Adicionar notificações push à sua app iOS
Descrição Geral
Neste tutorial, adiciona notificações push ao projeto de arranque rápido do iOS para que seja enviada uma notificação push para o dispositivo sempre que um registo é inserido.
Se não utilizar o projeto do servidor quickstart descarregado, necessitará do pacote de extensão de notificação push. Para obter mais informações, consulte Work with the .NET backend server SDK for Azure Mobile Apps guide.
O simulador iOS não suporta notificações push. Precisa de um dispositivo físico iOS e de um programa apple developer.
Centro de Notificação Configure
A funcionalidade de Aplicações Móveis de Serviço de Aplicações do Azure utiliza hubs de notificação Azure para enviar pushes, pelo que estará a configurar um centro de notificações para a sua aplicação móvel.
No portal do Azure, vá aos Serviços de Aplicações e, em seguida, selecione a sua app de volta. Em Definições, selecione Push.
Para adicionar um recurso de hub de notificação à aplicação, selecione Connect. Pode criar um hub ou ligar-se a um existente.
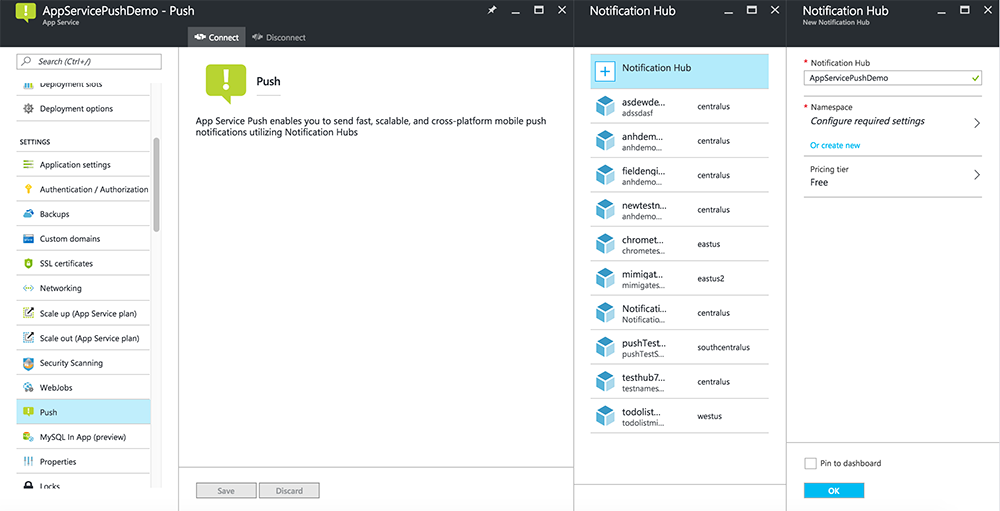
Agora ligou um centro de notificação ao seu projeto de back-end de Aplicações Móveis. Mais tarde, configura este centro de notificação para ligar a um sistema de notificação da plataforma (PNS) para empurrar para os dispositivos.
Registar aplicativo para notificações push
- Registe uma identificação de aplicativo para a sua aplicação. Crie um ID de aplicação explícito (não um ID de aplicativo wildcard) e, para o Bundle ID, use o ID do pacote exato que está no seu projeto quickstart Xcode. Também é crucial que selecione a opção 'Notificações push '.
- Em seguida, para preparar a configuração de notificações push, crie um certificado SSL de "Desenvolvimento" ou "Distribuição".
Configure Azure para enviar notificações push
- No seu Mac, lance o Keychain Access. Na barra de navegação à esquerda, na categoria, abra os Meus Certificados. Encontre o certificado SSL que descarregou na secção anterior e, em seguida, divulgue o seu conteúdo. Selecione apenas o certificado (não selecione a chave privada). Em seguida, exportá-lo.
- No portal do Azure, selecione Browse All>App Services. Em seguida, selecione as suas Aplicações Móveis de volta.
- Em Definições, selecione Serviço de Aplicações Push. Em seguida, selecione o nome do seu centro de notificação.
- Vá aoCertificado de Uploadde Serviços> de Notificação Apple Push. Faça o upload do ficheiro .p12, selecionando o modo correto (dependendo se o certificado SSL do seu cliente anteriormente é de produção ou caixa de areia). Guarde quaisquer alterações.
O seu serviço está agora configurado para trabalhar com notificações push no iOS.
