Turn on network protection
Applies to:
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Plan 1
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Plan 2
- Microsoft Defender XDR
- Microsoft Defender for Servers
- Microsoft Defender Antivirus
Platforms
- Windows
- Linux (See Network protection for Linux)
- macOS (See Network protection for macOS)
Tip
Want to experience Defender for Endpoint? Sign up for a free trial.
Network protection helps to prevent employees from using any application to access dangerous domains that might host phishing scams, exploits, and other malicious content on the internet. You can audit network protection in a test environment to view which apps would be blocked before enabling network protection.
Learn more about network filtering configuration options.
Check if network protection is enabled
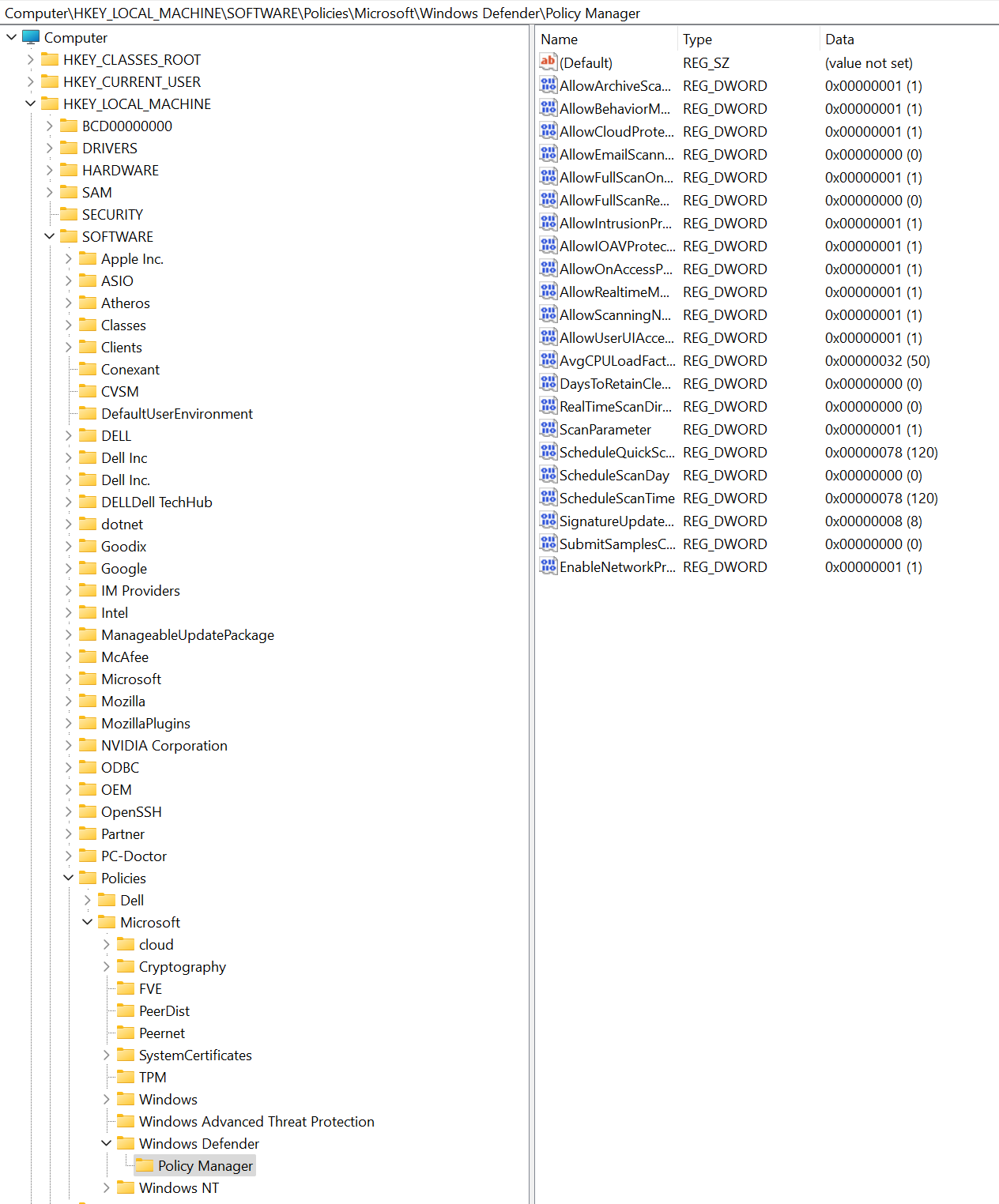
You can use Registry Editor to check the status of network protection.
