Blob storage to your data warehouse in Azure Synapse Analytics SQL pool. The tutorial uses the Azure portal and SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) to:
- Create a user designated for loading data
- Create external tables that use Azure blob as the data source
- Use the CTAS T-SQL statement to load data into your data warehouse
- View the progress of data as it is loading
- Generate a year of data in the date dimension and sales fact tables
- Create statistics on the newly loaded data
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a free Azure account before you begin.
Before you begin this tutorial, download and install the newest version of SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS).
This tutorial assumes you have already created a SQL dedicated pool from the following tutorial.
Note
It is recommended to use at least a DW1000c for this tutorial.
The server admin account is meant to perform management operations, and is not suited for running queries on user data. Loading data is a memory-intensive operation. Memory maximums are defined according to the Generation of SQL pool you're using, data warehouse units, and resource class.
It's best to create a login and user that is dedicated for loading data. Then add the loading user to a resource class that enables an appropriate maximum memory allocation.
Since you are currently connected as the server admin, you can create logins and users. Use these steps to create a login and user called LoaderRC60. Then assign the user to the staticrc60 resource class.
In SSMS, right-click master to show a drop-down menu, and choose New Query. A new query window opens.
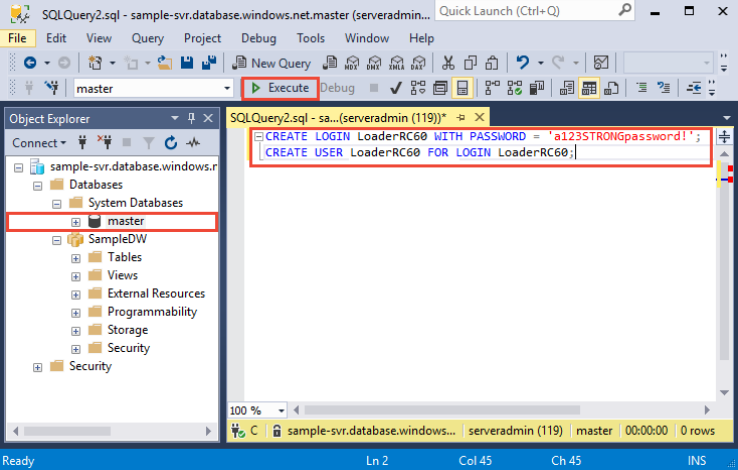
In the query window, enter these T-SQL commands to create a login and user named LoaderRC60, substituting your own password for 'a123STRONGpassword!'.
CREATE LOGIN LoaderRC60 WITH PASSWORD = 'a123STRONGpassword!'; CREATE USER LoaderRC60 FOR LOGIN LoaderRC60;Click Execute.
Right-click SampleDW, and choose New Query. A new query Window opens.
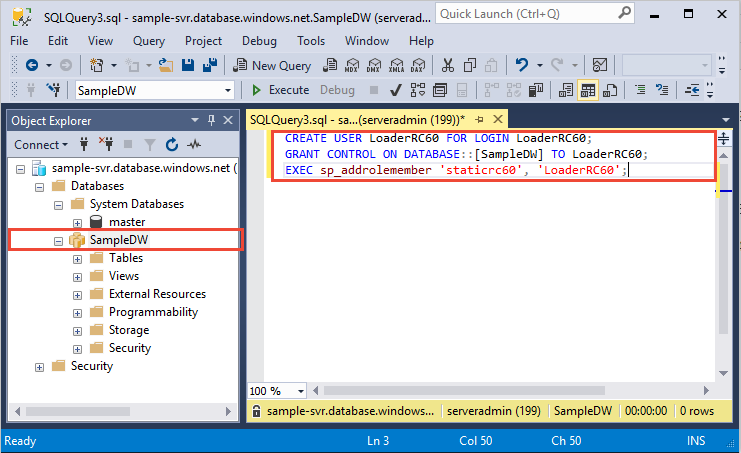
Enter the following T-SQL commands to create a database user named LoaderRC60 for the LoaderRC60 login. The second line grants the new user CONTROL permissions on the new data warehouse. These permissions are similar to making the user the owner of the database. The third line adds the new user as a member of the
staticrc60resource class.CREATE USER LoaderRC60 FOR LOGIN LoaderRC60; GRANT CONTROL ON DATABASE::[SampleDW] to LoaderRC60; EXEC sp_addrolemember 'staticrc60', 'LoaderRC60';Click Execute.
The first step toward loading data is to login as LoaderRC60.
In Object Explorer, click the Connect drop down menu and select Database Engine. The Connect to Server dialog box appears.
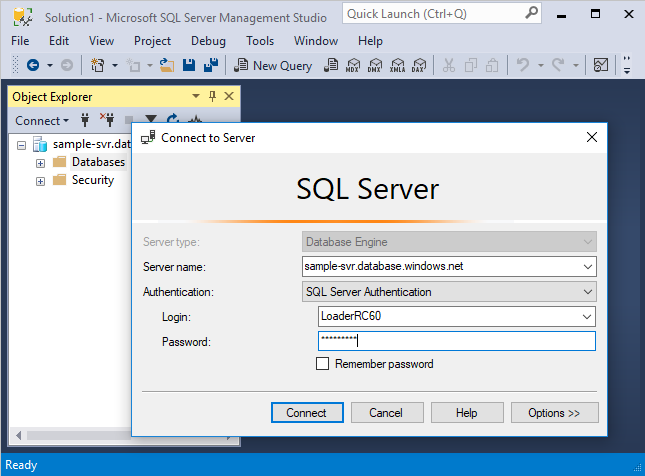
Enter the fully qualified server name, and enter LoaderRC60 as the Login. Enter your password for LoaderRC60.
Click Connect.
When your connection is ready, you will see two server connections in Object Explorer. One connection as ServerAdmin and one connection as LoaderRC60.
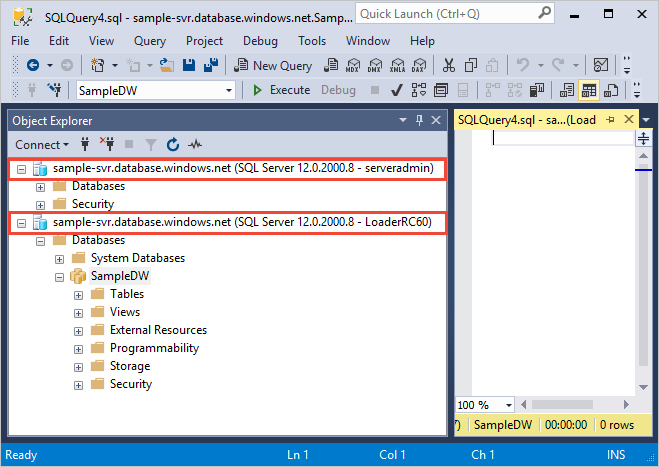
You are ready to begin the process of loading data into your new data warehouse. For future reference, to learn how to get your data to Azure Blob storage or to load it directly from your source into SQL pool, see the loading overview.
Run the following SQL scripts to specify information about the data you wish to load. This information includes where the data is located, the format of the contents of the data, and the table definition for the data. The data is located in a global Azure Blob.
