Dynamische Indizierung mit HLSL 5.1
Das D3D12DynamicIndexing-Beispiel veranschaulicht einige der neuen HLSL-Features, die im Shadermodell 5.1 verfügbar sind – insbesondere dynamische Indizierung und ungebundene Arrays –, um das gleiche Gitter mehrmals zu rendern, jedes Mal, wenn es mit einem dynamisch ausgewählten Material gerendert wird. Bei der dynamischen Indizierung können Shader jetzt in ein Array indiziert werden, ohne den Wert des Indexes zur Kompilierzeit zu kennen. In Kombination mit nicht gebundenen Arrays bietet dies eine weitere Dereferenzierungs- und Flexibilitätsebene für Shaderautoren und Kunstpipelines.
- Einrichten des Pixelshaders
- Einrichten der Stammsignatur
- Erstellen der Texturen
- Hochladen der Texturdaten
- Laden der diffusen Textur
- Erstellen eines Samplers
- Dynamisches Ändern des Stammparameterindexes
- Ausführen des Beispiels
- Zugehörige Themen
Einrichten des Pixelshaders
Sehen wir uns zunächst den Shader selbst an, der für dieses Beispiel ein Pixelshader ist.
Texture2D g_txDiffuse : register(t0);
Texture2D g_txMats[] : register(t1);
SamplerState g_sampler : register(s0);
struct PSSceneIn
{
float4 pos : SV_Position;
float2 tex : TEXCOORD0;
};
struct MaterialConstants
{
uint matIndex; // Dynamically set index for looking up from g_txMats[].
};
ConstantBuffer<MaterialConstants> materialConstants : register(b0, space0);
float4 PSSceneMain(PSSceneIn input) : SV_Target
{
float3 diffuse = g_txDiffuse.Sample(g_sampler, input.tex).rgb;
float3 mat = g_txMats[materialConstants.matIndex].Sample(g_sampler, input.tex).rgb;
return float4(diffuse * mat, 1.0f);
}
Das Feature für ungebundene Arrays wird durch das g_txMats[] Array veranschaulicht, da es keine Arraygröße angibt. Die dynamische Indizierung wird für die Indizierung g_txMats[] mit matIndexverwendet, die als Stammkonstante definiert ist. Der Shader hat keine Kenntnis von der Größe, dem Array oder dem Wert des Indexes zur Kompilierzeit. Beide Attribute werden in der Stammsignatur des Pipelinezustandsobjekts definiert, das mit dem Shader verwendet wird.
Um die dynamischen Indizierungsfeatures in HLSL nutzen zu können, muss der Shader mit SM 5.1 kompiliert werden. Darüber hinaus muss für die Verwendung von nicht gebundenen Arrays auch das Flag /enable_unbounded_descriptor_tables verwendet werden. Die folgenden Befehlszeilenoptionen werden verwendet, um diesen Shader mit dem Effect-Compiler Tool (FXC) zu kompilieren:
fxc /Zi /E"PSSceneMain" /Od /Fo"dynamic_indexing_pixel.cso" /ps"_5_1" /nologo /enable_unbounded_descriptor_tables
Einrichten der Stammsignatur
Sehen wir uns nun die Stammsignaturdefinition an, insbesondere, wie wir die Größe des nicht gebundenen Arrays definieren und eine Stammkonstante mit matIndexverknüpfen. Für den Pixelshader definieren wir drei Dinge: eine Deskriptortabelle für SRVs (unsere Texture2Ds), eine Deskriptortabelle für Sampler und eine einzelne Stammkonstante. Die Deskriptortabelle für unsere SRVs enthält CityMaterialCount + 1 Einträge.
CityMaterialCount ist eine Konstante, die die Länge von g_txMats[] definiert, und + 1 ist für g_txDiffuse. Die Deskriptortabelle für unsere Sampler enthält nur einen Eintrag, und wir definieren nur einen 32-Bit-Stammkonstantenwert über InitAsConstants(...) in der LoadAssets-Methode .
// Create the root signature.
