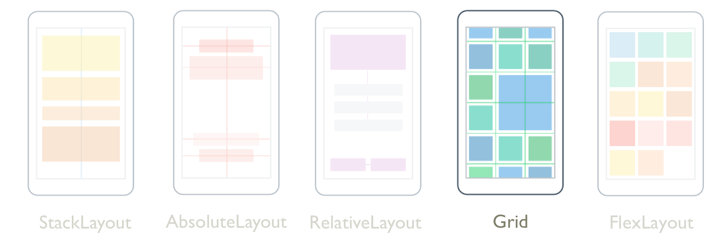
Xamarin.Forms グリッド
Grid は、子を行と列に編成するレイアウトであり、比例サイズまたは絶対サイズを指定できます。 既定では、Grid には 1 つの行と 1 つの列が含まれます。 さらに Grid は、他の子レイアウトを含む親レイアウトとして使用できます。
Grid レイアウトを表と混同しないでください。また、表形式データを表示することを目的としたものではありません。 HTML テーブルとは異なり、Grid はコンテンツをレイアウトするためのものです。 表形式データを表示するには、ListView、CollectionView、または TableView の使用を検討してください。
Grid クラスには、次のプロパティが定義されています。
int型のColumnは、親のGrid内のビューの列の配置を示す添付プロパティです。 このプロパティの既定値は 0です。 検証コールバックは、プロパティを設定するときに、その値が 0 以上であるようにします。ColumnDefinitionCollection型のColumnDefinitionsは、グリッドの列の幅を定義するColumnDefinitionオブジェクトのリストです。double型のColumnSpacingは、グリッドの列間の距離を示します。 このプロパティの既定値は、デバイスに依存しない 6 単位です。int型のColumnSpanは、ビューが親のGrid内にまたがる列の合計数を示す添付プロパティです。 このプロパティの既定値は 1です。 検証コールバックは、プロパティを設定するときに、その値が 1 以上であるようにします。int型のRowは、親のGrid内のビューの行の配置を示す添付プロパティです。 このプロパティの既定値は 0です。 検証コールバックは、プロパティを設定するときに、その値が 0 以上であるようにします。RowDefinitionCollection型のRowDefinitionsは、グリッド行の高さを定義するRowDefintionオブジェクトのリストです。double型のRowSpacingは、グリッド行の間の距離を示します。 このプロパティの既定値は、デバイスに依存しない 6 単位です。int型のRowSpanは、ビューが親のGrid内にまたがる行の合計数を示す添付プロパティです。 このプロパティの既定値は 1です。 検証コールバックは、プロパティを設定するときに、その値が 1 以上であるようにします。
これらのプロパティは、BindableProperty オブジェクトがサポートしています。つまり、プロパティをデータ バインディングの対象にして、スタイル設定することができます。
Grid クラスは、IList<T> 型の Children プロパティを定義する Layout<T> クラスから派生します。 Children プロパティは Layout<T> クラスの ContentProperty であるため、XAML から明示的に設定する必要はありません。
ヒント
可能な限り最適なレイアウト パフォーマンスを得るために、「レイアウトのパフォーマンスを最適化する」のガイドラインに従ってください。
行と列
既定では、Grid には 1 つの行と 1 つの列が含まれています。
<ContentPage xmlns="http://xamarin.com/schemas/2014/forms"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml"
x:Class="GridTutorial.MainPage">
<Grid Margin="20,35,20,20">
<Label Text="By default, a Grid contains one row and one column." />
</Grid>
</ContentPage>
この例では、Grid には 1 つの場所に自動的に配置される 1 つの子 Label が含まれています。
Grid のレイアウト動作は、RowDefinitions プロパティと ColumnDefinitions プロパティで定義できます。これらのプロパティは、それぞれ RowDefinition オブジェクトと ColumnDefinition オブジェクトのコレクションです。 これらのコレクションは、Grid の行と列の特性を定義するもので、Grid の行ごとに 1 つの RowDefinition オブジェクトと、Grid の列ごとに 1 つの ColumnDefinition オブジェクトを含んでいる必要があります。
RowDefinition クラスは GridLength 型の Height プロパティを定義し、ColumnDefinition クラスは GridLength 型の Width プロパティを定義します。 GridLength 構造体は、行の高さや列の幅を、次の 3 つのメンバーを持つ GridUnitType 列挙型で指定します。
Absolute: 行の高さや列の幅は、デバイスに依存しない単位で表される値 (XAML では数値) です。Auto: 行の高さや列の幅は、セルの内容に基づいて自動サイズ調整されます (XAML ではAuto)。Star: 残りの行の高さや列の幅は比例配分されます (XAML では数値の後に*が続きます)。
Height プロパティが Auto である Grid 行は、垂直方向の StackLayout と同じ方法でその行のビューの高さを制限します。 同様に、Width プロパティが Auto の列は、水平の StackLayout と動作がよく似ています。
注意