In the previous section, you logged into your data warehouse as LoaderRC60. In SSMS, right-click SampleDW under your LoaderRC60 connection and select New Query. A new query window appears.
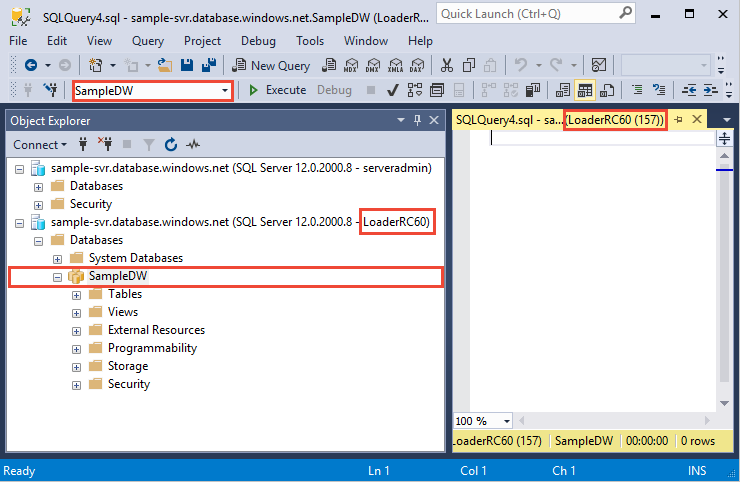
Compare your query window to the previous image. Verify your new query window is running as LoaderRC60 and performing queries on your SampleDW database. Use this query window to perform all of the loading steps.
Create a master key for the SampleDW database. You only need to create a master key once per database.
CREATE MASTER KEY;Run the following CREATE EXTERNAL DATA SOURCE statement to define the location of the Azure blob. This is the location of the external worldwide importers data. To run a command that you have appended to the query window, highlight the commands you wish to run and click Execute.
CREATE EXTERNAL DATA SOURCE WWIStorage WITH ( TYPE = Hadoop, LOCATION = 'wasbs://wideworldimporters@sqldwholdata.blob.core.windows.net' );Run the following CREATE EXTERNAL FILE FORMAT T-SQL statement to specify the formatting characteristics and options for the external data file. This statement specifies the external data is stored as text and the values are separated by the pipe ('|') character.
CREATE EXTERNAL FILE FORMAT TextFileFormat WITH ( FORMAT_TYPE = DELIMITEDTEXT, FORMAT_OPTIONS ( FIELD_TERMINATOR = '|', USE_TYPE_DEFAULT = FALSE ) );Run the following CREATE SCHEMA statements to create a schema for your external file format. The ext schema provides a way to organize the external tables you are about to create. The wwi schema organizes the standard tables that will contain the data.
CREATE SCHEMA ext; GO CREATE SCHEMA wwi;Create the external tables. The table definitions are stored in the database, but the tables reference data that is stored in Azure blob storage. Run the following T-SQL commands to create several external tables that all point to the Azure blob you defined previously in the external data source.
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE [ext].[dimension_City]( [City Key] [int] NOT NULL, [WWI City ID] [int] NOT NULL, [City] [nvarchar](50) NOT NULL, [State Province] [nvarchar](50) NOT NULL, [Country] [nvarchar](60) NOT NULL, [Continent] [nvarchar](30) NOT NULL, [Sales Territory] [nvarchar](50) NOT NULL, [Region] [nvarchar](30) NOT NULL, [Subregion] [nvarchar](30) NOT NULL, [Location] [nvarchar](76) NULL, [Latest Recorded Population] [bigint] NOT NULL, [Valid From] [datetime2](7) NOT NULL, [Valid To] [datetime2](7) NOT NULL, [Lineage Key] [int] NOT NULL ) WITH (LOCATION='/v1/dimension_City/', DATA_SOURCE = WWIStorage, FILE_FORMAT = TextFileFormat, REJECT_TYPE = VALUE, REJECT_VALUE = 0 ); CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE [ext].[dimension_Customer] ( [Customer Key] [int] NOT NULL, [WWI Customer ID] [int] NOT NULL, [Customer] [nvarchar](100) NOT NULL, [Bill To Customer] [nvarchar](100) NOT NULL, [Category] [nvarchar](50) NOT NULL, [Buying Group] [nvarchar](50) NOT NULL, [Primary Contact] [nvarchar](50) NOT NULL, [Postal Code] [nvarchar](10) NOT NULL, [Valid From] [datetime2](7) NOT NULL, [Valid To] [datetime2](7) NOT NULL, [Lineage Key] [int] NOT NULL ) WITH (LOCATION='/v1/dimension_Customer/', DATA_SOURCE = WWIStorage, FILE_FORMAT = TextFileFormat, REJECT_TYPE = VALUE, REJECT_VALUE = 0 ); CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE [ext].[dimension_Employee] ( [Employee Key] [int] NOT NULL, [WWI Employee ID] [int] NOT NULL, [Employee] [nvarchar](50) NOT NULL, [Preferred Name] [nvarchar](50) NOT NULL, [Is Salesperson] [bit] NOT NULL, [Photo] [varbinary](300) NULL, [Valid From] [datetime2](7) NOT NULL, [Valid To] [datetime2](7) NOT NULL, [Lineage Key] [int] NOT NULL ) WITH ( LOCATION='/v1/dimension_Employee/', DATA_SOURCE = WWIStorage, FILE_FORMAT = TextFileFormat, REJECT_TYPE = VALUE, REJECT_VALUE = 0 ); CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE [ext].[dimension_PaymentMethod] ( [Payment Method Key] [int] NOT NULL, [WWI Payment Method ID] [int] NOT NULL, [Payment Method] [nvarchar](50) NOT NULL, [Valid From] [datetime2](7) NOT NULL, [Valid To] [datetime2](7) NOT NULL, [Lineage Key] [int] NOT NULL ) WITH ( LOCATION ='/v1/dimension_PaymentMethod/', DATA_SOURCE = WWIStorage, FILE_FORMAT = TextFileFormat, REJECT_TYPE = VALUE, REJECT_VALUE = 0 ); CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE [ext].[dimension_StockItem]( [Stock Item Key] [int] NOT NULL, [WWI Stock Item ID] [int] NOT NULL, [Stock Item] [nvarchar](100) NOT NULL, [Color] [nvarchar](20) NOT NULL, [Selling Package] [nvarchar](50) NOT NULL, [Buying Package] [nvarchar](50) NOT NULL, [Brand] [nvarchar](50) NOT NULL, [Size] [nvarchar](20) NOT NULL, [Lead Time Days] [int] NOT NULL, [Quantity Per Outer] [int] NOT NULL, [Is Chiller Stock] [bit] NOT NULL, [Barcode] [nvarchar](50) NULL, [Tax Rate] [decimal](18, 3) NOT NULL, [Unit Price] [decimal](18, 2) NOT NULL, [Recommended Retail Price] [decimal](18, 2) NULL, [Typical Weight Per Unit] [decimal](18, 3) NOT NULL, [Photo] [varbinary](300) NULL, [Valid From] [datetime2](7) NOT NULL, [Valid To] [datetime2](7) NOT NULL, [Lineage Key] [int] NOT NULL ) WITH ( LOCATION ='/v1/dimension_StockItem/', DATA_SOURCE = WWIStorage, FILE_FORMAT = TextFileFormat, REJECT_TYPE = VALUE, REJECT_VALUE = 0 ); CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE [ext].