Atualizar backend para enviar notificações push
.NET backend (C#):
No Estúdio Visual, clique com o botão direito no projeto do servidor e clique em Gerir Pacotes NuGet, procurar
Microsoft.Azure.NotificationHubse, em seguida, clicar em Instalar. Isto instala a biblioteca 'Centros de Notificação' para o envio de notificações do seu backend.No projeto do Backend Visual Studio, os controladores abertos>TodoItemController.cs. No topo do ficheiro, adicione a seguinte
usingdeclaração:using Microsoft.Azure.Mobile.Server.Config; using Microsoft.Azure.NotificationHubs;Substitua o método
PostTodoItempelo código abaixo:public async Task<IHttpActionResult> PostTodoItem(TodoItem item) { TodoItem current = await InsertAsync(item); // Get the settings for the server project. HttpConfiguration config = this.Configuration; MobileAppSettingsDictionary settings = this.Configuration.GetMobileAppSettingsProvider().GetMobileAppSettings(); // Get the Notification Hubs credentials for the Mobile App. string notificationHubName = settings.NotificationHubName; string notificationHubConnection = settings .Connections[MobileAppSettingsKeys.NotificationHubConnectionString].ConnectionString; // Create a new Notification Hub client. NotificationHubClient hub = NotificationHubClient .CreateClientFromConnectionString(notificationHubConnection, notificationHubName); // iOS payload var appleNotificationPayload = "{\"aps\":{\"alert\":\"" + item.Text + "\"}}"; try { // Send the push notification and log the results. var result = await hub.SendAppleNativeNotificationAsync(appleNotificationPayload); // Write the success result to the logs. config.Services.GetTraceWriter().Info(result.State.ToString()); } catch (System.Exception ex) { // Write the failure result to the logs. config.Services.GetTraceWriter() .Error(ex.Message, null, "Push.SendAsync Error"); } return CreatedAtRoute("Tables", new { id = current.Id }, current); }Republicar o projeto do servidor.
Back-end do Node.js:
Crie o seu projeto de backend.
Substitua o todoitem.js script da tabela pelo seguinte código:
var azureMobileApps = require('azure-mobile-apps'), promises = require('azure-mobile-apps/src/utilities/promises'), logger = require('azure-mobile-apps/src/logger'); var table = azureMobileApps.table(); // When adding record, send a push notification via APNS table.insert(function (context) { // For details of the Notification Hubs JavaScript SDK, // see https://aka.ms/nodejshubs logger.info('Running TodoItem.insert'); // Create a payload that contains the new item Text. var payload = "{\"aps\":{\"alert\":\"" + context.item.text + "\"}}"; // Execute the insert; Push as a post-execute action when results are returned as a Promise. return context.execute() .then(function (results) { // Only do the push if configured if (context.push) { context.push.apns.send(null, payload, function (error) { if (error) { logger.error('Error while sending push notification: ', error); } else { logger.info('Push notification sent successfully!'); } }); } return results; }) .catch(function (error) { logger.error('Error while running context.execute: ', error); }); }); module.exports = table;Ao editar o ficheiro no seu computador local, reebine o projeto do servidor.
Adicionar notificações push à app
Objetivo C:
No QSAppDeegate.m, importe o iOS SDK e qSTodoService.h:
#import <MicrosoftAzureMobile/MicrosoftAzureMobile.h> #import "QSTodoService.h"Em
didFinishLaunchingWithOptionsQSAppDeegate.m, insira as seguintes linhas imediatamente antesreturn YES;:UIUserNotificationSettings* notificationSettings = [UIUserNotificationSettings settingsForTypes:UIUserNotificationTypeAlert | UIUserNotificationTypeBadge | UIUserNotificationTypeSound categories:nil]; [[UIApplication sharedApplication] registerUserNotificationSettings:notificationSettings]; [[UIApplication sharedApplication] registerForRemoteNotifications];No QSAppDeegate.m, adicione os seguintes métodos de manipulador. A sua aplicação está agora atualizada para suportar notificações push.