Auto サイズに設定する行と列をできるだけ少なくしてください。 自動サイズ調整された行または列はそれぞれ、レイアウト エンジンに追加のレイアウト計算を実行させることになります。 その代わりに可能であれば、固定サイズの行と列を使用してください。 または、GridUnitType.Star 列挙値を利用し、比率によって領域を占めるように行と列を設定します。
次の XAML は、3 つの行と 2 つの列を含む Grid を作成する方法を示しています。
<ContentPage xmlns="http://xamarin.com/schemas/2014/forms"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml"
x:Class="GridDemos.Views.BasicGridPage"
Title="Basic Grid demo">
<Grid>
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="2*" />
<RowDefinition Height="*" />
<RowDefinition Height="100" />
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition Width="*" />
<ColumnDefinition Width="*" />
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
...
</Grid>
</ContentPage>
この例では、Grid の全体の高さはページの高さになります。 Grid は、3 行目の高さがデバイスに依存しない 100 単位であることを認識しています。 その高さを自身の高さから減算し、星の前の数字に基づいて、残りの高さを 1 行目と 2 行目に比例して割り当てます。 この例では、最初の行の高さは 2 行目の高さの 2 倍です。
2 つの ColumnDefinition オブジェクトは両方とも、Width を * (1* と同じ) に設定します。つまり、画面の幅が 2 つの列の下で均等に分割されます。
重要
RowDefinition.Height プロパティの既定値は * です。 同様に、ColumnDefinition.Width プロパティの既定値は * です。 したがって、これらの既定値が許容される場合は、これらのプロパティを設定する必要はありません。
子ビューは、Grid.Column と Grid.Row の添付プロパティを持つ特定の Grid セルに配置できます。 さらに、子ビューを複数の行と列にまたがるようにするには、Grid.RowSpan と Grid.ColumnSpan の添付プロパティを使用します。
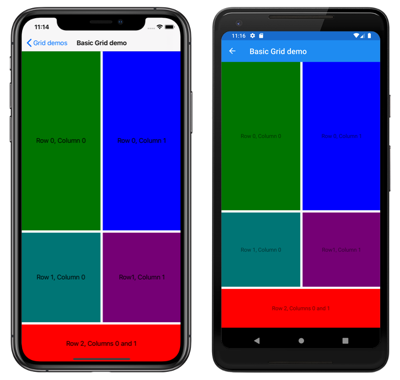
次の XAML は、同じ Grid 定義を示し、特定の Grid セルに子ビューを配置します。
<ContentPage xmlns="http://xamarin.com/schemas/2014/forms"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml"
x:Class="GridDemos.Views.BasicGridPage"
Title="Basic Grid demo">
<Grid>
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="2*" />
<RowDefinition />
<RowDefinition Height="100" />
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition />
<ColumnDefinition />
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<BoxView Color="Green" />
<Label Text="Row 0, Column 0"
HorizontalOptions="Center"
VerticalOptions="Center" />
<BoxView Grid.Column="1"
Color="Blue" />
<Label Grid.Column="1"
Text="Row 0, Column 1"
HorizontalOptions="Center"
VerticalOptions="Center" />
<BoxView Grid.Row="1"
Color="Teal" />
<Label Grid.Row="1"
Text="Row 1, Column 0"
HorizontalOptions="Center"
VerticalOptions="Center" />
<BoxView Grid.Row="1"
Grid.Column="1"
Color="Purple" />
<Label Grid.Row="1"
Grid.Column="1"
Text="Row1, Column 1"
HorizontalOptions="Center"
VerticalOptions="Center" />
<BoxView Grid.Row="2"
Grid.ColumnSpan="2"
Color="Red" />
<Label Grid.Row="2"
Grid.ColumnSpan="2"
Text="Row 2, Columns 0 and 1"
HorizontalOptions="Center"
VerticalOptions="Center" />
