Overview of Disk Management
**
Disk Management is a system utility in Windows for advanced storage operations. Here are some tasks you can complete with Disk Management:
Set up a new drive. For more information, see Initialize new disks.
Extend a volume into space that's not already part of a volume on the same drive. For more information, see Extend a basic volume.
Shrink a partition, such as to enable extending into a neighboring partition. For more information, see Shrink a basic volume.
Change a drive letter or assign a new drive letter. For more information, see Change a drive letter.
Disk Management shows the details for each drive on your PC and all partitions for each drive. The details include statistics about the partitions, including the amount of space allocated or used.
The following image shows the Disk Management overview for several drives. Disk 0 has three partitions, and Disk 1 has two partitions. On Disk 0, the C: drive for Windows uses the most disk space. Two other partitions for system operations and recovery use a smaller amount of disk space.
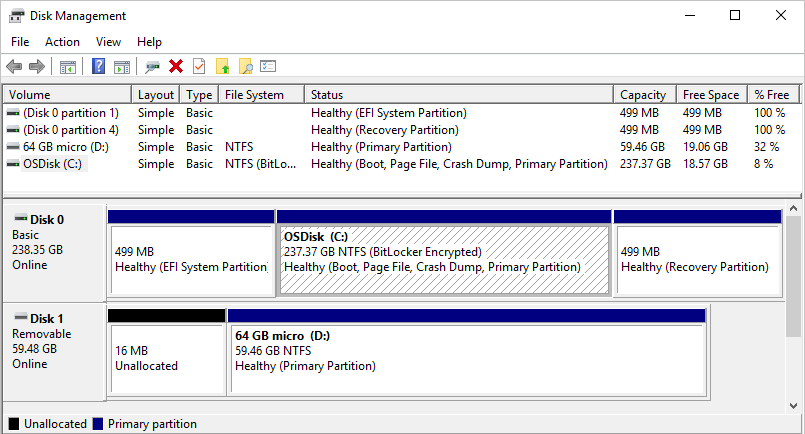
Windows typically includes three partitions on your main drive (usually the C:\ drive). These partitions include the EFI System Partition, the Local Disk (C:) Partition, and a Recovery Partition.
The Windows operating system is installed on the Local Disk (C:) Partition. This partition is the common storage location for your other apps and files.
Modern PCs use the EFI System Partition to start (boot) your PC and your operating system.
The Recovery Partition stores special tools to help you recover Windows, in case there's a problem starting the PC or other serious issues.
Important
Disk Management might show the EFI System Partition and Recovery Partition as 100 percent free. However, these partitions store critical files that your PC needs to operate properly, and the partitions are generally nearly full. It's recommended to not modify these partitions in any way.
Sometimes a Disk Management task reports an error, or a procedure doesn't work as expected. There are several options available to help you resolve the issue.
Review suggestions in the Troubleshooting Disk Management article.
Search the Microsoft Community website for posts about files, folders, and storage.
If you don't find an answer on the site, you can post a question for input from Microsoft or other members of the community. You can also Contact Microsoft Support.
Disk Management supports a wide range of drive tasks, but some tasks need to be completed by using a different tool. Here are some common disk management tasks to complete with other tools in Windows:
Free up disk space. For more information, see Free up drive space in Windows.
Defragment or optimize your drives. For more information, see Ways to improve your computer's performance.
Pool multiple hard drives together, similar to a RAID (redundant array of independent disks). For more information, see Storage Spaces in Windows.