Select the Start button in the task bar and type
regedit. In the list of results, select Registry editor to open it.Choose HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE from the side menu.
Navigate through the nested menus to SOFTWARE > Policies > Microsoft > Windows Defender > Policy Manager.
If the key is missing, navigate to SOFTWARE > Microsoft > Windows Defender > Windows Defender Exploit Guard > Network Protection.
Select EnableNetworkProtection to see the current state of network protection on the device:
- 0, or Off
- 1, or On
- 2, or Audit mode
Enable network protection
To enable network protection, you can use one of the following methods:
- PowerShell
- Mobile Device Management (MDM)
- Microsoft Intune
- Group Policy
- Microsoft Configuration Manager
PowerShell
On your Windows device, select Start, type
powershell, right-click Windows PowerShell, and then select Run as administrator.Run the following cmdlet:
Set-MpPreference -EnableNetworkProtection EnabledFor Windows Server, use the additional commands that listed in the following table:
Windows Server version Commands Windows Server 2019 and later set-mpPreference -AllowNetworkProtectionOnWinServer $trueWindows Server 2016
Windows Server 2012 R2 with the unified agent for Microsoft Defender for Endpointset-MpPreference -AllowNetworkProtectionDownLevel $true
set-MpPreference -AllowNetworkProtectionOnWinServer $true(This step is optional.) To set network protection to audit mode, use the following cmdlet:
Set-MpPreference -EnableNetworkProtection AuditModeTo turn off network protection, use the
Disabledparameter instead ofAuditModeorEnabled.
Mobile device management (MDM)
Use the EnableNetworkProtection configuration service provider (CSP) to enable or disable network protection or enable audit mode.
Update Microsoft Defender antimalware platform to the latest version before you enable or disable network protection or enable audit mode.
Microsoft Intune
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Baseline method
Sign into the Microsoft Intune admin center.
Go to Endpoint security > Security baselines > Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Baseline.
Select Create a profile, then provide a name for your profile, and then select Next.
In the Configuration settings section, go to Attack Surface Reduction Rules > set Block, Enable, or Audit for Enable network protection. Select Next.
Select the appropriate Scope tags and Assignments as required by your organization.
Review all the information, and then select Create.
Antivirus policy method
Sign into the Microsoft Intune admin center.
Go to Endpoint security > Antivirus.
Select Create a policy.
In the Create a policy flyout, choose Windows 10, Windows 11, and Windows Server from the Platform list.
Choose Microsoft Defender Antivirus from the Profile list then choose Create.
Provide a name for your profile, and then select Next.
In the Configuration settings section, select Disabled, Enabled (block mode) or Enabled (audit mode) for Enable Network Protection, then select Next.
Select the appropriate Assignments and Scope tags as required by your organization.
Review all the information, and then select Create.
Configuration profile method
Sign into the Microsoft Intune admin center (https://intune.microsoft.com).
Go to Devices > Configuration profiles > Create profile.
In the Create a profile flyout, select Platform and choose the Profile Type as Templates.
In the Template name, Choose Endpoint protection from the list of templates, and then select Create.
Go to Endpoint protection > Basics, provide a name for your profile, and then select Next.