</Grid>
</ContentPage>
Note
Grid.Row と Grid.Column のプロパティはどちらも 0 からインデックスが作成されるため、Grid.Row="2" は 3 番目の行を参照し、Grid.Column="1" は 2 番目の列を参照します。 さらに、これらのプロパティの既定値は両方とも 0 であるため、Grid の最初の行または最初の列を占有する子ビューでは設定する必要はありません。
この例では、3 つの Grid 行すべてが BoxView と Label のビューによって占有されています。 3 行目はデバイスに依存しない 100 単位の高さあり、最初の 2 行は残りの領域を占有します (最初の行の高さは 2 行目の 2 倍です)。 2 つの列は幅が等しく、Grid を半分に分割します。 3 行目の BoxView は両方の列にまたがります。
また、Grid の子ビューではセルを共有できます。 子が XAML に表示される順序は、子が Grid に配置される順序です。 前の例では、Label オブジェクトは、BoxView オブジェクトの上にレンダリングされるため、表示されるだけです。 Label オブジェクトは、BoxView オブジェクトの上にレンダリングされた場合は表示されません。
同等の C# コードを次に示します。
public class BasicGridPageCS : ContentPage
{
public BasicGridPageCS()
{
Grid grid = new Grid
{
RowDefinitions =
{
new RowDefinition { Height = new GridLength(2, GridUnitType.Star) },
new RowDefinition(),
new RowDefinition { Height = new GridLength(100) }
},
ColumnDefinitions =
{
new ColumnDefinition(),
new ColumnDefinition()
}
};
// Row 0
// The BoxView and Label are in row 0 and column 0, and so only needs to be added to the
// Grid.Children collection to get default row and column settings.
grid.Children.Add(new BoxView
{
Color = Color.Green
});
grid.Children.Add(new Label
{
Text = "Row 0, Column 0",
HorizontalOptions = LayoutOptions.Center,
VerticalOptions = LayoutOptions.Center
});
// This BoxView and Label are in row 0 and column 1, which are specified as arguments
// to the Add method.
grid.Children.Add(new BoxView
{
Color = Color.Blue
}, 1, 0);
grid.Children.Add(new Label
{
Text = "Row 0, Column 1",
HorizontalOptions = LayoutOptions.Center,
VerticalOptions = LayoutOptions.Center
}, 1, 0);
// Row 1
// This BoxView and Label are in row 1 and column 0, which are specified as arguments
// to the Add method overload.
grid.Children.Add(new BoxView
{
Color = Color.Teal
}, 0, 1, 1, 2);
grid.Children.Add(new Label
{
Text = "Row 1, Column 0",
HorizontalOptions = LayoutOptions.Center,
VerticalOptions = LayoutOptions.Center
}, 0, 1, 1, 2); // These arguments indicate that that the child element goes in the column starting at 0 but ending before 1.
// They also indicate that the child element goes in the row starting at 1 but ending before 2.
grid.Children.Add(new BoxView
{
Color = Color.Purple
}, 1, 2, 1, 2);
grid.Children.Add(new Label
{
Text = "Row1, Column 1",
HorizontalOptions = LayoutOptions.Center,
VerticalOptions = LayoutOptions.Center
}, 1, 2, 1, 2);
// Row 2
// Alternatively, the BoxView and Label can be positioned in cells with the Grid.SetRow
// and Grid.SetColumn methods.