{
CD3DX12_DESCRIPTOR_RANGE ranges[3];
ranges[0].Init(D3D12_DESCRIPTOR_RANGE_TYPE_SRV, 1 + CityMaterialCount, 0); // Diffuse texture + array of materials.
ranges[1].Init(D3D12_DESCRIPTOR_RANGE_TYPE_SAMPLER, 1, 0);
ranges[2].Init(D3D12_DESCRIPTOR_RANGE_TYPE_CBV, 1, 0);
CD3DX12_ROOT_PARAMETER rootParameters[4];
rootParameters[0].InitAsDescriptorTable(1, &ranges[0], D3D12_SHADER_VISIBILITY_PIXEL);
rootParameters[1].InitAsDescriptorTable(1, &ranges[1], D3D12_SHADER_VISIBILITY_PIXEL);
rootParameters[2].InitAsDescriptorTable(1, &ranges[2], D3D12_SHADER_VISIBILITY_VERTEX);
rootParameters[3].InitAsConstants(1, 0, 0, D3D12_SHADER_VISIBILITY_PIXEL);
CD3DX12_ROOT_SIGNATURE_DESC rootSignatureDesc;
rootSignatureDesc.Init(_countof(rootParameters), rootParameters, 0, nullptr, D3D12_ROOT_SIGNATURE_FLAG_ALLOW_INPUT_ASSEMBLER_INPUT_LAYOUT);
ComPtr<ID3DBlob> signature;
ComPtr<ID3DBlob> error;
ThrowIfFailed(D3D12SerializeRootSignature(&rootSignatureDesc, D3D_ROOT_SIGNATURE_VERSION_1, &signature, &error));
ThrowIfFailed(m_device->CreateRootSignature(0, signature->GetBufferPointer(), signature->GetBufferSize(), IID_PPV_ARGS(&m_rootSignature)));
}
Erstellen der Texturen
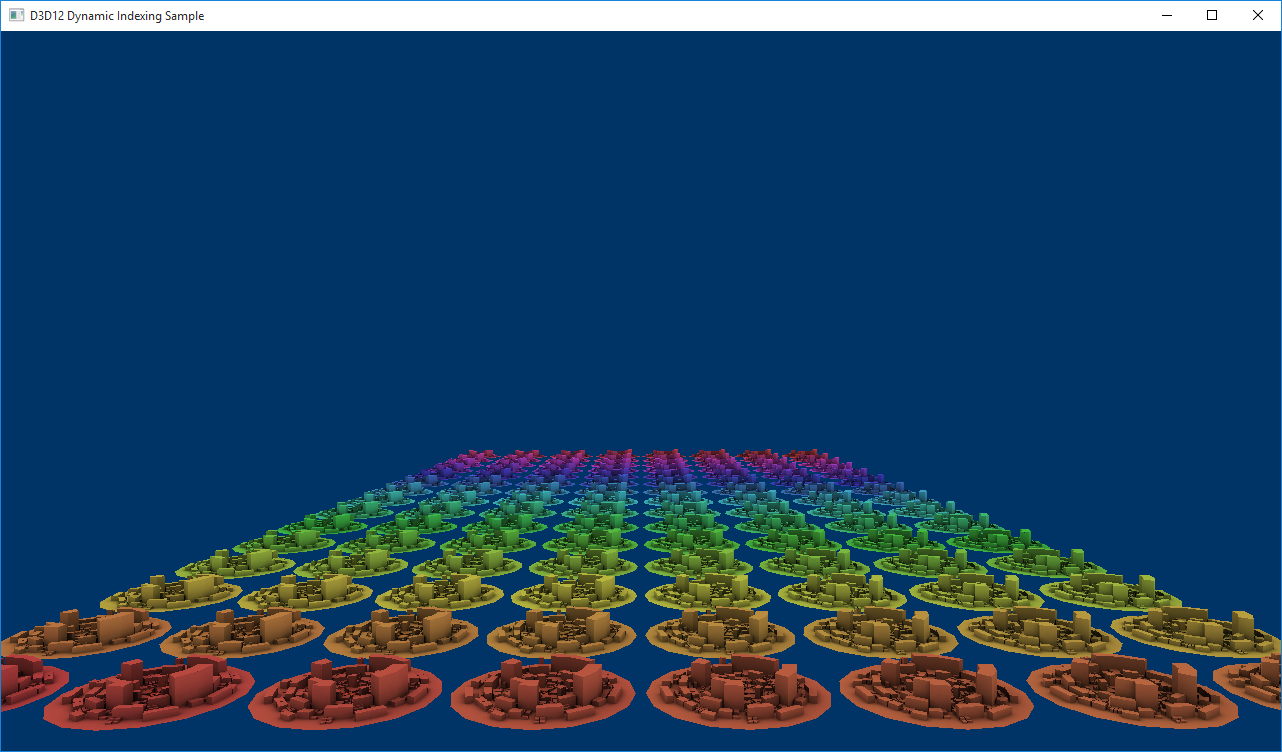
Die Inhalte von g_txMats[] sind prozedural generierte Texturen, die in LoadAssets erstellt wurden. Jede stadt, die in der Szene gerendert wird, teilt sich dieselbe diffuse Textur, verfügt aber auch über eine eigene prozedural generierte Textur. Das Array von Texturen umfasst das Regenbogenspektrum, um die Indizierungsmethode einfach zu visualisieren.
// Create the textures and sampler.
{
// Procedurally generate an array of textures to use as city materials.
{
// All of these materials use the same texture desc.
