Bot Service templates
APPLIES TO: SDK v3
Bot Service includes five templates to help you get started with building bots. These templates provide a fully functional bot out of the box to help you get started quickly. When you create a bot, you choose a template and the SDK language for your bot.
Each template provides a starting point that is based on a core capability for a bot.
To create a bot that uses dialogs to respond to user input, choose the Basic template. The Basic template creates a bot that has the minimum set of files and code to get started. The bot echoes back to the user whatever they type in. You can use this template to get started building conversation flow in your bot.
To create a bot that collects input from a user via a guided conversation, choose the Form template. A form bot is designed to collect a specific set of information from the user. For example, a bot that is designed to obtain a user's sandwich order would need to collect information such as type of bread, choice of toppings, size of sandwich, and so on.
Bots created with the Form template in the C# language use FormFlow to manage forms, and bots created with the Form template in the Node.js language use waterfalls to manage forms.
To create a bot that uses natural language models to understand user intent, choose the Language understanding template. This template leverages Language Understanding (LUIS) to provide natural language understanding.
If a user sends a message such as "get news about virtual reality companies," your bot can use LUIS to interpret the meaning of the message. Using LUIS, you can quickly deploy an HTTP endpoint that will interpret user input in terms of the intention that it conveys (find news) and the key entities that are present (virtual reality companies). LUIS enables you to specify the set of intents and entities that are relevant to your application, and then guides you through the process of building a language understanding application.
When you create a bot using the Language understanding template, Bot Service creates a corresponding LUIS application that is empty (i.e., that always returns None). To update your LUIS application model so that it is capable of interpreting user input, you must sign-in to LUIS, click My applications, select the application that the service created for you, and then create intents, specify entities, and train the application.
To create a bot that distills semi-structured data like question and answer pairs into distinct, helpful answers, choose the Question and Answer template. This template leverages the QnA Maker service to parse questions and provide answers.
When you create a bot with the Question and Answer template, you must sign-in to QnA Maker and create a new QnA service. This QnA service will give you the knowledge base ID and subscription key that you can use to update your App Settings values for QnAKnowldegebasedId and QnASubscriptionKey. Once those values are set, your bot can answer any questions that the QnA service has in its knowledge base.
To create a bot that can send proactive messages to the user, choose the Proactive template. Typically, each message that a bot sends to the user directly relates to the user's prior input. In some cases though, a bot may need to send the user information that is not directly related to the user's most recent message. These types of messages are called proactive messages. Proactive messages can be useful in a variety of scenarios. For example, if a bot sets a timer or reminder, it may need to notify the user when the time arrives. Or, if a bot receives a notification about an external event, it may need to communicate that information to the user.
When you create a bot by using the Proactive template, several Azure resources are automatically created and added to your resource group. By default, these Azure resources are already configured to enable a very simple proactive messaging scenario.
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| Azure Storage | Used to create the queue. |
| Azure Function App | A queueTrigger Azure Function that is triggered whenever there is a message in the queue. It communicates to Bot Service by using Direct Line. This function uses bot binding to send the message as part of the trigger’s payload. Our example function forwards the user’s message as-is from the queue. |
| Bot Service | Your bot. Contains the logic that receives the message from user, adds the message to the Azure queue, receives triggers from Azure Function, and sends back the message it received via trigger's payload. |
The following diagram shows how triggered events work when you create a bot using the Proactive template.
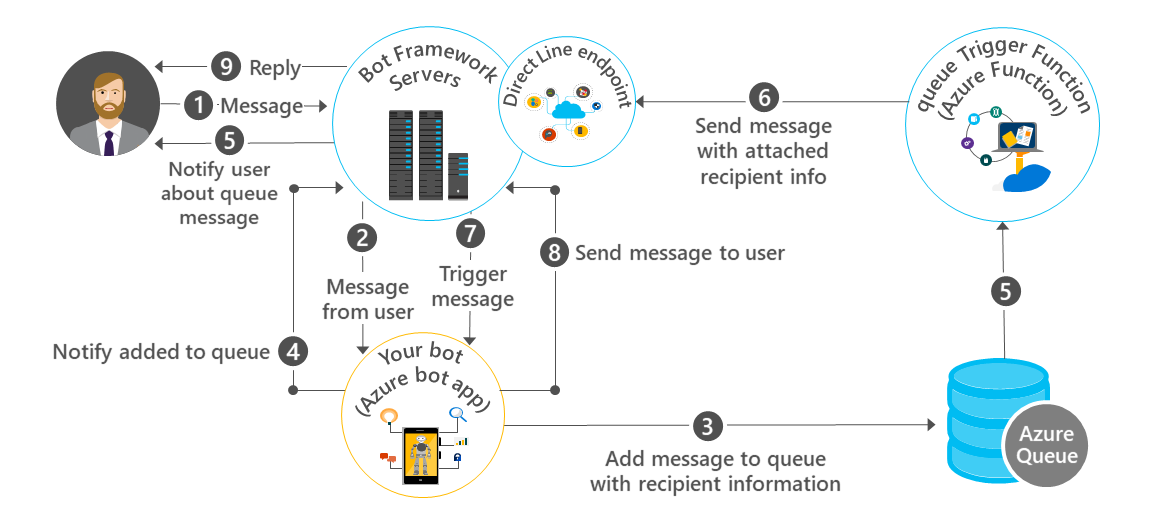
The process begins when the user sends a message to your bot via Bot Framework servers (step 1).
Now that you know about the different templates, learn about Cognitive Services for use within bots.