BoxView boxView = new BoxView { Color = Color.Red };
Grid.SetRow(boxView, 2);
Grid.SetColumnSpan(boxView, 2);
Label label = new Label
{
Text = "Row 2, Column 0 and 1",
HorizontalOptions = LayoutOptions.Center,
VerticalOptions = LayoutOptions.Center
};
Grid.SetRow(label, 2);
Grid.SetColumnSpan(label, 2);
grid.Children.Add(boxView);
grid.Children.Add(label);
Title = "Basic Grid demo";
Content = grid;
}
}
コードでは、RowDefinition オブジェクトの高さと ColumnDefinition オブジェクトの幅を指定するために、GridLength 構造体の値を使用します。多くの場合、GridUnitType 列挙型と組み合わせて使用します。
上記のコード例は、子を Grid に追加し、子が存在するセルを指定するためのいくつかの異なるアプローチも示しています。 left、right、top、bottom 引数を指定する Add オーバーロードを使う場合、left と top 引数は常に Grid の内側のセルを参照し、right と bottom 引数は Grid の外側のセルを参照しているように見えます。 これは、right 引数は常に left 引数より大きくなければならず、bottom 引数は常に top 引数より大きくなければならないためです。 次の例は 2x2 の Grid を想定しており、両方の Add オーバーロードを使った同等のコードを示しています。
// left, top
grid.Children.Add(topLeft, 0, 0); // first column, first row
grid.Children.Add(topRight, 1, 0); // second column, first tow
grid.Children.Add(bottomLeft, 0, 1); // first column, second row
grid.Children.Add(bottomRight, 1, 1); // second column, second row
// left, right, top, bottom
grid.Children.Add(topLeft, 0, 1, 0, 1); // first column, first row
grid.Children.Add(topRight, 1, 2, 0, 1); // second column, first tow
grid.Children.Add(bottomLeft, 0, 1, 1, 2); // first column, second row
grid.Children.Add(bottomRight, 1, 2, 1, 2); // second column, second row
Note
さらに、子を 1 行または 1 列の Grid に追加する AddHorizontal メソッドと AddVertical メソッドを使って子ビューを Grid に追加できます。 Grid では、これらの呼び出しが行われると、行または列が展開され、子が正しいセルに自動的に配置されます。
行と列の定義を簡略化する
XAML では、各行と列の RowDefinition と ColumnDefinition のオブジェクトの定義の必要性を回避する簡略化された構文を使用して、Grid の行と列の特性を指定できます。 代わりに、RowDefinitions プロパティと ColumnDefinitions プロパティを、コンマ区切りの GridUnitType 値を含む文字列に設定できます。この値から、Xamarin.Forms に組み込まれた型コンバーターが RowDefinition オブジェクトと ColumnDefinition オブジェクトを作成します。
<Grid RowDefinitions="1*, Auto, 25, 14, 20"
ColumnDefinitions="*, 2*, Auto, 300">
...
</Grid>
この例では、 Grid には 5 つの行と 4 つの列があります。 3 行目、4 行目、5 行目の高さは絶対値に設定され、2 行目は内容に合わせて自動的にサイズ調整されます。 その後、残りの高さが最初の行に割り当てられます。
4 番目の列の幅は絶対値に設定され、3 番目の列はその内容に合わせて自動的にサイズ調整されます。 残りの幅は、星の前の数に基づいて、最初の列と 2 番目の列の間に比例して割り当てられます。 この例では、2 番目の列の幅は最初の列の幅の 2 倍です (* は 1* と同じであるため)。
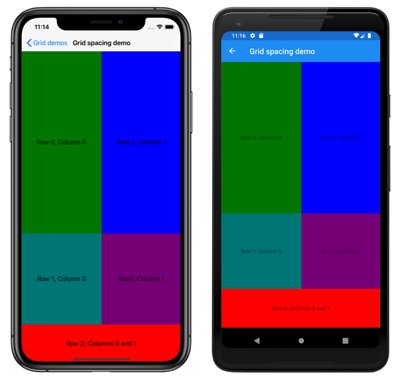
行と列の間のスペース
既定では、Grid 行はデバイスに依存しない 6 単位のスペースで区切られます。 同様に、Grid 列は、デバイスに依存しない 6 単位のスペースで区切られます。 これらの既定値は、それぞれ RowSpacing プロパティと ColumnSpacing プロパティを設定することで変更できます。
<ContentPage xmlns="http://xamarin.com/schemas/2014/forms"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml"
x:Class="GridDemos.Views.GridSpacingPage"
Title="Grid spacing demo">
<Grid RowSpacing="0"
ColumnSpacing="0">
..