[dimension_Supplier]( [Supplier Key] [int] NOT NULL, [WWI Supplier ID] [int] NOT NULL, [Supplier] [nvarchar](100) NOT NULL, [Category] [nvarchar](50) NOT NULL, [Primary Contact] [nvarchar](50) NOT NULL, [Supplier Reference] [nvarchar](20) NULL, [Payment Days] [int] NOT NULL, [Postal Code] [nvarchar](10) NOT NULL, [Valid From] [datetime2](7) NOT NULL, [Valid To] [datetime2](7) NOT NULL, [Lineage Key] [int] NOT NULL ) WITH ( LOCATION ='/v1/dimension_Supplier/', DATA_SOURCE = WWIStorage, FILE_FORMAT = TextFileFormat, REJECT_TYPE = VALUE, REJECT_VALUE = 0 ); CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE [ext].[dimension_TransactionType]( [Transaction Type Key] [int] NOT NULL, [WWI Transaction Type ID] [int] NOT NULL, [Transaction Type] [nvarchar](50) NOT NULL, [Valid From] [datetime2](7) NOT NULL, [Valid To] [datetime2](7) NOT NULL, [Lineage Key] [int] NOT NULL ) WITH ( LOCATION ='/v1/dimension_TransactionType/', DATA_SOURCE = WWIStorage, FILE_FORMAT = TextFileFormat, REJECT_TYPE = VALUE, REJECT_VALUE = 0 ); CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE [ext].[fact_Movement] ( [Movement Key] [bigint] NOT NULL, [Date Key] [date] NOT NULL, [Stock Item Key] [int] NOT NULL, [Customer Key] [int] NULL, [Supplier Key] [int] NULL, [Transaction Type Key] [int] NOT NULL, [WWI Stock Item Transaction ID] [int] NOT NULL, [WWI Invoice ID] [int] NULL, [WWI Purchase Order ID] [int] NULL, [Quantity] [int] NOT NULL, [Lineage Key] [int] NOT NULL ) WITH ( LOCATION ='/v1/fact_Movement/', DATA_SOURCE = WWIStorage, FILE_FORMAT = TextFileFormat, REJECT_TYPE = VALUE, REJECT_VALUE = 0 ); CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE [ext].[fact_Order] ( [Order Key] [bigint] NOT NULL, [City Key] [int] NOT NULL, [Customer Key] [int] NOT NULL, [Stock Item Key] [int] NOT NULL, [Order Date Key] [date] NOT NULL, [Picked Date Key] [date] NULL, [Salesperson Key] [int] NOT NULL, [Picker Key] [int] NULL, [WWI Order ID] [int] NOT NULL, [WWI Backorder ID] [int] NULL, [Description] [nvarchar](100) NOT NULL, [Package] [nvarchar](50) NOT NULL, [Quantity] [int] NOT NULL, [Unit Price] [decimal](18, 2) NOT NULL, [Tax Rate] [decimal](18, 3) NOT NULL, [Total Excluding Tax] [decimal](18, 2) NOT NULL, [Tax Amount] [decimal](18, 2) NOT NULL, [Total Including Tax] [decimal](18, 2) NOT NULL, [Lineage Key] [int] NOT NULL ) WITH ( LOCATION ='/v1/fact_Order/', DATA_SOURCE = WWIStorage, FILE_FORMAT = TextFileFormat, REJECT_TYPE = VALUE, REJECT_VALUE = 0 ); CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE [ext].[fact_Purchase] ( [Purchase Key] [bigint] NOT NULL, [Date Key] [date] NOT NULL, [Supplier Key] [int] NOT NULL, [Stock Item Key] [int] NOT NULL, [WWI Purchase Order ID] [int] NULL, [Ordered Outers] [int] NOT NULL, [Ordered Quantity] [int] NOT NULL, [Received Outers] [int] NOT NULL, [Package] [nvarchar](50) NOT NULL, [Is Order Finalized] [bit] NOT NULL, [Lineage Key] [int] NOT NULL ) WITH ( LOCATION ='/v1/fact_Purchase/', DATA_SOURCE = WWIStorage, FILE_FORMAT = TextFileFormat, REJECT_TYPE = VALUE, REJECT_VALUE = 0 ); CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE [ext].[fact_Sale] ( [Sale Key] [bigint] NOT NULL, [City Key] [int] NOT NULL, [Customer Key] [int] NOT NULL, [Bill To Customer Key] [int] NOT NULL, [Stock Item Key] [int] NOT NULL, [Invoice Date Key] [date] NOT NULL, [Delivery Date Key] [date] NULL, [Salesperson Key] [int] NOT NULL, [WWI Invoice ID] [int] NOT NULL, [Description] [nvarchar](100) NOT NULL, [Package] [nvarchar](50) NOT NULL, [Quantity] [int] NOT NULL, [Unit Price] [decimal](18, 2) NOT NULL, [Tax Rate] [decimal](18, 3) NOT NULL, [Total Excluding Tax] [decimal](18, 2) NOT NULL, [Tax Amount] [decimal](18, 2) NOT NULL, [Profit] [decimal](18, 2) NOT NULL, [Total Including Tax] [decimal](18, 2) NOT NULL, [Total Dry Items] [int] NOT NULL, [Total Chiller Items] [int] NOT NULL, [Lineage Key] [int] NOT NULL ) WITH ( LOCATION ='/v1/fact_Sale/', DATA_SOURCE = WWIStorage, FILE_FORMAT = TextFileFormat, REJECT_TYPE = VALUE, REJECT_VALUE = 0 ); CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE [ext].[fact_StockHolding] ( [Stock Holding Key] [bigint] NOT NULL, [Stock Item Key] [int] NOT NULL, [Quantity On Hand] [int] NOT NULL, [Bin Location] [nvarchar](20) NOT NULL, [Last Stocktake Quantity] [int] NOT NULL, [Last Cost Price] [decimal](18, 2) NOT NULL, [Reorder Level] [int] NOT NULL, [Target Stock Level] [int] NOT NULL, [Lineage Key] [int] NOT NULL ) WITH ( LOCATION ='/v1/fact_StockHolding/', DATA_SOURCE = WWIStorage, FILE_FORMAT = TextFileFormat, REJECT_TYPE = VALUE, REJECT_VALUE = 0 ); CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE [ext].[fact_Transaction] ( [Transaction Key] [bigint] NOT NULL, [Date Key] [date] NOT NULL, [Customer Key] [int] NULL, [Bill To Customer Key] [int] NULL, [Supplier Key] [int] NULL, [Transaction Type Key] [int] NOT NULL, [Payment Method Key] [int] NULL, [WWI Customer Transaction ID] [int] NULL, [WWI Supplier Transaction ID] [int] NULL, [WWI Invoice ID] [int] NULL, [WWI Purchase Order ID] [int] NULL, [Supplier Invoice Number] [nvarchar](20) NULL, [Total Excluding Tax] [decimal](18, 2) NOT NULL, [Tax Amount] [decimal](18, 2) NOT NULL, [Total Including Tax] [decimal](18, 2) NOT NULL, [Outstanding Balance] [decimal](18, 2) NOT NULL, [Is Finalized] [bit] NOT NULL, [Lineage Key] [int] NOT NULL ) WITH ( LOCATION ='/v1/fact_Transaction/', DATA_SOURCE = WWIStorage, FILE_FORMAT = TextFileFormat, REJECT_TYPE = VALUE, REJECT_VALUE = 0 );In Object Explorer, expand SampleDW to see the list of external tables you created.