In the Configuration settings section, go to Microsoft Defender Exploit Guard > Network filtering > Network protection > Enable or Audit. Select Next.
Select the appropriate Scope tags, Assignments, and Applicability rules as required by your organization. Admins can set more requirements.
Review all the information, and then select Create.
Group Policy
Use the following procedure to enable network protection on domain-joined computers or on a standalone computer.
On a standalone computer, go to Start and then type and select Edit group policy.
-Or-
On a domain-joined Group Policy management computer, open the Group Policy Management Console, right-click the Group Policy Object you want to configure and select Edit.
In the Group Policy Management Editor, go to Computer configuration and select Administrative templates.
Expand the tree to Windows components > Microsoft Defender Antivirus > Microsoft Defender Exploit Guard > Network protection.
Note that on older versions of Windows, the Group Policy path might have Windows Defender Antivirus instead of Microsoft Defender Antivirus.
Double-click the Prevent users and apps from accessing dangerous websites setting and set the option to Enabled. In the options section, you must specify one of the following options:
- Block - Users can't access malicious IP addresses and domains.
- Disable (Default) - The Network protection feature won't work. Users aren't blocked from accessing malicious domains.
- Audit Mode - If a user visits a malicious IP address or domain, an event will be recorded in the Windows event log. However, the user won't be blocked from visiting the address.
Important
To fully enable network protection, you must set the Group Policy option to Enabled and also select Block in the options drop-down menu.
(This step is optional.) Follow the steps in Check if network protection is enabled to verify that your Group Policy settings are correct.
Microsoft Configuration Manager
Open the Configuration Manager console.
Go to Assets and Compliance > Endpoint Protection > Windows Defender Exploit Guard.
Select Create Exploit Guard Policy from the ribbon to create a new policy.
- To edit an existing policy, select the policy, then select Properties from either the ribbon or the right-click menu. Edit the Configure network protection option from the Network Protection tab.
On the General page, specify a name for the new policy and verify the Network protection option is enabled.
On the Network protection page, select one of the following settings for the Configure network protection option:
- Block
- Audit
- Disabled
Complete the rest of the steps, and save the policy.
From the ribbon, select Deploy to deploy the policy to a collection.
Important information about removing Exploit Guard settings from a device
Once an Exploit Guard policy is deployed using Configuration Manager, Exploit Guard settings aren't removed from the clients if you remove the deployment. Furthermore, if you remove the client's Exploit Guard deployment, Delete not supported is recorded in the client's ExploitGuardHandler.log in Configuration Manager.
Use the following PowerShell script in the SYSTEM context to remove Exploit Guard settings correctly:
$defenderObject = Get-WmiObject -Namespace "root/cimv2/mdm/dmmap" -Class "MDM_Policy_Config01_Defender02" -Filter "InstanceID='Defender' and ParentID='./Vendor/MSFT/Policy/Config'"
$defenderObject.AttackSurfaceReductionRules = $null
$defenderObject.AttackSurfaceReductionOnlyExclusions = $null
$defenderObject.EnableControlledFolderAccess = $null
$defenderObject.ControlledFolderAccessAllowedApplications = $null
$defenderObject.ControlledFolderAccessProtectedFolders = $null
$defenderObject.EnableNetworkProtection = $null
$defenderObject.Put()
$exploitGuardObject = Get-WmiObject -Namespace "root/cimv2/mdm/dmmap" -Class "MDM_Policy_Config01_ExploitGuard02" -Filter "InstanceID='ExploitGuard' and ParentID='./Vendor/MSFT/Policy/Config'"
$exploitGuardObject.ExploitProtectionSettings = $null
$exploitGuardObject.Put()
See also
- Network protection
- Network protection for Linux
- Network protection for macOS
- Network protection and the TCP three-way handshake
- Evaluate network protection
- Troubleshoot network protection
Tip
Do you want to learn more? Engage with the Microsoft Security community in our Tech Community: Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Tech Community.