// Registration with APNs is successful - (void)application:(UIApplication *)application didRegisterForRemoteNotificationsWithDeviceToken:(NSData *)deviceToken { QSTodoService *todoService = [QSTodoService defaultService]; MSClient *client = todoService.client; [client.push registerDeviceToken:deviceToken completion:^(NSError *error) { if (error != nil) { NSLog(@"Error registering for notifications: %@", error); } }]; } // Handle any failure to register - (void)application:(UIApplication *)application didFailToRegisterForRemoteNotificationsWithError: (NSError *)error { NSLog(@"Failed to register for remote notifications: %@", error); } // Use userInfo in the payload to display an alert. - (void)application:(UIApplication *)application didReceiveRemoteNotification:(NSDictionary *)userInfo { NSLog(@"%@", userInfo); NSDictionary *apsPayload = userInfo[@"aps"]; NSString *alertString = apsPayload[@"alert"]; // Create alert with notification content. UIAlertController *alertController = [UIAlertController alertControllerWithTitle:@"Notification" message:alertString preferredStyle:UIAlertControllerStyleAlert]; UIAlertAction *cancelAction = [UIAlertAction actionWithTitle:NSLocalizedString(@"Cancel", @"Cancel") style:UIAlertActionStyleCancel handler:^(UIAlertAction *action) { NSLog(@"Cancel"); }]; UIAlertAction *okAction = [UIAlertAction actionWithTitle:NSLocalizedString(@"OK", @"OK") style:UIAlertActionStyleDefault handler:^(UIAlertAction *action) { NSLog(@"OK"); }]; [alertController addAction:cancelAction]; [alertController addAction:okAction]; // Get current view controller. UIViewController *currentViewController = [[[[UIApplication sharedApplication] delegate] window] rootViewController]; while (currentViewController.presentedViewController) { currentViewController = currentViewController.presentedViewController; } // Display alert. [currentViewController presentViewController:alertController animated:YES completion:nil]; }
Rápido:
Adicione ficheiro ClienteManager.swift com os seguintes conteúdos. Substitua %AppUrl% pelo URL do backend da Aplicação Móvel Azure.
class ClientManager { static let sharedClient = MSClient(applicationURLString: "%AppUrl%") }No ToDoTableViewController.swift, substitua a
let clientlinha que inicializa umaMSClientcom esta linha:let client = ClientManager.sharedClientNo AppDeegate.swift, substitua o corpo da
func applicationseguinte forma:func application(application: UIApplication, didFinishLaunchingWithOptions launchOptions: [NSObject: AnyObject]?) -> Bool { application.registerUserNotificationSettings( UIUserNotificationSettings(forTypes: [.Alert, .Badge, .Sound], categories: nil)) application.registerForRemoteNotifications() return true }No AppDeegate.swift, adicione os seguintes métodos de manipulador. A sua aplicação está agora atualizada para suportar notificações push.
func application(application: UIApplication, didRegisterForRemoteNotificationsWithDeviceToken deviceToken: NSData) { ClientManager.sharedClient.push?.registerDeviceToken(deviceToken) { error in print("Error registering for notifications: ", error?.description) } } func application(application: UIApplication, didFailToRegisterForRemoteNotificationsWithError error: NSError) { print("Failed to register for remote notifications: ", error.description) } func application(application: UIApplication, didReceiveRemoteNotification userInfo: [NSObject: AnyObject]) { print(userInfo) let apsNotification = userInfo["aps"] as? NSDictionary let apsString = apsNotification?["alert"] as? String let alert = UIAlertController(title: "Alert", message: apsString, preferredStyle: .Alert) let okAction = UIAlertAction(title: "OK", style: .Default) { _ in print("OK") } let cancelAction = UIAlertAction(title: "Cancel", style: .Default) { _ in print("Cancel") } alert.addAction(okAction) alert.addAction(cancelAction) var currentViewController = self.window?.rootViewController while currentViewController?.presentedViewController != nil { currentViewController = currentViewController?.presentedViewController } currentViewController?.presentViewController(alert, animated: true) {} }
Teste notificações push
- No Xcode, prima Executar e inicie a aplicação num dispositivo iOS (note que o push não funcionará em simuladores). Clique em OK para aceitar notificações push; este pedido ocorre na primeira vez que a aplicação é executado.
- Na aplicação, adicione um novo item e clique +.
- Verifique se uma notificação é recebida e, em seguida, clique em OK para rejeitar a notificação. Já concluiu este tutorial com sucesso.
Mais
- Os modelos dão-lhe flexibilidade para enviar impulsos de plataforma cruzada e impulsos localizados. Como utilizar a biblioteca de clientes iOS para aplicações móveis Azure mostra-lhe como registar modelos.