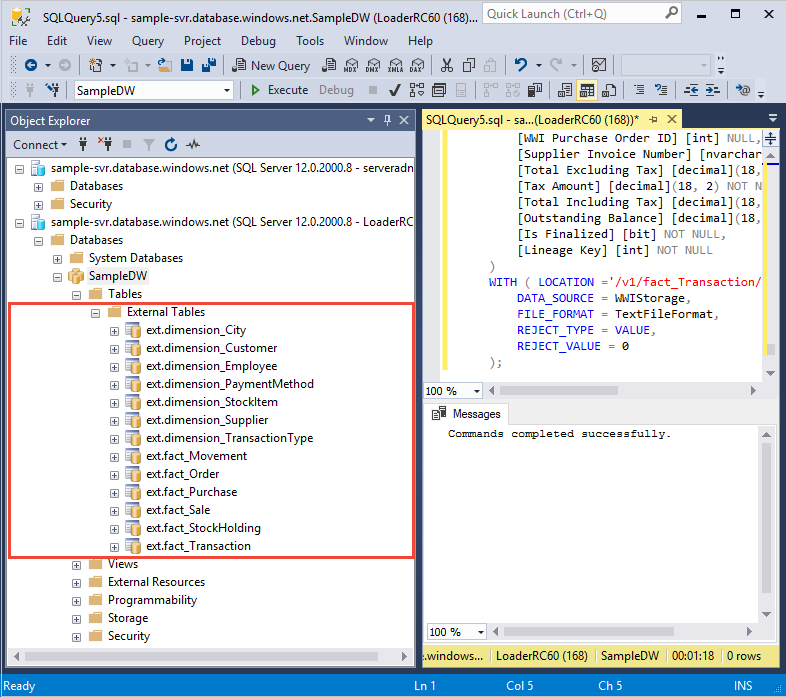
This section uses the external tables you defined to load the sample data from Azure Blob to SQL pool.
Note
This tutorial loads the data directly into the final table. In a production environment, you will usually use CREATE TABLE AS SELECT to load into a staging table. While data is in the staging table you can perform any necessary transformations. To append the data in the staging table to a production table, you can use the INSERT...SELECT statement. For more information, see Inserting data into a production table.
The script uses the CREATE TABLE AS SELECT (CTAS) T-SQL statement to load the data from Azure Storage Blob into new tables in your data warehouse. CTAS creates a new table based on the results of a select statement. The new table has the same columns and data types as the results of the select statement. When the select statement selects from an external table, the data is imported into a relational table in the data warehouse.
This script does not load data into the wwi.dimension_Date and wwi.fact_Sale tables. These tables are generated in a later step in order to make the tables have a sizeable number of rows.
Run the following script to load the data into new tables in your data warehouse.
CREATE TABLE [wwi].[dimension_City] WITH ( DISTRIBUTION = REPLICATE, CLUSTERED COLUMNSTORE INDEX ) AS SELECT * FROM [ext].[dimension_City] OPTION (LABEL = 'CTAS : Load [wwi].[dimension_City]') ; CREATE TABLE [wwi].[dimension_Customer] WITH ( DISTRIBUTION = REPLICATE, CLUSTERED COLUMNSTORE INDEX ) AS SELECT * FROM [ext].[dimension_Customer] OPTION (LABEL = 'CTAS : Load [wwi].[dimension_Customer]') ; CREATE TABLE [wwi].[dimension_Employee] WITH ( DISTRIBUTION = REPLICATE, CLUSTERED COLUMNSTORE INDEX ) AS SELECT * FROM [ext].[dimension_Employee] OPTION (LABEL = 'CTAS : Load [wwi].[dimension_Employee]') ; CREATE TABLE [wwi].[dimension_PaymentMethod] WITH ( DISTRIBUTION = REPLICATE, CLUSTERED COLUMNSTORE INDEX ) AS SELECT * FROM [ext].[dimension_PaymentMethod] OPTION (LABEL = 'CTAS : Load [wwi].[dimension_PaymentMethod]') ; CREATE TABLE [wwi].[dimension_StockItem] WITH ( DISTRIBUTION = REPLICATE, CLUSTERED COLUMNSTORE INDEX ) AS SELECT * FROM [ext].[dimension_StockItem] OPTION (LABEL = 'CTAS : Load [wwi].[dimension_StockItem]') ; CREATE TABLE [wwi].[dimension_Supplier] WITH ( DISTRIBUTION = REPLICATE, CLUSTERED COLUMNSTORE INDEX ) AS SELECT * FROM [ext].[dimension_Supplier] OPTION (LABEL = 'CTAS : Load [wwi].[dimension_Supplier]') ; CREATE TABLE [wwi].[dimension_TransactionType] WITH ( DISTRIBUTION = REPLICATE, CLUSTERED COLUMNSTORE INDEX ) AS SELECT * FROM [ext].[dimension_TransactionType] OPTION (LABEL = 'CTAS : Load [wwi].[dimension_TransactionType]') ; CREATE TABLE [wwi].[fact_Movement] WITH ( DISTRIBUTION = HASH([Movement Key]), CLUSTERED COLUMNSTORE INDEX ) AS SELECT * FROM [ext].[fact_Movement] OPTION (LABEL = 'CTAS : Load [wwi].[fact_Movement]') ; CREATE TABLE [wwi].[fact_Order] WITH ( DISTRIBUTION = HASH([Order Key]), CLUSTERED COLUMNSTORE INDEX ) AS SELECT * FROM [ext].[fact_Order] OPTION (LABEL = 'CTAS : Load [wwi].[fact_Order]') ; CREATE TABLE [wwi].[fact_Purchase] WITH ( DISTRIBUTION = HASH([Purchase Key]), CLUSTERED COLUMNSTORE INDEX ) AS SELECT * FROM [ext].[fact_Purchase] OPTION (LABEL = 'CTAS : Load [wwi].[fact_Purchase]') ; CREATE TABLE [wwi].[seed_Sale] WITH ( DISTRIBUTION = HASH([WWI Invoice ID]), CLUSTERED COLUMNSTORE INDEX ) AS SELECT * FROM [ext].[fact_Sale] OPTION (LABEL = 'CTAS : Load [wwi].[seed_Sale]') ; CREATE TABLE [wwi].[fact_StockHolding] WITH ( DISTRIBUTION = HASH([Stock Holding Key]), CLUSTERED COLUMNSTORE INDEX ) AS SELECT * FROM [ext].[fact_StockHolding] OPTION (LABEL = 'CTAS : Load [wwi].[fact_StockHolding]') ; CREATE TABLE [wwi].[fact_Transaction] WITH ( DISTRIBUTION = HASH([Transaction Key]), CLUSTERED COLUMNSTORE INDEX ) AS SELECT * FROM [ext].[fact_Transaction] OPTION (LABEL = 'CTAS : Load [wwi].[fact_Transaction]') ;View your data as it loads. You're loading several GBs of data and compressing it into highly performant clustered columnstore indexes. Open a new query window on SampleDW, and run the following query to show the status of the load. After starting the query, grab a coffee and a snack while SQL pool does some heavy lifting.