D3D12_RESOURCE_DESC textureDesc = {};
textureDesc.MipLevels = 1;
textureDesc.Format = DXGI_FORMAT_R8G8B8A8_UNORM;
textureDesc.Width = CityMaterialTextureWidth;
textureDesc.Height = CityMaterialTextureHeight;
textureDesc.Flags = D3D12_RESOURCE_FLAG_NONE;
textureDesc.DepthOrArraySize = 1;
textureDesc.SampleDesc.Count = 1;
textureDesc.SampleDesc.Quality = 0;
textureDesc.Dimension = D3D12_RESOURCE_DIMENSION_TEXTURE2D;
// The textures evenly span the color rainbow so that each city gets
// a different material.
float materialGradStep = (1.0f / static_cast<float>(CityMaterialCount));
// Generate texture data.
vector<vector<unsigned char>> cityTextureData;
cityTextureData.resize(CityMaterialCount);
for (int i = 0; i < CityMaterialCount; ++i)
{
CD3DX12_HEAP_PROPERTIES heapProps(D3D12_HEAP_TYPE_DEFAULT);
ThrowIfFailed(m_device->CreateCommittedResource(
&heapProps,
D3D12_HEAP_FLAG_NONE,
&textureDesc,
D3D12_RESOURCE_STATE_COPY_DEST,
nullptr,
IID_PPV_ARGS(&m_cityMaterialTextures[i])));
// Fill the texture.
float t = i * materialGradStep;
cityTextureData[i].resize(CityMaterialTextureWidth * CityMaterialTextureHeight * CityMaterialTextureChannelCount);
for (int x = 0; x < CityMaterialTextureWidth; ++x)
{
for (int y = 0; y < CityMaterialTextureHeight; ++y)
{
// Compute the appropriate index into the buffer based on the x/y coordinates.
int pixelIndex = (y * CityMaterialTextureChannelCount * CityMaterialTextureWidth) + (x * CityMaterialTextureChannelCount);
// Determine this row's position along the rainbow gradient.
float tPrime = t + ((static_cast<float>(y) / static_cast<float>(CityMaterialTextureHeight)) * materialGradStep);
// Compute the RGB value for this position along the rainbow
// and pack the pixel value.
