Set up your environment (preview)
This article is aimed at developers who are looking to build a workload using the Microsoft Fabric Workload Development Kit. The article will guide you through the process of setting up your development environment so that you can start building your workload.
Prerequisites
The following steps are required before getting started with workload development.
Git
A distributed version control system that we use to manage and track changes to our project.
npm (Node Package Manager)
Default package manager for Node.js used to manage and share the packages that you use in your project.
Node.js
An open-source, cross-platform, JavaScript runtime environment that executes JavaScript code outside a web browser. We'll use this to run our server-side JavaScript code.
Webpack
A static module bundler for modern JavaScript applications. It helps to bundle JavaScript files for usage in a browser.
Webpack CLI
The command line interface for Webpack. This allows us to use Webpack from the command line.
DevGateway
In local mode only is required to allow the workload backend, which is locally hosted, to communicate with the tenant. The workload operates on the developer's machine. Workload API calls from Fabric to the workload are channeled through Azure Relay, with the workload's side of the Azure Relay channel managed by the DevGateway command-line utility. Workload control API calls are made directly from the workload to Fabric, not requiring the Azure Relay channel. The DevGateway utility also manages the registration of the workload's local (development) instance with Fabric within a specific capacity context, making the workload accessible in all workspaces assigned to that capacity.
Note
Terminating the DevGateway utility automatically removes the workload instance registration.
Create your environment
Follow the stages below to create your environment.
Workload environment authentication
Setting up workload access to Fabric tenant requires configuration of Microsoft Entra ID for your workload application. Microsoft Entra ID is necessary to ensure secure access and operation of your application's data plane API.
Key steps include:
Adding scopes for data plane API: These scopes represent groups of operations exposed by your data plane API. Four example scopes are provided in the backend sample, covering read and write operations for workload items and Lakehouse files.