SELECT r.command, s.request_id, r.status, count(distinct input_name) as nbr_files, sum(s.bytes_processed)/1024/1024/1024 as gb_processed FROM sys.dm_pdw_exec_requests r INNER JOIN sys.dm_pdw_dms_external_work s ON r.request_id = s.request_id WHERE r.[label] = 'CTAS : Load [wwi].[dimension_City]' OR r.[label] = 'CTAS : Load [wwi].[dimension_Customer]' OR r.[label] = 'CTAS : Load [wwi].[dimension_Employee]' OR r.[label] = 'CTAS : Load [wwi].[dimension_PaymentMethod]' OR r.[label] = 'CTAS : Load [wwi].[dimension_StockItem]' OR r.[label] = 'CTAS : Load [wwi].[dimension_Supplier]' OR r.[label] = 'CTAS : Load [wwi].[dimension_TransactionType]' OR r.[label] = 'CTAS : Load [wwi].[fact_Movement]' OR r.[label] = 'CTAS : Load [wwi].[fact_Order]' OR r.[label] = 'CTAS : Load [wwi].[fact_Purchase]' OR r.[label] = 'CTAS : Load [wwi].[fact_StockHolding]' OR r.[label] = 'CTAS : Load [wwi].[fact_Transaction]' GROUP BY r.command, s.request_id, r.status ORDER BY nbr_files desc, gb_processed desc;View all system queries.
SELECT * FROM sys.dm_pdw_exec_requests;Enjoy seeing your data nicely loaded into your data warehouse.
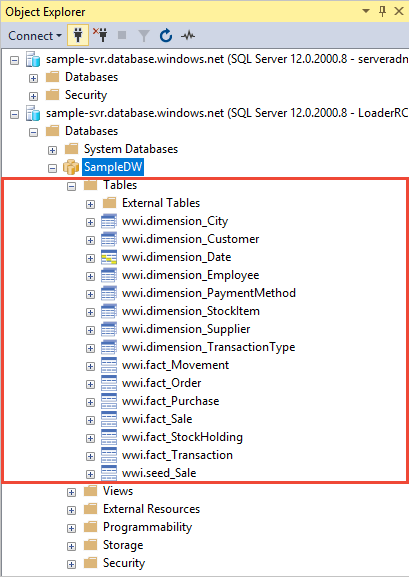
This section creates the wwi.dimension_Date and wwi.fact_Sale tables. It also creates stored procedures that can generate millions of rows in the wwi.dimension_Date and wwi.fact_Sale tables.
Create the dimension_Date and fact_Sale tables.
CREATE TABLE [wwi].[dimension_Date] ( [Date] [datetime] NOT NULL, [Day Number] [int] NOT NULL, [Day] [nvarchar](10) NOT NULL, [Month] [nvarchar](10) NOT NULL, [Short Month] [nvarchar](3) NOT NULL, [Calendar Month Number] [int] NOT NULL, [Calendar Month Label] [nvarchar](20) NOT NULL, [Calendar Year] [int] NOT NULL, [Calendar Year Label] [nvarchar](10) NOT NULL, [Fiscal Month Number] [int] NOT NULL, [Fiscal Month Label] [nvarchar](20) NOT NULL, [Fiscal Year] [int] NOT NULL, [Fiscal Year Label] [nvarchar](10) NOT NULL, [ISO Week Number] [int] NOT NULL ) WITH ( DISTRIBUTION = REPLICATE, CLUSTERED INDEX ([Date]) ); CREATE TABLE [wwi].[fact_Sale] ( [Sale Key] [bigint] IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL, [City Key] [int] NOT NULL, [Customer Key] [int] NOT NULL, [Bill To Customer Key] [int] NOT NULL, [Stock Item Key] [int] NOT NULL, [Invoice Date Key] [date] NOT NULL, [Delivery Date Key] [date] NULL, [Salesperson Key] [int] NOT NULL, [WWI Invoice ID] [int] NOT NULL, [Description] [nvarchar](100) NOT NULL, [Package] [nvarchar](50) NOT NULL, [Quantity] [int] NOT NULL, [Unit Price] [decimal](18, 2) NOT NULL, [Tax Rate] [decimal](18, 3) NOT NULL, [Total Excluding Tax] [decimal](18, 2) NOT NULL, [Tax Amount] [decimal](18, 2) NOT NULL, [Profit] [decimal](18, 2) NOT NULL, [Total Including Tax] [decimal](18, 2) NOT NULL, [Total Dry Items] [int] NOT NULL, [Total Chiller Items] [int] NOT NULL, [Lineage Key] [int] NOT NULL ) WITH ( DISTRIBUTION = HASH ( [WWI Invoice ID] ), CLUSTERED COLUMNSTORE INDEX )Create [wwi].[InitialSalesDataPopulation] to increase the number of rows in [wwi].[seed_Sale] by a factor of eight.
CREATE PROCEDURE [wwi].[InitialSalesDataPopulation] AS BEGIN INSERT INTO [wwi].[seed_Sale] ( [Sale Key], [City Key], [Customer Key], [Bill To Customer Key], [Stock Item Key], [Invoice Date Key], [Delivery Date Key], [Salesperson Key], [WWI Invoice ID], [Description], [Package], [Quantity], [Unit Price], [Tax Rate], [Total Excluding Tax], [Tax Amount], [Profit], [Total Including Tax], [Total Dry Items], [Total Chiller Items], [Lineage Key] ) SELECT [Sale Key], [City Key], [Customer Key], [Bill To Customer Key], [Stock Item Key], [Invoice Date Key], [Delivery Date Key], [Salesperson Key], [WWI Invoice ID], [Description], [Package], [Quantity], [Unit Price], [Tax Rate], [Total Excluding Tax], [Tax Amount], [Profit], [Total Including Tax], [Total Dry Items], [Total Chiller Items], [Lineage Key] FROM [wwi].[seed_Sale] INSERT INTO [wwi].[seed_Sale] ( [Sale Key], [City Key], [Customer Key], [Bill To Customer Key], [Stock Item Key], [Invoice Date Key], [Delivery Date Key], [Salesperson Key], [WWI Invoice ID], [Description], [Package], [Quantity], [Unit Price], [Tax Rate], [Total Excluding Tax], [Tax Amount], [Profit], [Total Including Tax], [Total Dry Items], [Total Chiller Items], [Lineage Key] ) SELECT [Sale Key], [City Key], [Customer Key], [Bill To Customer Key], [Stock Item Key], [Invoice Date Key], [Delivery Date Key], [Salesperson Key], [WWI Invoice ID], [Description], [Package], [Quantity], [Unit Price], [Tax Rate], [Total Excluding Tax], [Tax Amount], [Profit], [Total Including Tax], [Total Dry Items], [Total Chiller Items], [Lineage Key] FROM [wwi].[seed_Sale] INSERT INTO [wwi].[seed_Sale] ( [Sale Key], [City Key], [Customer Key], [Bill To Customer Key], [Stock Item Key], [Invoice Date Key], [Delivery Date Key], [Salesperson Key], [WWI Invoice ID], [Description], [Package], [Quantity], [Unit Price], [Tax Rate], [Total Excluding Tax], [Tax Amount], [Profit], [Total Including Tax], [Total Dry Items], [Total Chiller Items], [Lineage Key] ) SELECT [Sale Key], [City Key], [Customer Key], [Bill To Customer Key], [Stock Item Key], [Invoice Date Key], [Delivery Date Key], [Salesperson Key], [WWI Invoice ID], [Description], [Package], [Quantity], [Unit Price], [Tax Rate], [Total Excluding Tax], [Tax Amount], [Profit], [Total Including Tax], [Total Dry Items], [Total Chiller Items], [Lineage Key] FROM [wwi].[seed_Sale] ENDCreate this stored procedure that populates rows into wwi.dimension_Date.