</Grid>
</ContentPage>
この例では、行と列の間にスペースのない Grid を作成します。
ヒント
RowSpacing と ColumnSpacing のプロパティを負の値に設定すれば、セルの内容を重ね合わせることができます。
同等の C# コードを次に示します。
public GridSpacingPageCS()
{
Grid grid = new Grid
{
RowSpacing = 0,
ColumnSpacing = 0,
// ...
};
// ...
Content = grid;
}
Alignment
Grid 内の子ビューは、セル内で、HorizontalOptions と VerticalOptions のプロパティによって配置できます。 これらのプロパティは、LayoutOptions 構造体から次のフィールドに設定できます。
重要
LayoutOptions 構造体の AndExpands フィールドは、StackLayout オブジェクトにのみ適用されます。
次の XAML では、9 つの等しいサイズのセルを持つ Grid を作成し、Label を異なる配置を持つ各セルにを配置します。
<ContentPage xmlns="http://xamarin.com/schemas/2014/forms"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml"
x:Class="GridDemos.Views.GridAlignmentPage"
Title="Grid alignment demo">
<Grid RowSpacing="0"
ColumnSpacing="0">
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition />
<RowDefinition />
<RowDefinition />
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition />
<ColumnDefinition />
<ColumnDefinition />
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<BoxView Color="AliceBlue" />
<Label Text="Upper left"
HorizontalOptions="Start"
VerticalOptions="Start" />
<BoxView Grid.Column="1"
Color="LightSkyBlue" />
<Label Grid.Column="1"
Text="Upper center"
HorizontalOptions="Center"
VerticalOptions="Start"/>
<BoxView Grid.Column="2"
Color="CadetBlue" />
<Label Grid.Column="2"
Text="Upper right"
HorizontalOptions="End"
VerticalOptions="Start" />
<BoxView Grid.Row="1"
Color="CornflowerBlue" />
<Label Grid.Row="1"
Text="Center left"
HorizontalOptions="Start"
VerticalOptions="Center" />
<BoxView Grid.Row="1"
Grid.Column="1"
Color="DodgerBlue" />
<Label Grid.Row="1"
Grid.Column="1"
Text="Center center"
HorizontalOptions="Center"
VerticalOptions="Center" />
<BoxView Grid.Row="1"
Grid.Column="2"
Color="DarkSlateBlue" />
<Label Grid.Row="1"
Grid.Column="2"
Text="Center right"
HorizontalOptions="End"
VerticalOptions="Center" />
<BoxView Grid.Row="2"
Color="SteelBlue" />
<Label Grid.Row="2"
Text="Lower left"
HorizontalOptions="Start"
VerticalOptions="End" />
<BoxView Grid.Row="2"
Grid.Column="1"
Color="LightBlue" />
<Label Grid.Row="2"
Grid.Column="1"
Text="Lower center"
HorizontalOptions="Center"
VerticalOptions="End" />
<BoxView Grid.Row="2"
Grid.Column="2"
Color="BlueViolet" />
<Label Grid.Row="2"
Grid.Column="2"
Text="Lower right"
HorizontalOptions="End"
VerticalOptions="End" />
</Grid>
</ContentPage>
この例では、各行の Label オブジェクトはすべて垂直方向に同じように配置されますが、水平方向の配置は異なります。 または、これは、各列の Label オブジェクトが同じように水平方向に配置されているものの、異なる垂直方向の配置を使用すると考えることができます。
同等の C# コードを次に示します。
public class GridAlignmentPageCS : ContentPage
{
public GridAlignmentPageCS()
{
Grid grid = new Grid
{
RowSpacing = 0,
ColumnSpacing = 0,
RowDefinitions =
{
new RowDefinition(),
new RowDefinition(),
new RowDefinition()
},
ColumnDefinitions =
{
new ColumnDefinition(),
new ColumnDefinition(),
new ColumnDefinition()
}
};
// Row 0
grid.Children.Add(new BoxView
{
Color = Color.AliceBlue
});
grid.Children.Add(new Label
{
Text = "Upper left",
HorizontalOptions = LayoutOptions.Start,
VerticalOptions = LayoutOptions.Start
});
grid.Children.Add(new BoxView
{