XMVECTOR hsl = XMVectorSet(tPrime, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f);
XMVECTOR rgb = XMColorHSLToRGB(hsl);
cityTextureData[i][pixelIndex + 0] = static_cast<unsigned char>((255 * XMVectorGetX(rgb)));
cityTextureData[i][pixelIndex + 1] = static_cast<unsigned char>((255 * XMVectorGetY(rgb)));
cityTextureData[i][pixelIndex + 2] = static_cast<unsigned char>((255 * XMVectorGetZ(rgb)));
cityTextureData[i][pixelIndex + 3] = 255;
}
}
}
}
| Anrufverlauf | Parameter |
|---|---|
| D3D12_RESOURCE_DESC |
D3D12_RESOURCE_FLAGS [D3D12_RESOURCE_DIMENSION] (/windows/desktop/api/d3d12/ne-d3d12-d3d12_resource_dimension) |
| CreateCommittedResource |
D3D12_HEAP_TYPE [D3D12_HEAP_FLAG] (/windows/desktop/api/d3d12/ne-d3d12-d3d12_heap_flags) CD3DX12_RESOURCE_DESC [D3D12_RESOURCE_STATES] (/windows/desktop/api/d3d12/ne-d3d12-d3d12_resource_states) |
| XMVECTOR |
[XMColorHSLToRGB] (/windows/desktop/api/directxmath/nf-directxmath-xmcolorhsltorgb) |
Hochladen der Texturdaten
Texturdaten werden über einen Uploadheap auf die GPU hochgeladen, und FÜR jeden werden SRVs erstellt und in einem SRV-Deskriptorheap gespeichert.
// Upload texture data to the default heap resources.
{
const UINT subresourceCount = textureDesc.DepthOrArraySize * textureDesc.MipLevels;
const UINT64 uploadBufferStep = GetRequiredIntermediateSize(m_cityMaterialTextures[0].Get(), 0, subresourceCount); // All of our textures are the same size in this case.
const UINT64 uploadBufferSize = uploadBufferStep * CityMaterialCount;
CD3DX12_HEAP_PROPERTIES uploadHeap(D3D12_HEAP_TYPE_UPLOAD);
auto uploadDesc = CD3DX12_RESOURCE_DESC::Buffer(uploadBufferSize);
ThrowIfFailed(m_device->CreateCommittedResource(
&uploadHeap,
D3D12_HEAP_FLAG_NONE,
&uploadDesc,
D3D12_RESOURCE_STATE_GENERIC_READ,
nullptr,
IID_PPV_ARGS(&materialsUploadHeap)));
for (int i = 0; i < CityMaterialCount; ++i)
{
// Copy data to the intermediate upload heap and then schedule
// a copy from the upload heap to the appropriate texture.
D3D12_SUBRESOURCE_DATA textureData = {};
textureData.pData = &cityTextureData[i][0];
textureData.RowPitch = static_cast<LONG_PTR>((CityMaterialTextureChannelCount * textureDesc.Width));
textureData.SlicePitch = textureData.RowPitch * textureDesc.Height;
UpdateSubresources(m_commandList.Get(), m_cityMaterialTextures[i].Get(), materialsUploadHeap.Get(), i * uploadBufferStep, 0, subresourceCount, &textureData);
auto barrier = CD3DX12_RESOURCE_BARRIER::Transition(m_cityMaterialTextures[i].Get(), D3D12_RESOURCE_STATE_COPY_DEST, D3D12_RESOURCE_STATE_PIXEL_SHADER_RESOURCE);
m_commandList->ResourceBarrier(1, &barrier);
}
}
| Anrufverlauf | Parameter |
|---|---|
| GetRequiredIntermediateSize | |
| CreateCommittedResource | |
| D3D12_SUBRESOURCE_DATA | |
| UpdateSubresources | |
| ResourceBarrier |
Laden der diffusen Textur
Die diffuse Textur, g_txDiffuse, wird auf ähnliche Weise hochgeladen und erhält auch eine eigene SRV, aber die Texturdaten sind bereits in occcity.bin definiert.
// Load the occcity diffuse texture with baked-in ambient lighting.
// This texture will be blended with a texture from the materials
// array in the pixel shader.