CREATE PROCEDURE [wwi].[PopulateDateDimensionForYear] @Year [int] AS BEGIN IF OBJECT_ID('tempdb..#month', 'U') IS NOT NULL DROP TABLE #month CREATE TABLE #month ( monthnum int, numofdays int ) WITH ( DISTRIBUTION = ROUND_ROBIN, heap ) INSERT INTO #month SELECT 1, 31 UNION SELECT 2, CASE WHEN (@YEAR % 4 = 0 AND @YEAR % 100 <> 0) OR @YEAR % 400 = 0 THEN 29 ELSE 28 END UNION SELECT 3,31 UNION SELECT 4,30 UNION SELECT 5,31 UNION SELECT 6,30 UNION SELECT 7,31 UNION SELECT 8,31 UNION SELECT 9,30 UNION SELECT 10,31 UNION SELECT 11,30 UNION SELECT 12,31 IF OBJECT_ID('tempdb..#days', 'U') IS NOT NULL DROP TABLE #days CREATE TABLE #days (days int) WITH (DISTRIBUTION = ROUND_ROBIN, HEAP) INSERT INTO #days SELECT 1 UNION SELECT 2 UNION SELECT 3 UNION SELECT 4 UNION SELECT 5 UNION SELECT 6 UNION SELECT 7 UNION SELECT 8 UNION SELECT 9 UNION SELECT 10 UNION SELECT 11 UNION SELECT 12 UNION SELECT 13 UNION SELECT 14 UNION SELECT 15 UNION SELECT 16 UNION SELECT 17 UNION SELECT 18 UNION SELECT 19 UNION SELECT 20 UNION SELECT 21 UNION SELECT 22 UNION SELECT 23 UNION SELECT 24 UNION SELECT 25 UNION SELECT 26 UNION SELECT 27 UNION SELECT 28 UNION SELECT 29 UNION SELECT 30 UNION SELECT 31 INSERT [wwi].[dimension_Date] ( [Date], [Day Number], [Day], [Month], [Short Month], [Calendar Month Number], [Calendar Month Label], [Calendar Year], [Calendar Year Label], [Fiscal Month Number], [Fiscal Month Label], [Fiscal Year], [Fiscal Year Label], [ISO Week Number] ) SELECT CAST(CAST(monthnum AS VARCHAR(2)) + '/' + CAST([days] AS VARCHAR(3)) + '/' + CAST(@year AS CHAR(4)) AS DATE) AS [Date] ,DAY(CAST(CAST(monthnum AS VARCHAR(2)) + '/' + CAST([days] AS VARCHAR(3)) + '/' + CAST(@year AS CHAR(4)) AS DATE)) AS [Day Number] ,CAST(DATENAME(day, CAST(CAST(monthnum AS VARCHAR(2)) + '/' + CAST([days] AS VARCHAR(3)) + '/' + CAST(@year AS CHAR(4)) AS DATE)) AS NVARCHAR(10)) AS [Day] ,CAST(DATENAME(month, CAST(CAST(monthnum AS VARCHAR(2)) + '/' + CAST([days] AS VARCHAR(3)) + '/' + CAST(@year as char(4)) AS DATE)) AS nvarchar(10)) AS [Month] ,CAST(SUBSTRING(DATENAME(month, CAST(CAST(monthnum as varchar(2)) + '/' + CAST([days] as varchar(3)) + '/' + CAST(@year as char(4)) AS DATE)), 1, 3) AS nvarchar(3)) AS [Short Month] ,MONTH(CAST(CAST(monthnum as varchar(2)) + '/' + CAST([days] as varchar(3)) + '/' + CAST(@year as char(4)) AS DATE)) AS [Calendar Month Number] ,CAST(N'CY' + CAST(YEAR(CAST(CAST(monthnum as varchar(2)) + '/' + CAST([days] as varchar(3)) + '/' + CAST(@year as char(4)) AS DATE)) AS nvarchar(4)) + N'-' + SUBSTRING(DATENAME(month, CAST(CAST(monthnum as varchar(2)) + '/' + CAST([days] as varchar(3)) + '/' + CAST(@year as char(4)) AS DATE)), 1, 3) AS nvarchar(10)) AS [Calendar Month Label] ,YEAR(CAST(CAST(monthnum as varchar(2)) + '/' + CAST([days] as varchar(3)) + '/' + CAST(@year as char(4)) AS DATE)) AS [Calendar Year] ,CAST(N'CY' + CAST(YEAR(CAST(CAST(monthnum as varchar(2)) + '/' + CAST([days] as varchar(3)) + '/' + CAST(@year as char(4)) AS DATE)) AS nvarchar(4)) AS nvarchar(10)) AS [Calendar Year Label] ,CASE WHEN MONTH(CAST(CAST(monthnum as varchar(2)) + '/' + CAST([days] as varchar(3)) + '/' + CAST(@year as char(4)) AS DATE)) IN (11, 12) THEN MONTH(CAST(CAST(monthnum as varchar(2)) + '/' + CAST([days] as varchar(3)) + '/' + CAST(@year as char(4)) AS DATE)) - 10 ELSE MONTH(CAST(CAST(monthnum as varchar(2)) + '/' + CAST([days] as varchar(3)) + '/' + CAST(@year as char(4)) AS DATE)) + 2 END AS [Fiscal Month Number] ,CAST(N'FY' + CAST(CASE WHEN MONTH(CAST(CAST(monthnum as varchar(2)) + '/' + CAST([days] as varchar(3)) + '/' + CAST(@year as char(4)) AS DATE)) IN (11, 12) THEN YEAR(CAST(CAST(monthnum as varchar(2)) + '/' + CAST([days] as varchar(3)) + '/' + CAST(@year as char(4)) AS DATE)) + 1 ELSE YEAR(CAST(CAST(monthnum as varchar(2)) + '/' + CAST([days] as varchar(3)) + '/' + CAST(@year as char(4)) AS DATE)) END AS nvarchar(4)) + N'-' + SUBSTRING(DATENAME(month, CAST(CAST(monthnum as varchar(2)) + '/' + CAST([days] as varchar(3)) + '/' + CAST(@year as char(4)) AS DATE)), 1, 3) AS nvarchar(20)) AS [Fiscal Month Label] ,CASE WHEN MONTH(CAST(CAST(monthnum as varchar(2)) + '/' + CAST([days] as varchar(3)) + '/' + CAST(@year as char(4)) AS DATE)) IN (11, 12) THEN YEAR(CAST(CAST(monthnum as varchar(2)) + '/' + CAST([days] as varchar(3)) + '/' + CAST(@year as char(4)) AS DATE)) + 1 ELSE YEAR(CAST(CAST(monthnum as varchar(2)) + '/' + CAST([days] as varchar(3)) + '/' + CAST(@year as char(4)) AS DATE)) END AS [Fiscal Year] ,CAST(N'FY' + CAST(CASE WHEN MONTH(CAST(CAST(monthnum as varchar(2)) + '/' + CAST([days] as varchar(3)) + '/' + CAST(@year as char(4)) AS DATE)) IN (11, 12) THEN YEAR(CAST(CAST(monthnum as varchar(2)) + '/' + CAST([days] as varchar(3)) + '/' + CAST(@year as char(4)) AS DATE)) + 1 ELSE YEAR(CAST(CAST(monthnum as varchar(2)) + '/' + CAST([days] as varchar(3)) + '/' + CAST(@year as char(4)) AS DATE))END AS nvarchar(4)) AS nvarchar(10)) AS [Fiscal Year Label] , DATEPART(ISO_WEEK, CAST(CAST(monthnum as varchar(2)) + '/' + CAST([days] as varchar(3)) + '/' + CAST(@year as char(4)) AS DATE)) AS [ISO Week Number] FROM #month m CROSS JOIN #days d WHERE d.days <= m.numofdays DROP table #month; DROP table #days; END;Create this procedure that populates the wwi.dimension_Date and wwi.fact_Sale tables. It calls [wwi].[PopulateDateDimensionForYear] to populate wwi.dimension_Date.