Color = Color.LightSkyBlue
}, 1, 0);
grid.Children.Add(new Label
{
Text = "Upper center",
HorizontalOptions = LayoutOptions.Center,
VerticalOptions = LayoutOptions.Start
}, 1, 0);
grid.Children.Add(new BoxView
{
Color = Color.CadetBlue
}, 2, 0);
grid.Children.Add(new Label
{
Text = "Upper right",
HorizontalOptions = LayoutOptions.End,
VerticalOptions = LayoutOptions.Start
}, 2, 0);
// Row 1
grid.Children.Add(new BoxView
{
Color = Color.CornflowerBlue
}, 0, 1);
grid.Children.Add(new Label
{
Text = "Center left",
HorizontalOptions = LayoutOptions.Start,
VerticalOptions = LayoutOptions.Center
}, 0, 1);
grid.Children.Add(new BoxView
{
Color = Color.DodgerBlue
}, 1, 1);
grid.Children.Add(new Label
{
Text = "Center center",
HorizontalOptions = LayoutOptions.Center,
VerticalOptions = LayoutOptions.Center
}, 1, 1);
grid.Children.Add(new BoxView
{
Color = Color.DarkSlateBlue
}, 2, 1);
grid.Children.Add(new Label
{
Text = "Center right",
HorizontalOptions = LayoutOptions.End,
VerticalOptions = LayoutOptions.Center
}, 2, 1);
// Row 2
grid.Children.Add(new BoxView
{
Color = Color.SteelBlue
}, 0, 2);
grid.Children.Add(new Label
{
Text = "Lower left",
HorizontalOptions = LayoutOptions.Start,
VerticalOptions = LayoutOptions.End
}, 0, 2);
grid.Children.Add(new BoxView
{
Color = Color.LightBlue
}, 1, 2);
grid.Children.Add(new Label
{
Text = "Lower center",
HorizontalOptions = LayoutOptions.Center,
VerticalOptions = LayoutOptions.End
}, 1, 2);
grid.Children.Add(new BoxView
{
Color = Color.BlueViolet
}, 2, 2);
grid.Children.Add(new Label
{
Text = "Lower right",
HorizontalOptions = LayoutOptions.End,
VerticalOptions = LayoutOptions.End
}, 2, 2);
Title = "Grid alignment demo";
Content = grid;
}
}
入れ子になった Grid オブジェクト
Grid は、入れ子になった子 Grid オブジェクトまたはその他の子レイアウトを含む親レイアウトとして使用できます。 Grid オブジェクトを入れ子にすると、Grid.Row、Grid.Column、Grid.RowSpan、Grid.ColumnSpan の各添付プロパティは、常に親 Grid 内のビューの位置を参照します。
次の XAML は、Grid オブジェクトを入れ子にする例を示しています。
<ContentPage xmlns="http://xamarin.com/schemas/2014/forms"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml"
xmlns:converters="clr-namespace:GridDemos.Converters"
x:Class="GridDemos.Views.ColorSlidersGridPage"
Title="Nested Grids demo">
<ContentPage.Resources>
<converters:DoubleToIntConverter x:Key="doubleToInt" />
<Style TargetType="Label">
<Setter Property="HorizontalTextAlignment"
Value="Center" />
</Style>
</ContentPage.Resources>
<Grid>
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition />
<RowDefinition Height="Auto" />
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<BoxView x:Name="boxView"
Color="Black" />
<Grid Grid.Row="1"
Margin="20">
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition />
<RowDefinition />
<RowDefinition />
<RowDefinition />
<RowDefinition />
<RowDefinition />
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<Slider x:Name="redSlider"
ValueChanged="OnSliderValueChanged" />
<Label Grid.Row="1"
Text="{Binding Source={x:Reference redSlider},
Path=Value,
Converter={StaticResource doubleToInt},
ConverterParameter=255,
StringFormat='Red = {0}'}" />
<Slider x:Name="greenSlider"
Grid.Row="2"