{
D3D12_RESOURCE_DESC textureDesc = {};
textureDesc.MipLevels = SampleAssets::Textures[0].MipLevels;
textureDesc.Format = SampleAssets::Textures[0].Format;
textureDesc.Width = SampleAssets::Textures[0].Width;
textureDesc.Height = SampleAssets::Textures[0].Height;
textureDesc.Flags = D3D12_RESOURCE_FLAG_NONE;
textureDesc.DepthOrArraySize = 1;
textureDesc.SampleDesc.Count = 1;
textureDesc.SampleDesc.Quality = 0;
textureDesc.Dimension = D3D12_RESOURCE_DIMENSION_TEXTURE2D;
CD3DX12_HEAP_PROPERTIES heapProps(D3D12_HEAP_TYPE_DEFAULT);
ThrowIfFailed(m_device->CreateCommittedResource(
&heapProps,
D3D12_HEAP_FLAG_NONE,
&textureDesc,
D3D12_RESOURCE_STATE_COPY_DEST,
nullptr,
IID_PPV_ARGS(&m_cityDiffuseTexture)));
const UINT subresourceCount = textureDesc.DepthOrArraySize * textureDesc.MipLevels;
const UINT64 uploadBufferSize = GetRequiredIntermediateSize(m_cityDiffuseTexture.Get(), 0, subresourceCount);
CD3DX12_HEAP_PROPERTIES uploadHeap(D3D12_HEAP_TYPE_UPLOAD);
auto uploadDesc = CD3DX12_RESOURCE_DESC::Buffer(uploadBufferSize);
ThrowIfFailed(m_device->CreateCommittedResource(
&uploadHeap,
D3D12_HEAP_FLAG_NONE,
&uploadDesc,
D3D12_RESOURCE_STATE_GENERIC_READ,
nullptr,
IID_PPV_ARGS(&textureUploadHeap)));
// Copy data to the intermediate upload heap and then schedule
// a copy from the upload heap to the diffuse texture.
D3D12_SUBRESOURCE_DATA textureData = {};
textureData.pData = pMeshData + SampleAssets::Textures[0].Data[0].Offset;
textureData.RowPitch = SampleAssets::Textures[0].Data[0].Pitch;
textureData.SlicePitch = SampleAssets::Textures[0].Data[0].Size;
UpdateSubresources(m_commandList.Get(), m_cityDiffuseTexture.Get(), textureUploadHeap.Get(), 0, 0, subresourceCount, &textureData);
auto barrier = CD3DX12_RESOURCE_BARRIER::Transition(m_cityDiffuseTexture.Get(), D3D12_RESOURCE_STATE_COPY_DEST, D3D12_RESOURCE_STATE_PIXEL_SHADER_RESOURCE);
m_commandList->ResourceBarrier(1, &barrier);
}
| Anrufverlauf | Parameter |
|---|---|
| D3D12_RESOURCE_DESC | |
| CreateCommittedResource | |
| GetRequiredIntermediateSize | |
| CreateCommittedResource | |
| D3D12_SUBRESOURCE_DATA | |
| ResourceBarrier |
Erstellen eines Samplers
Schließlich wird für LoadAssets ein einzelner Sampler erstellt, um ein Beispiel aus der diffusen Textur oder dem Texturarray zu erstellen.
// Describe and create a sampler.
D3D12_SAMPLER_DESC samplerDesc = {};
samplerDesc.Filter = D3D12_FILTER_MIN_MAG_MIP_LINEAR;
samplerDesc.AddressU = D3D12_TEXTURE_ADDRESS_MODE_WRAP;
samplerDesc.AddressV = D3D12_TEXTURE_ADDRESS_MODE_WRAP;
samplerDesc.AddressW = D3D12_TEXTURE_ADDRESS_MODE_WRAP;
samplerDesc.MinLOD = 0;
samplerDesc.MaxLOD = D3D12_FLOAT32_MAX;
samplerDesc.MipLODBias = 0.0f;
samplerDesc.MaxAnisotropy = 1;
samplerDesc.ComparisonFunc = D3D12_COMPARISON_FUNC_ALWAYS;
m_device->CreateSampler(&samplerDesc, m_samplerHeap->GetCPUDescriptorHandleForHeapStart());
// Create SRV for the city's diffuse texture.