CREATE PROCEDURE [wwi].[Configuration_PopulateLargeSaleTable] @EstimatedRowsPerDay [bigint],@Year [int] AS BEGIN SET NOCOUNT ON; SET XACT_ABORT ON; EXEC [wwi].[PopulateDateDimensionForYear] @Year; DECLARE @OrderCounter bigint = 0; DECLARE @NumberOfSalesPerDay bigint = @EstimatedRowsPerDay; DECLARE @DateCounter date; DECLARE @StartingSaleKey bigint; DECLARE @MaximumSaleKey bigint = (SELECT MAX([Sale Key]) FROM wwi.seed_Sale); DECLARE @MaxDate date; SET @MaxDate = (SELECT MAX([Invoice Date Key]) FROM wwi.fact_Sale) IF ( @MaxDate < CAST(@YEAR AS CHAR(4)) + '1231') AND (@MaxDate > CAST(@YEAR AS CHAR(4)) + '0101') SET @DateCounter = @MaxDate ELSE SET @DateCounter= CAST(@Year as char(4)) + '0101'; PRINT 'Targeting ' + CAST(@NumberOfSalesPerDay AS varchar(20)) + ' sales per day.'; DECLARE @OutputCounter varchar(20); DECLARE @variance DECIMAL(18,10); DECLARE @VariantNumberOfSalesPerDay BIGINT; WHILE @DateCounter < CAST(@YEAR AS CHAR(4)) + '1231' BEGIN SET @OutputCounter = CONVERT(varchar(20), @DateCounter, 112); RAISERROR(@OutputCounter, 0, 1); SET @variance = (SELECT RAND() * 10)*.01 + .95 SET @VariantNumberOfSalesPerDay = FLOOR(@NumberOfSalesPerDay * @variance) SET @StartingSaleKey = @MaximumSaleKey - @VariantNumberOfSalesPerDay - FLOOR(RAND() * 20000); SET @OrderCounter = 0; INSERT [wwi].[fact_Sale] ( [City Key], [Customer Key], [Bill To Customer Key], [Stock Item Key], [Invoice Date Key], [Delivery Date Key], [Salesperson Key], [WWI Invoice ID], [Description], Package, Quantity, [Unit Price], [Tax Rate], [Total Excluding Tax], [Tax Amount], Profit, [Total Including Tax], [Total Dry Items], [Total Chiller Items], [Lineage Key] ) SELECT TOP(@VariantNumberOfSalesPerDay) [City Key], [Customer Key], [Bill To Customer Key], [Stock Item Key], @DateCounter, DATEADD(day, 1, @DateCounter), [Salesperson Key], [WWI Invoice ID], [Description], Package, Quantity, [Unit Price], [Tax Rate], [Total Excluding Tax], [Tax Amount], Profit, [Total Including Tax], [Total Dry Items], [Total Chiller Items], [Lineage Key] FROM [wwi].[seed_Sale] WHERE --[Sale Key] > @StartingSaleKey and /* IDENTITY DOES NOT WORK THE SAME IN SQLDW AND CAN'T USE THIS METHOD FOR VARIANT */ [Invoice Date Key] >=cast(@YEAR AS CHAR(4)) + '-01-01' ORDER BY [Sale Key]; SET @DateCounter = DATEADD(day, 1, @DateCounter); END; END;
Use the stored procedures you created to generate millions of rows in the wwi.fact_Sale table, and corresponding data in the wwi.dimension_Date table.
Run this procedure to seed the [wwi].[seed_Sale] with more rows.
EXEC [wwi].[InitialSalesDataPopulation]Run this procedure to populate wwi.fact_Sale with 100,000 rows per day for each day in the year 2000.
EXEC [wwi].[Configuration_PopulateLargeSaleTable] 100000, 2000The data generation in the previous step might take a while as it progresses through the year. To see which day the current process is on, open a new query and run this SQL command:
SELECT MAX([Invoice Date Key]) FROM wwi.fact_Sale;Run the following command to see the space used.
EXEC sp_spaceused N'wwi.fact_Sale';
SQL pool replicates a table by caching the data to each Compute node. The cache gets populated when a query runs against the table. Therefore, the first query on a replicated table might require extra time to populate the cache. After the cache is populated, queries on replicated tables run faster.
Run these SQL queries to populate the replicated table cache on the Compute nodes.
SELECT TOP 1 * FROM [wwi].[dimension_City];
SELECT TOP 1 * FROM [wwi].[dimension_Customer];
SELECT TOP 1 * FROM [wwi].[dimension_Date];
SELECT TOP 1 * FROM [wwi].[dimension_Employee];
SELECT TOP 1 * FROM [wwi].[dimension_PaymentMethod];
SELECT TOP 1 * FROM [wwi].[dimension_StockItem];
SELECT TOP 1 * FROM [wwi].[dimension_Supplier];
SELECT TOP 1 * FROM [wwi].[dimension_TransactionType];
To achieve high query performance, it's important to create statistics on each column of each table after the first load. It's also important to update statistics after substantial changes in the data.