Preauthorizing the Fabric client application: The Fabric client application needs to be preauthorized for the scopes you've defined. This ensures it can perform the necessary operations on your workload items and Lakehouse files.
Generating a secret for your application: This secret is used to secure your application and will be used when configuring the backend sample.
Adding optional claim 'idtyp': This claim is added to the access token and is used for identity purposes.
These steps are required when setting up the workload, For a detailed guide on how to perform these steps, see Authentication setup.
Web app (cloud mode only)
Cloud mode (in conjunction to local machine mode) workload deployment requires setting up a web app domain for the Frontend (FE) and Backend (BE). These must be subdomains of the resource ID with a maximum of one more segment. The reply URL host domain should be the same as the FE host domain. For more information, see Creating and deploying the boilerplate backend web app.
Setting up a Fabric development tenant
In the context of executing the workload SDK sample and building a workload, it's recommended to employ a dedicated development tenant. This practice ensures an isolated environment, minimizing the risk of inadvertent disruptions or modifications to production systems. Moreover, it provides an additional layer of security, safeguarding production data from potential exposure or compromise. Adherence to this recommendation aligns with industry best practices and contributes to a robust, reliable, and secure development lifecycle.
Tenant setting and development settings
The Fabric admin's permission is required to be able to begin development and connect with your local machine to a Fabric capacity. Only developers with capacity admin permission can connect and register their workload on to a capacity. Frontend development doesn't require capacity admin permissions.
To enable a user to begin development, include them in the Capacity admins can develop additional workloads tenant setting.
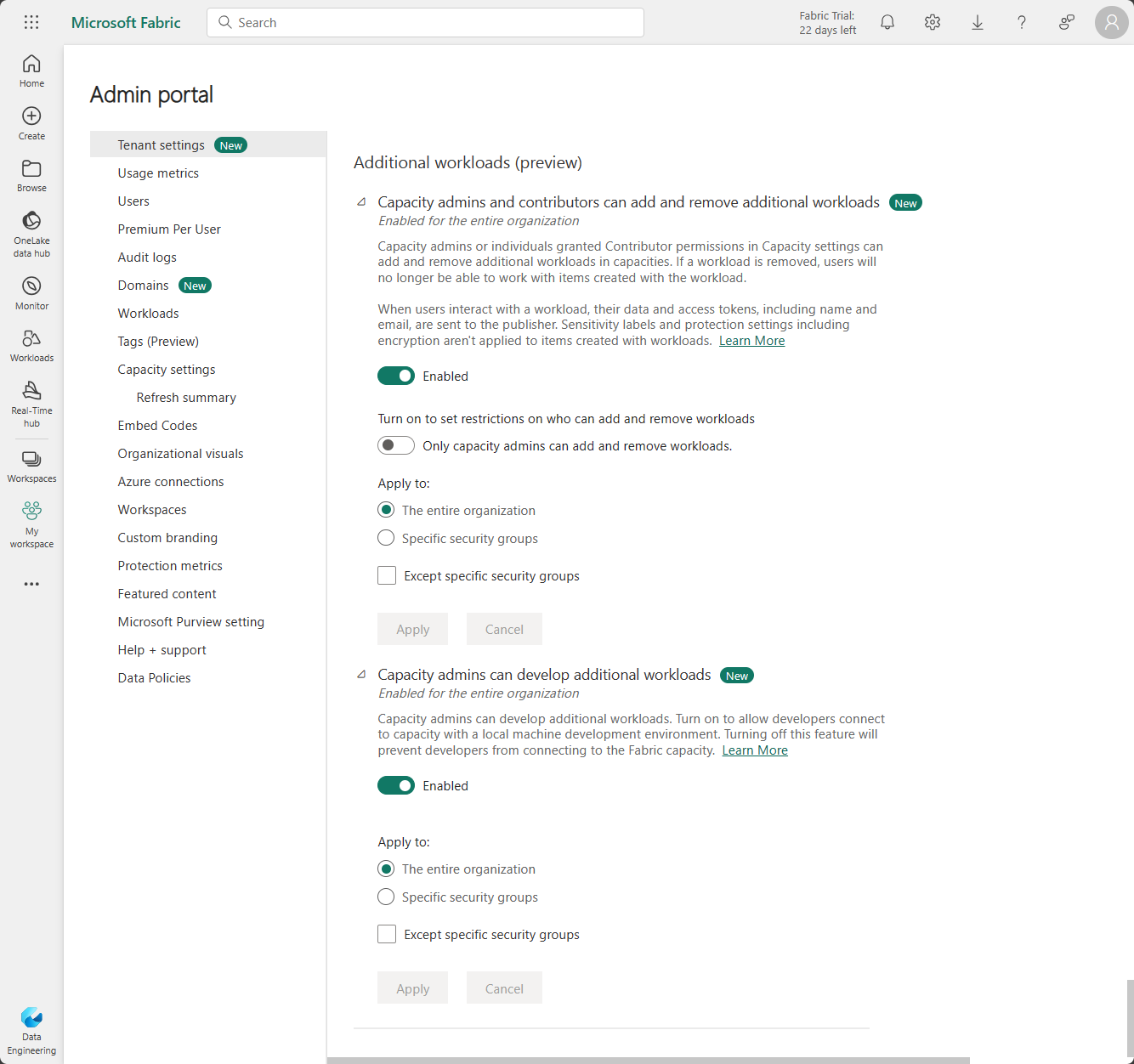
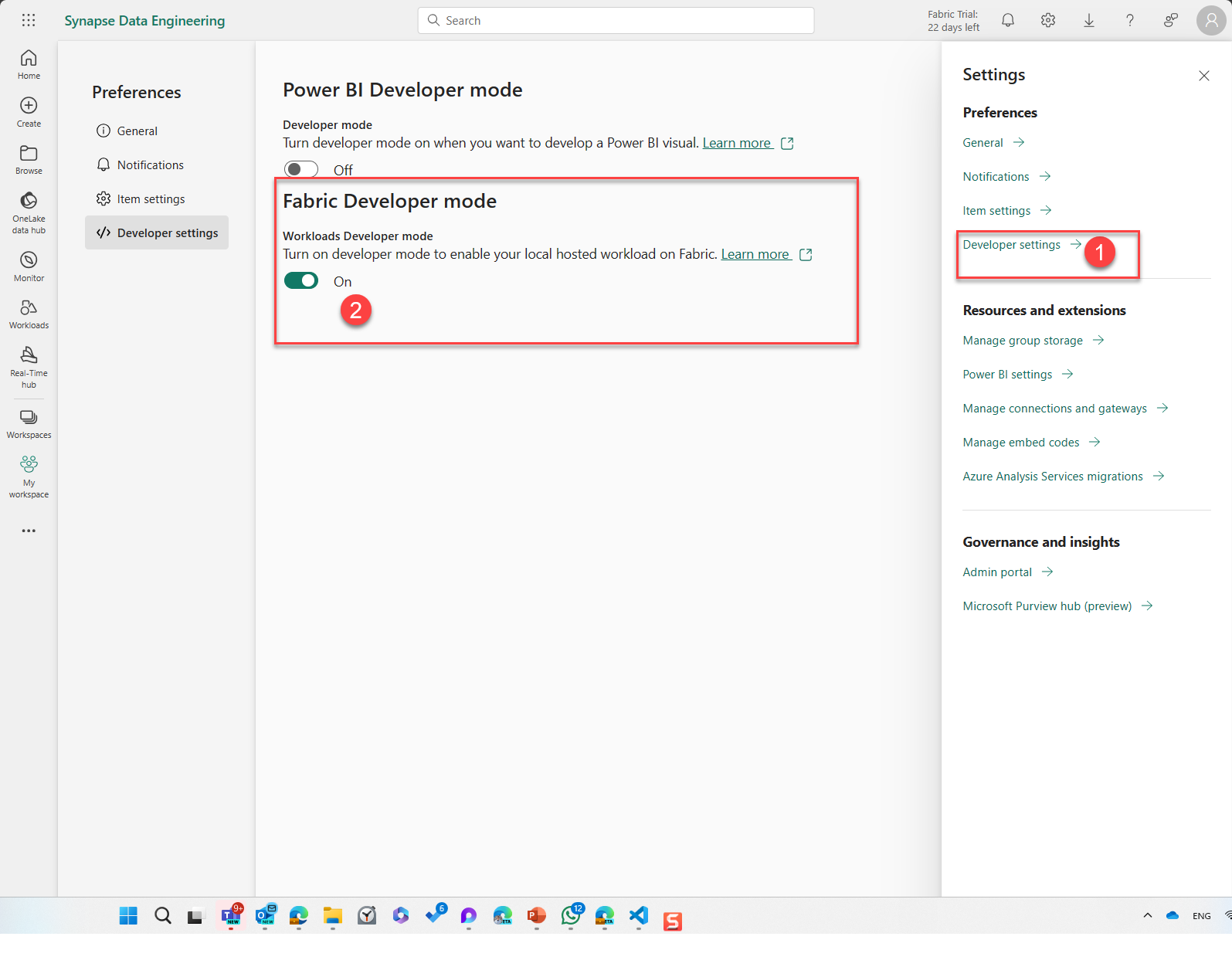
After the user has been granted permission in the previous step, each user can enable development mode for the development settings area under Fabric developer mode.
Related content
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for