ValueChanged="OnSliderValueChanged" />
<Label Grid.Row="3"
Text="{Binding Source={x:Reference greenSlider},
Path=Value,
Converter={StaticResource doubleToInt},
ConverterParameter=255,
StringFormat='Green = {0}'}" />
<Slider x:Name="blueSlider"
Grid.Row="4"
ValueChanged="OnSliderValueChanged" />
<Label Grid.Row="5"
Text="{Binding Source={x:Reference blueSlider},
Path=Value,
Converter={StaticResource doubleToInt},
ConverterParameter=255,
StringFormat='Blue = {0}'}" />
</Grid>
</Grid>
</ContentPage>
この例では、ルート Grid レイアウトの最初の行に BoxView が含まれ、2 行目に子 Grid が含まれています。 子 Grid には、BoxView で表示される色を操作する Slider オブジェクトと、それぞれの Slider の値を表示する Label オブジェクトが含まれています。
重要
Grid オブジェクトやその他のレイアウトを入れ子にするほど、入れ子になったレイアウトがパフォーマンスに影響します。 詳細については、「正しいレイアウトの選択」を参照してください。
同等の C# コードを次に示します。
public class ColorSlidersGridPageCS : ContentPage
{
BoxView boxView;
Slider redSlider;
Slider greenSlider;
Slider blueSlider;
public ColorSlidersGridPageCS()
{
// Create an implicit style for the Labels
Style labelStyle = new Style(typeof(Label))
{
Setters =
{
new Setter { Property = Label.HorizontalTextAlignmentProperty, Value = TextAlignment.Center }
}
};
Resources.Add(labelStyle);
// Root page layout
Grid rootGrid = new Grid
{
RowDefinitions =
{
new RowDefinition(),
new RowDefinition()
}
};
boxView = new BoxView { Color = Color.Black };
rootGrid.Children.Add(boxView);
// Child page layout
Grid childGrid = new Grid
{
Margin = new Thickness(20),
RowDefinitions =
{
new RowDefinition(),
new RowDefinition(),
new RowDefinition(),
new RowDefinition(),
new RowDefinition(),
new RowDefinition()
}
};
DoubleToIntConverter doubleToInt = new DoubleToIntConverter();
redSlider = new Slider();
redSlider.ValueChanged += OnSliderValueChanged;
childGrid.Children.Add(redSlider);
Label redLabel = new Label();
redLabel.SetBinding(Label.TextProperty, new Binding("Value", converter: doubleToInt, converterParameter: "255", stringFormat: "Red = {0}", source: redSlider));
Grid.SetRow(redLabel, 1);
childGrid.Children.Add(redLabel);
greenSlider = new Slider();
greenSlider.ValueChanged += OnSliderValueChanged;
Grid.SetRow(greenSlider, 2);
childGrid.Children.Add(greenSlider);
Label greenLabel = new Label();
greenLabel.SetBinding(Label.TextProperty, new Binding("Value", converter: doubleToInt, converterParameter: "255", stringFormat: "Green = {0}", source: greenSlider));
Grid.SetRow(greenLabel, 3);
childGrid.Children.Add(greenLabel);
blueSlider = new Slider();
blueSlider.ValueChanged += OnSliderValueChanged;
Grid.SetRow(blueSlider, 4);
childGrid.Children.Add(blueSlider);
Label blueLabel = new Label();
blueLabel.SetBinding(Label.TextProperty, new Binding("Value", converter: doubleToInt, converterParameter: "255", stringFormat: "Blue = {0}", source: blueSlider));
Grid.SetRow(blueLabel, 5);
childGrid.Children.Add(blueLabel);
// Place the child Grid in the root Grid
rootGrid.Children.Add(childGrid, 0, 1);
Title = "Nested Grids demo";
Content = rootGrid;
}
void OnSliderValueChanged(object sender, ValueChangedEventArgs e)
{
boxView.Color = new Color(redSlider.Value, greenSlider.Value, blueSlider.Value);
}
}