Create this stored procedure that updates statistics on all columns of all tables.
CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[prc_sqldw_create_stats] ( @create_type tinyint -- 1 default 2 Fullscan 3 Sample , @sample_pct tinyint ) AS IF @create_type IS NULL BEGIN SET @create_type = 1; END; IF @create_type NOT IN (1,2,3) BEGIN THROW 151000,'Invalid value for @stats_type parameter. Valid range 1 (default), 2 (fullscan) or 3 (sample).',1; END; IF @sample_pct IS NULL BEGIN; SET @sample_pct = 20; END; IF OBJECT_ID('tempdb..#stats_ddl') IS NOT NULL BEGIN; DROP TABLE #stats_ddl; END; CREATE TABLE #stats_ddl WITH ( DISTRIBUTION = HASH([seq_nmbr]) , LOCATION = USER_DB ) AS WITH T AS ( SELECT t.[name] AS [table_name] , s.[name] AS [table_schema_name] , c.[name] AS [column_name] , c.[column_id] AS [column_id] , t.[object_id] AS [object_id] , ROW_NUMBER() OVER(ORDER BY (SELECT NULL)) AS [seq_nmbr] FROM sys.[tables] t JOIN sys.[schemas] s ON t.[schema_id] = s.[schema_id] JOIN sys.[columns] c ON t.[object_id] = c.[object_id] LEFT JOIN sys.[stats_columns] l ON l.[object_id] = c.[object_id] AND l.[column_id] = c.[column_id] AND l.[stats_column_id] = 1 LEFT JOIN sys.[external_tables] e ON e.[object_id] = t.[object_id] WHERE l.[object_id] IS NULL AND e.[object_id] IS NULL -- not an external table ) SELECT [table_schema_name] , [table_name] , [column_name] , [column_id] , [object_id] , [seq_nmbr] , CASE @create_type WHEN 1 THEN CAST('CREATE STATISTICS '+QUOTENAME('stat_'+table_schema_name+ '_' + table_name + '_'+column_name)+' ON '+QUOTENAME(table_schema_name)+'.'+QUOTENAME(table_name)+'('+QUOTENAME(column_name)+')' AS VARCHAR(8000)) WHEN 2 THEN CAST('CREATE STATISTICS '+QUOTENAME('stat_'+table_schema_name+ '_' + table_name + '_'+column_name)+' ON '+QUOTENAME(table_schema_name)+'.'+QUOTENAME(table_name)+'('+QUOTENAME(column_name)+') WITH FULLSCAN' AS VARCHAR(8000)) WHEN 3 THEN CAST('CREATE STATISTICS '+QUOTENAME('stat_'+table_schema_name+ '_' + table_name + '_'+column_name)+' ON '+QUOTENAME(table_schema_name)+'.'+QUOTENAME(table_name)+'('+QUOTENAME(column_name)+') WITH SAMPLE '+CONVERT(varchar(4),@sample_pct)+' PERCENT' AS VARCHAR(8000)) END AS create_stat_ddl FROM T ; DECLARE @i INT = 1 , @t INT = (SELECT COUNT(*) FROM #stats_ddl) , @s NVARCHAR(4000) = N'' ; WHILE @i <= @t BEGIN SET @s=(SELECT create_stat_ddl FROM #stats_ddl WHERE seq_nmbr = @i); PRINT @s EXEC sp_executesql @s SET @i+=1; END DROP TABLE #stats_ddl;Run this command to create statistics on all columns of all tables in the data warehouse.
EXEC [dbo].[prc_sqldw_create_stats] 1, NULL;
You are being charged for compute resources and data that you loaded into your data warehouse. These are billed separately.
Follow these steps to clean up resources as you desire.
Sign in to the Azure portal, click on your data warehouse.
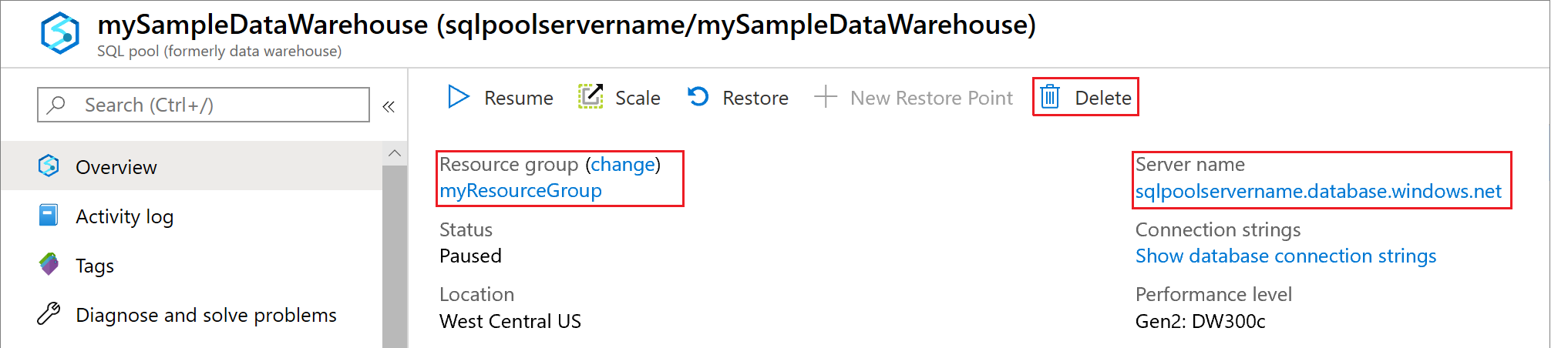
If you want to keep the data in storage, you can pause compute when you aren't using the data warehouse. By pausing compute, you will only be charge for data storage and you can resume the compute whenever you are ready to work with the data. To pause compute, click the Pause button. When the data warehouse is paused, you will see a Start button. To resume compute, click Start.
If you want to remove future charges, you can delete the data warehouse. To remove the data warehouse so you won't be charged for compute or storage, click Delete.
To remove the server you created, click sample-svr.database.windows.net in the previous image, and then click Delete. Be careful with this as deleting the server will delete all databases assigned to the server.
To remove the resource group, click SampleRG, and then click Delete resource group.
In this tutorial, you learned how to create a data warehouse and create a user for loading data. You created external tables to define the structure for data stored in Azure Storage Blob, and then used the PolyBase CREATE TABLE AS SELECT statement to load data into your data warehouse.
You did these things:
- Created a data warehouse using SQL pool in the Azure portal
- Set up a server-level firewall rule in the Azure portal
- Connected to the SQL pool with SSMS
- Created a user designated for loading data
- Created external tables for data in Azure Storage Blob
- Used the CTAS T-SQL statement to load data into your data warehouse
- Viewed the progress of data as it is loading
- Created statistics on the newly loaded data
Advance to the development overview to learn how to migrate an existing database to Azure Synapse SQL pool.