CD3DX12_CPU_DESCRIPTOR_HANDLE srvHandle(m_cbvSrvHeap->GetCPUDescriptorHandleForHeapStart(), 0, m_cbvSrvDescriptorSize);
D3D12_SHADER_RESOURCE_VIEW_DESC diffuseSrvDesc = {};
diffuseSrvDesc.Shader4ComponentMapping = D3D12_DEFAULT_SHADER_4_COMPONENT_MAPPING;
diffuseSrvDesc.Format = SampleAssets::Textures->Format;
diffuseSrvDesc.ViewDimension = D3D12_SRV_DIMENSION_TEXTURE2D;
diffuseSrvDesc.Texture2D.MipLevels = 1;
m_device->CreateShaderResourceView(m_cityDiffuseTexture.Get(), &diffuseSrvDesc, srvHandle);
srvHandle.Offset(m_cbvSrvDescriptorSize);
// Create SRVs for each city material.
for (int i = 0; i < CityMaterialCount; ++i)
{
D3D12_SHADER_RESOURCE_VIEW_DESC materialSrvDesc = {};
materialSrvDesc.Shader4ComponentMapping = D3D12_DEFAULT_SHADER_4_COMPONENT_MAPPING;
materialSrvDesc.Format = DXGI_FORMAT_R8G8B8A8_UNORM;
materialSrvDesc.ViewDimension = D3D12_SRV_DIMENSION_TEXTURE2D;
materialSrvDesc.Texture2D.MipLevels = 1;
m_device->CreateShaderResourceView(m_cityMaterialTextures[i].Get(), &materialSrvDesc, srvHandle);
srvHandle.Offset(m_cbvSrvDescriptorSize);
}
Dynamisches Ändern des Stammparameterindexes
Wenn wir die Szene jetzt rendern würden, würden alle Städte gleich aussehen, da wir den Wert unserer Stammkonstante matIndexnicht festgelegt haben. Jeder Pixel-Shader würde in den 0. Slot von g_txMats indiziert, und die Szene würde wie folgt aussehen:

Der Wert der Stammkonstante wird in FrameResource::P opulateCommandLists festgelegt. In der Double for-Schleife , in der ein Draw-Befehl für jede Stadt aufgezeichnet wird, zeichnen wir einen Aufruf von SetGraphicsRoot32BitConstants auf, der unseren Stammparameterindex in Bezug auf die Stammsignatur – in diesem Fall 3 – den Wert des dynamischen Index und einen Offset – in diesem Fall 0 – angibt. Da die Länge von g_txMats gleich der Anzahl der städte ist, die wir rendern, wird der Wert des Indexes für jede Stadt inkrementell festgelegt.
for (UINT i = 0; i < m_cityRowCount; i++)
{
for (UINT j = 0; j < m_cityColumnCount; j++)
{
pCommandList->SetPipelineState(pPso);
// Set the city's root constant for dynamically indexing into the material array.
pCommandList->SetGraphicsRoot32BitConstant(3, (i * m_cityColumnCount) + j, 0);
// Set this city's CBV table and move to the next descriptor.
pCommandList->SetGraphicsRootDescriptorTable(2, cbvSrvHandle);
cbvSrvHandle.Offset(cbvSrvDescriptorSize);
pCommandList->DrawIndexedInstanced(numIndices, 1, 0, 0, 0);
}
}
| Anrufverlauf | Parameter |
|---|---|
| SetPipelineState | |
| SetGraphicsRoot32BitConstant | |
| SetGraphicsRootDescriptorTable | |
| DrawIndexedInstanced |
Ausführen des Beispiels
Wenn wir nun die Szene rendern, hat jede Stadt einen anderen Wert für matIndex und wird daher eine andere Textur nachschlagen, als g_txMats[] dass die Szene wie folgt aussieht: